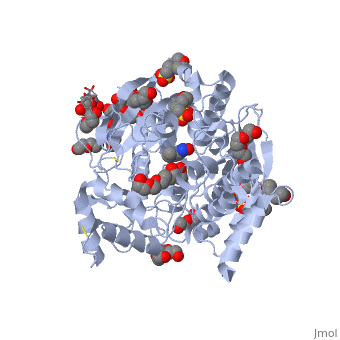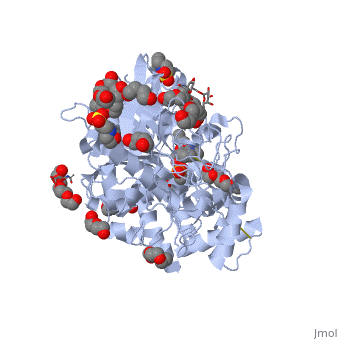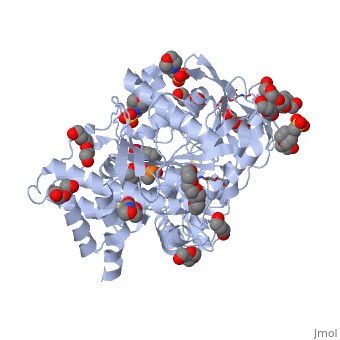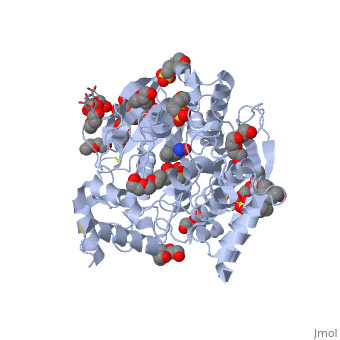Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <!-- Please use the "3D" button above this box to insert a Jmol applet (molecule) on this page. Or use the four-green-boxes-button to insert scrollable text adjacent to a Jmol applet. Che...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <!-- | + | ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')==<StructureSection load='2wg1' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of AChE with Soman and 2 PAM (PDB entry [[2wg1]])' scene=''> |
| + | Anything in this section will appear adjacent to the 3D structure and will be scrollable.</StructureSection><!-- | ||
Please use the "3D" button above this box to insert a Jmol applet (molecule) on this page. | Please use the "3D" button above this box to insert a Jmol applet (molecule) on this page. | ||
Or use the four-green-boxes-button to insert scrollable text adjacent | Or use the four-green-boxes-button to insert scrollable text adjacent | ||
to a Jmol applet. Check out the other buttons as well! | to a Jmol applet. Check out the other buttons as well! | ||
| - | --> | + | -->==<StructureSection load='2wg1' size='500' side='left' caption='Structure of AChE with Soman and 2 PAM (PDB entry [[2wg1]])' scene=''> |
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to acetate and choline, and plays a crucial role in terminating the nerve impulse at cholinergic synapses. Reversible inhibitors of AChE are used to treat diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease and myasthenia gravis. Conversely, irreversible inhibition of AChE by organophosphates (OP), such as soman, can lead to death. In this process, the OP covalently attaches to a serine residue in the active site to generate a phosphorylated enzyme. Subsequently, the OP is dealkylated, a process that is termed aging, generating a form of the enzyme that cannot be reactivated by antidotes, such as pralidoxime (2-PAM). Recently, the structures of Torpedo californica (Tc) AChE conjugated with soman, in both the non-aged and aged forms, and 2-PAM have been solved. From these structures, it is clear that a structural reorientation of His440, a component of the active site, occurs during the aging process. Additionally, the structure of the ternary complex of the aged AChE complex with 2-PAM, revealed that the oxime functional group is not optimally positioned for nucleophilic attack on the phosphorous atom. To increase our understanding of this process, we have generated a model of the aged ternary TcAChE/soman/2-PAM complex | Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to acetate and choline, and plays a crucial role in terminating the nerve impulse at cholinergic synapses. Reversible inhibitors of AChE are used to treat diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease and myasthenia gravis. Conversely, irreversible inhibition of AChE by organophosphates (OP), such as soman, can lead to death. In this process, the OP covalently attaches to a serine residue in the active site to generate a phosphorylated enzyme. Subsequently, the OP is dealkylated, a process that is termed aging, generating a form of the enzyme that cannot be reactivated by antidotes, such as pralidoxime (2-PAM). Recently, the structures of Torpedo californica (Tc) AChE conjugated with soman, in both the non-aged and aged forms, and 2-PAM have been solved. From these structures, it is clear that a structural reorientation of His440, a component of the active site, occurs during the aging process. Additionally, the structure of the ternary complex of the aged AChE complex with 2-PAM, revealed that the oxime functional group is not optimally positioned for nucleophilic attack on the phosphorous atom. To increase our understanding of this process, we have generated a model of the aged ternary TcAChE/soman/2-PAM complex | ||
Revision as of 01:13, 4 July 2011
==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')==
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||