Journal:Cell:1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| (48 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' scene='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening/2' caption='Solved Structures of IFNAR1/2/IFN Complexes, [[1dq8]]'> |
=== Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons === | === Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons === | ||
| - | <big>Christoph Thomas, Ignacio Moraga, Doron Levin, Peter O. Krutzik, Yulia Podoplelova, Angelica Trejo, Choongho Lee, Ganit Yarden, Susan E. Vleck, Jeffrey S. Glenn, Garry P. Nolan, Jacob Piehler, Gideon Schreiber, K. Christopher Garcia</big><ref> | + | <big>Christoph Thomas, Ignacio Moraga, Doron Levin, Peter O. Krutzik, Yulia Podoplelova, Angelica Trejo, Choongho Lee, Ganit Yarden, Susan E. Vleck, Jeffrey S. Glenn, Garry P. Nolan, Jacob Piehler, Gideon Schreiber, K. Christopher Garcia</big><ref>DOI 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.048</ref> |
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
| - | + | ===Introduction=== | |
| - | IFNs were the first cytokines discovered more than half a century ago as agents that interfere with viral infection. Since then, IFNs have been established as pleiotropic, multifunctional proteins in the early immune response, exhibiting pronounced antiproliferative effects on cells, in addition to their strong immunomodulatory and antiviral | + | IFNs were the first cytokines discovered more than half a century ago as agents that interfere with viral infection. Since then, IFNs have been established as pleiotropic, multifunctional proteins in the early immune response, exhibiting pronounced antiproliferative effects on cells, in addition to their strong immunomodulatory and antiviral activities. Due to their potency and diverse biological activities, IFNs are used for the treatment of several human diseases, including hepatitis C, multiple sclerosis and certain types of cancer. |
| - | + | All <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ifna/2'>type I IFNs</scene> initiate signaling by binding to the same cell surface receptor composed of two subunits called <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ifnar1/3'>IFNAR1</scene> and <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ifnar2/2'>IFNAR2</scene>. The intracellular domains (ICDs) of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 are associated with the Janus kinases (Jaks) Tyk2 and Jak1, respectively. Upon ligand binding by the IFNAR chains and formation of the signaling complex, these tyrosine kinases trans-phosphorylate and thereby activate each other. Subsequently, the activated Jaks phosphorylate STAT transcription factors, which translocate into the nucleus and activate the expression of hundreds of IFN-stimulated genes. To gain insight into how type I IFNs engage their receptor chains, how the receptor system is able to recognize the large number of different ligands, and how different IFN ligands can evoke different physiological activities, we determined the crystal structures of unliganded <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ifnar1_alone/2'>IFNAR1 (SD1-SD3: sub-domains 1-3)</scene>, the binary complex <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ifnar2_binary/1'>between IFNa2 and IFNAR2</scene>, and the ternary ligand-receptor complexes of <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ternary_alpha/2'>IFNa2</scene> and <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ternary_gamma/3'>IFNw</scene> binding both receptor chains. A final theoretical ternary structure including <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_sd4_ternary/1'>the membrane-proximal sub-domain (SD4) of IFNAR1</scene> was also created. These structures, in conjunction with biochemical and cellular experiments, reveal that the type I IFN receptor uses a mode of ligand interaction that is unique among cytokine receptors, but conserved between different IFNs. Furthermore, ligand discrimination occurs through distinct energetics of shared receptor contacts, and differential IFN signaling is mediated by specific ligand-receptor interface chemistries that lead to different ternary complex stabilities. | |
===Interactions Between IFNAR & IFN=== | ===Interactions Between IFNAR & IFN=== | ||
| + | A superposition of the two ternary complexes reveals that they have very similar overall architectures, despite the different physiological activities of the IFN ligands. This suggests that the activity differences are not due to different signaling complex architectures. The functional differences are rather mediated by specific interface chemistries that form the basis for different ternary complex stabilities. | ||
====IFNAR2-IFN interaction==== | ====IFNAR2-IFN interaction==== | ||
[[Image:IFNa_IFNAR2_interaction_map.png|300px||right|]] | [[Image:IFNa_IFNAR2_interaction_map.png|300px||right|]] | ||
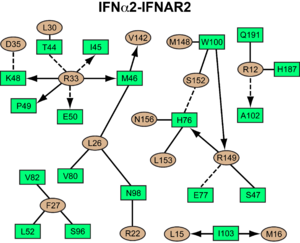
| - | <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ifna/2'>Interferon</scene> interacts primarily with the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifn_ifnar2_interaction/1'>D1 domain of IFNAR2</scene>. | + | {{Clear}} |
| + | <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench/Opening_ifna/2'>Interferon</scene> interacts primarily with the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifn_ifnar2_interaction/1'>D1 domain of IFNAR2</scene>. Arg33(IFN) appears to be the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifn_arg_33/1'>single most important residue</scene> for the interaction of the IFN ligand with IFNAR2. It forms an extensive hydrogen-bonding network with the main chain carbonyl oxygen atoms of Ile45(IFNAR2) and Glu50(IFNAR2) and the side chain of Thr44(IFNAR2). This residue is present in IFNa, IFNw, IFNb and IFNe. Two hydrophobic interaction clusters are part of the IFNa-IFNAR2 interface: the first one is formed between Leu15 and Met16 of the IFN molecule and Trp100 and Ile103 of IFNAR2; the second one comprises Leu26, Phe27, Leu30 and Val142 of the ligand and Met46, Leu52, Val80 and the methyl group of Thr44 of the receptor. Replacing <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifn_ifnar2_leu_30/1'>Leu30(IFN) with alanine</scene> reduces affinity by three orders of magnitude (the second most important residue for binding). This is surprising, as it is not engaged in any intimate contacts with IFNAR2 residues. One reason for its importance might be a <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifn_ifnar2_arg_stabilized/1'>stabilizing effect on the position of Arg33(IFN)</scene>. | ||
| + | Most of the residues involved in the IFNa2-IFNAR2 interaction are also found in the IFNw-IFNAR2 interface of the IFNw ternary complex. | ||
| + | [[Image:IFNw_IFNAR2_interaction_map.png|300px|left|]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | A significant difference in the IFNAR2 interface between <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifn_ifnar2_interaction_dif/5'>IFNa2</scene> and IFNw is related to <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifn_ifnar2_interaction_salt/1'>Arg149 in IFNa2</scene>, which is replaced with Lys152 in <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnw_ifnar21_structure/3'>IFNw</scene>. In the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnw_ifnar2_interface/3'>IFNw-IFNAR2 interface</scene>, this residue forms an <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnw_ifnar2_salt/1'>intramolecular salt bridge</scene> with Glu149(IFN), but <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnw_ifnar2_no_interact/1'>does not contact Glu77 of the receptor</scene>. | ||
====IFNAR1-IFN interaction==== | ====IFNAR1-IFN interaction==== | ||
| - | Because of the lower resolution of the | + | Because of the lower resolution of the IFNa ternary complex, we focused on the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnw_ifnar21_structure/3'>IFNw complex</scene> in our analysis of the IFN-IFNAR1 interface. In the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnw_ifnar21_structure/3'>IFNw-IFNAR1 complex</scene>, the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnw_ifnar21_zoomed/1'>ligand-binding site of IFNAR1</scene> only contains two hotspot residues we could experimentally confirm, <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/W-1-tyr_70/1'>Tyr70(IFNAR1)</scene> and Phe238(IFNAR1). Substituting these residues by alanine reduces the affinity to all tested IFN ligands by more than 10-fold. On IFNw, mutation studies have shown that a charge-reversal mutation of Arg123 (Arg 120 on IFNa) leads to a total loss of activity. [[Image:IFNw_IFNAR1_interaction_map.png|300px||left|]] |
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | Indeed, this residue forms a salt bridge with Asp132(IFNAR1) in addition to a hydrogen bond with Ser182(IFNAR1). Substitution of glutamate for Arg123(IFN) would lead to electrostatic repulsion with Asp132(IFNAR1). | ||
| + | The low affinity of IFNAR1 for the ligand appears to be functionally relevant, as weak binding to IFNAR1 is conserved between all alpha IFNs. Three amino acid substitutions on IFNa2 at positions His57, Glu58 and Ser61 to alanine or to Tyr, Asn, and Ser, respectively, confer tighter binding to IFNAR1, but leave the affinity to IFNAR2 essentially unaltered. | ||
| - | ====Implications for the binding mode of | + | ====Implications for the binding mode of IFNb==== |
| - | <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnbeta/1'> | + | <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnbeta/1'>IFNb exhibits</scene> 30% and 33% sequence identity with <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnbeta/2'>IFNw </scene>and IFNa2, respectively.<scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnbeta_gamma_overlay/3'> Superimposing human IFNb onto IFNw</scene> in our ternary complex structure leads <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnbeta_gamma_clashing_out/1'>to only two clashes</scene> of side chains (Tyr92 and <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Ifnbeta_gamma_clashing_155/3'>Tyr155</scene>) with the receptors, indicating that the IFNb ligand could be easily accommodated by the receptors in a position similar to IFNw and IFNa2. Furthermore, the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Superimosed_beta_alpha/6'>superposition of IFNb onto IFNa2 in complex with IFNAR2</scene> shows that <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Superimosed_1922/1'>Trp22 in IFNb and Ala19 in IFNa2 overlay onto each other</scene>. As a result, Ala19(IFN), when mutated to tryptophan, promotes an increased binding affinity to IFNAR2, which is a result of the <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench2/Superimosed_1922100/2'>contact made to Trp100 in IFNAR2</scene> (as shown by double mutant cycle analysis). |
| + | |||
===Structural Movements=== | ===Structural Movements=== | ||
====Structural pertubations upon binding==== | ====Structural pertubations upon binding==== | ||
| - | + | One of the more controversial aspects of cytokine signaling is whether receptor binding is sufficient to generate activity, or if it has to be accompanied by structural perturbations. The type I interferon signaling complex is a rare example of a cytokine receptor complex were the structures of all the components making up the biologically active complex were determined to high resolution in both their free and bound forms. <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench3/Morph_1/6'>A comparison</scene> of the unbound NMR structure with the ternary complex structure of interferon shows a small expansion during complex formation. | |
| - | + | Both IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, however, undergo significant domain movements upon binding. Using the D1 domain as anchor, a <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench3/Morph_2/10'>clear outwards movement of the D2 domain</scene> of IFNAR2 upon binding, on a scale of 6-12 Å, is observed (comparison of the unbound receptor ([[1n6u]]) with the binary IFNa2-IFNAR2 complex). The superimposition of the IFNa2-IFNAR2 binary complex with IFN-IFNAR2 in the ternary complexes <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench3/Morph3/7'>reveals an additional domain movement</scene> of 6-9 Å, and even between the ternary IFNa and IFNw complexes a movement of 3-5 Å is observed. The D2 domain is engaged in crystal contacts in all three structures, and it remains an open question if the conformational changes in IFNAR2 are physiologically relevant. Still, these movements could change the proximity or orientation of the ICDs and associated Jaks within the cell. | |
| - | + | The low-affinity receptor chain, IFNAR1, also <scene name='User:David_Canner/Workbench3/Morph_4/4'>undergoes major conformational changes</scene> upon ligand binding. When using D1 as anchor, D3 is moving inwards (toward the ligand) by ~15 Å. This would generate an even larger movement of the membrane-proximal SD4 domain and the transmembrane helix. The conformational changes in IFNAR1 are necessary to form the full spectrum of interactions with the IFN ligand, and to form a stable signaling complex that is able to instigate downstream signaling. In contrast to SD3, SD4 seems to be highly flexible (even more than D2 of IFNAR2). One might suggest that the conformational changes in IFNAR1 by itself will be responsible for a reduced binding affinity of IFNAR1 and may slow down the rate of ligand association to IFNAR1 directly from solution. | |
| + | |||
| + | Coordinates and structure factors have been deposited within the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB) Protein Data Bank (PDB) under accession codes [[3s98]] (IFNAR1ΔSD4), [[3s8w]] (IFNAR2-D2), [[3s9d]] (binary IFNα-IFNAR2 complex), [[3se4]] (ternary IFNω complex), and [[3se3]] (ternary IFNα complex). | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Thomas C, Moraga I, Levin D, Krutzik PO, Podoplelova Y, Trejo A, Lee C, Yarden G, Vleck SE, Glenn JS, Nolan GP, Piehler J, Schreiber G, Garcia KC. Structural Linkage between Ligand Discrimination and Receptor Activation by Type I Interferons. Cell. 2011 Aug 19;146(4):621-32. PMID:21854986 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.048
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Christoph Thomas, Jaime Prilusky, Joel L. Sussman, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.