Ribonuclease inhibitor
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | '''Ribonuclease inhibitors (RI)''' are a family of large (~450 residues, ~49 kDa), acidic (pI ~4.7), proteins that catalyze the degradation of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ribonuclease ribonucleases]. Human RI(hRI) is a major cellular protein, comprising ~0.1% of all cellular protein by weight. <ref>PMID: 11582809</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | '''Ribonuclease inhibitors (RI)''' are a family of large (~450 residues, ~49 kDa), acidic (pI ~4.7), proteins that catalyze the degradation of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ribonuclease ribonucleases]. Human RI(hRI) is a major cellular protein, comprising ~0.1% of all cellular protein by weight. <ref>PMID: 11582809</ref> | + | |
'''Ribonucleases (RNase)''' are enzymes that degrade RNA and are often [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytotoxicity cytotoxic] which gives them chemotherapeutic properties. However, when bound to an RI they are no longer functional. Understanding the mechanism through which RI identifies and binds to RNases will allow scientists to design/modify RNases to evade hRI. In fact, one drug, Onconase (ONC), a ribonuclease from the Northern Leopard Frog ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Northern_Leopard_Frog Rana pipiens]), is now in Phase III clinical trials as a cancer chemotherapeutic agent <ref>PMID:20173221</ref>. | '''Ribonucleases (RNase)''' are enzymes that degrade RNA and are often [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytotoxicity cytotoxic] which gives them chemotherapeutic properties. However, when bound to an RI they are no longer functional. Understanding the mechanism through which RI identifies and binds to RNases will allow scientists to design/modify RNases to evade hRI. In fact, one drug, Onconase (ONC), a ribonuclease from the Northern Leopard Frog ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Northern_Leopard_Frog Rana pipiens]), is now in Phase III clinical trials as a cancer chemotherapeutic agent <ref>PMID:20173221</ref>. | ||
| - | + | ||
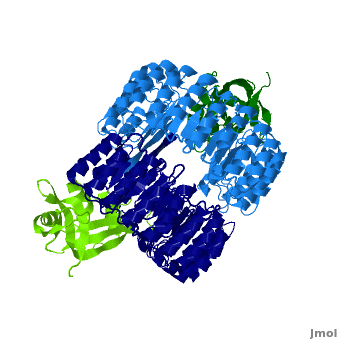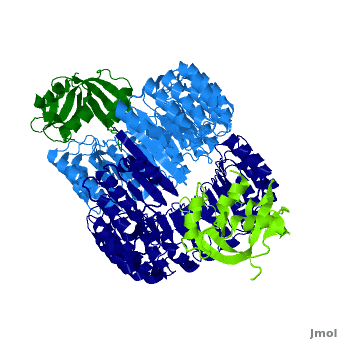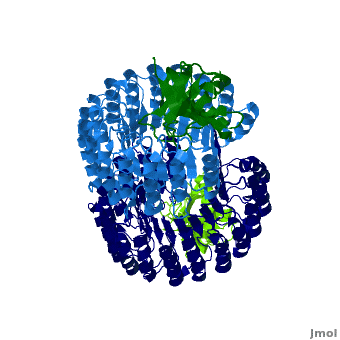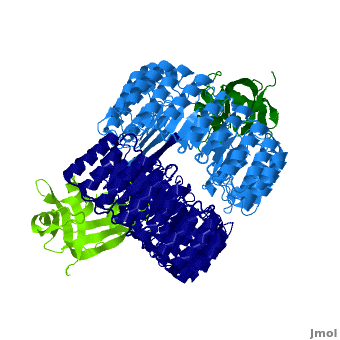
| + | <structuresection load='1z7x' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='hRI(blue) complexed with RNase 1(green) ' scene='Ribonuclease_inhibitor/1z7x/3' > | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Interactions between hRI and RNase 1== | ==Interactions between hRI and RNase 1== | ||
Revision as of 02:53, 9 November 2011
Ribonuclease inhibitors (RI) are a family of large (~450 residues, ~49 kDa), acidic (pI ~4.7), proteins that catalyze the degradation of ribonucleases. Human RI(hRI) is a major cellular protein, comprising ~0.1% of all cellular protein by weight. [1]
Ribonucleases (RNase) are enzymes that degrade RNA and are often cytotoxic which gives them chemotherapeutic properties. However, when bound to an RI they are no longer functional. Understanding the mechanism through which RI identifies and binds to RNases will allow scientists to design/modify RNases to evade hRI. In fact, one drug, Onconase (ONC), a ribonuclease from the Northern Leopard Frog (Rana pipiens), is now in Phase III clinical trials as a cancer chemotherapeutic agent [2].
| |||||||||||
3d structures
References
- ↑ Shapiro R. Cytoplasmic ribonuclease inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 2001;341:611-28. PMID:11582809
- ↑ Zwolinska M, Smolewski P. [Onconase: a ribonuclease with antitumor activity]. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2010 Feb 19;64:58-66. PMID:20173221
- ↑ Johnson RJ, McCoy JG, Bingman CA, Phillips GN Jr, Raines RT. Inhibition of human pancreatic ribonuclease by the human ribonuclease inhibitor protein. J Mol Biol. 2007 Apr 27;368(2):434-49. Epub 2007 Feb 9. PMID:17350650 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.005
- ↑ Johnson RJ, McCoy JG, Bingman CA, Phillips GN Jr, Raines RT. Inhibition of human pancreatic ribonuclease by the human ribonuclease inhibitor protein. J Mol Biol. 2007 Apr 27;368(2):434-49. Epub 2007 Feb 9. PMID:17350650 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.005
- ↑ Kobe B, Deisenhofer J. Mechanism of ribonuclease inhibition by ribonuclease inhibitor protein based on the crystal structure of its complex with ribonuclease A. J Mol Biol. 1996 Dec 20;264(5):1028-43. PMID:9000628 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1996.0694
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Abe Weintraub, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman