Rho-associated protein kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
**[[3o0z]] – hROCK1 coiled-coil domain <br /> | **[[3o0z]] – hROCK1 coiled-coil domain <br /> | ||
**[[1uix]] – hROCK1 Rho-binding domain <br /> | **[[1uix]] – hROCK1 Rho-binding domain <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5hvu]], [[4yvc]], [[4yve]], [[5bml]], [[4w7p]], [[3twj]], [[3tv7]], [[3v8s]], [[3ncz]], [[3ndm]], [[3d9v]], [[2esm]], [[2etk]], [[2etr]], [[5hvu]], [[5kks]], [[5kkt]], [[4w7p]], [[5uzj]], [[5wne]], [[5wnf]], [[5wng]], [[5wnh]] – hROCK1 kinase domain + inhibitor <br /> | + | **[[5hvu]], [[4yvc]], [[4yve]], [[5bml]], [[4w7p]], [[3twj]], [[3tv7]], [[3v8s]], [[3ncz]], [[3ndm]], [[3d9v]], [[2esm]], [[2etk]], [[2etr]], [[5hvu]], [[5kks]], [[5kkt]], [[4w7p]], [[5uzj]], [[5wne]], [[5wnf]], [[5wng]], [[5wnh]], [[6e9w]] – hROCK1 kinase domain + inhibitor <br /> |
**[[5f5p]] – hROCK1 Shroom-binding domain + Shroom2 <br /> | **[[5f5p]] – hROCK1 Shroom-binding domain + Shroom2 <br /> | ||
**[[2v55]] – hROCK1 kinase domain + RhoE + GDP + ANP <br /> | **[[2v55]] – hROCK1 kinase domain + RhoE + GDP + ANP <br /> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
**[[2f2u]] – hROCK2 kinase domain <br /> | **[[2f2u]] – hROCK2 kinase domain <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4wot]], [[4l6q]], [[2h9v]], [[5u7q]], [[5u7r]] – hROCK2 kinase domain + inhibitor <br /> | + | **[[4wot]], [[4l6q]], [[2h9v]], [[5u7q]], [[5u7r]], [[6ed6]] – hROCK2 kinase domain + inhibitor <br /> |
**[[2rov]] – hROCK2 split PH domain - NMR<br /> | **[[2rov]] – hROCK2 split PH domain - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2row]] – hROCK2 C1 domain - NMR<br /> | **[[2row]] – hROCK2 C1 domain - NMR<br /> | ||
Revision as of 10:27, 15 December 2019
| |||||||||||
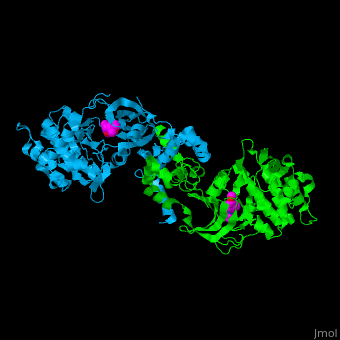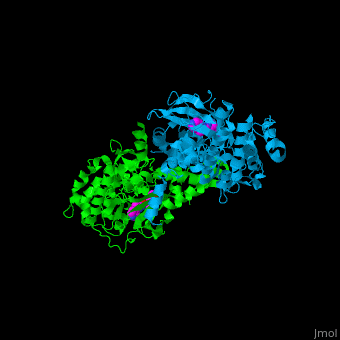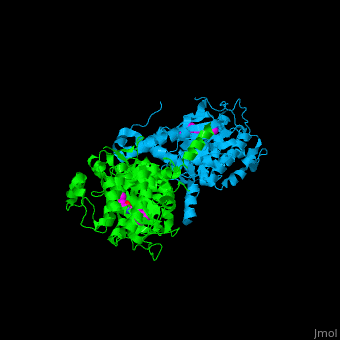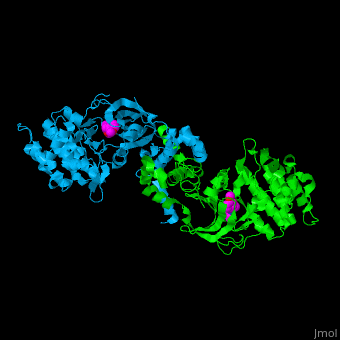
3D structures of Rho-associated protein kinase
Updated on 15-December-2019
References
- ↑ Smith AL, Dohn MR, Brown MV, Reynolds AB. Association of Rho-associated protein kinase 1 with E-cadherin complexes is mediated by p120-catenin. Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jan;23(1):99-110. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0497. Epub 2011 Oct, 26. PMID:22031287 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0497
- ↑ Schofield AV, Bernard O. Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) signaling and disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Jul-Aug;48(4):301-16. doi:, 10.3109/10409238.2013.786671. Epub 2013 Apr 19. PMID:23601011 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2013.786671
- ↑ Honjo M, Tanihara H, Inatani M, Kido N, Sawamura T, Yue BY, Narumiya S, Honda Y. Effects of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on intraocular pressure and outflow facility. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001 Jan;42(1):137-44. PMID:11133858
- ↑ Green J, Cao J, Bandarage UK, Gao H, Court J, Marhefka C, Jacobs M, Taslimi P, Newsome D, Nakayama T, Shah S, Rodems S. Design, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationships of Pyridine-Based Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2015 Jun 12. PMID:26039570 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00424