|
|
| (23 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
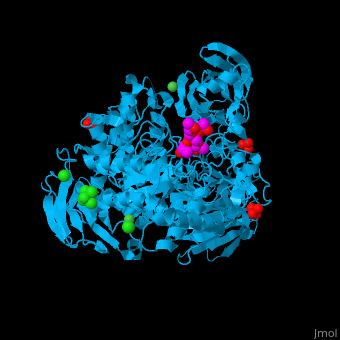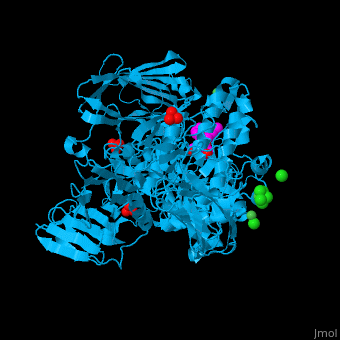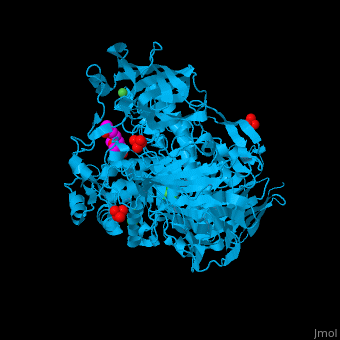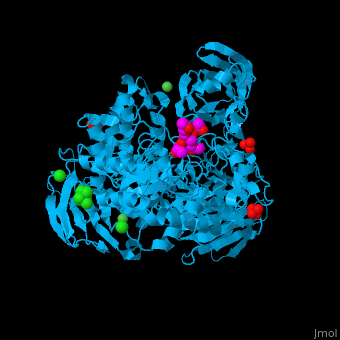
| - | <StructureSection load='2xvl' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of α-xylosidase family 31 complex with xylobiose, sulfate, Ni+2 and Cl- ions (PDB entry [[2xvl]])' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of α-xylosidase family 31 complex with pentaerythritol propoxylate, sulfate, Ni+2 (small green) and Cl- (large green) ions (PDB entry [[2xvl]])' scene='55/551220/Cv/1'> |
| | + | __TOC__ |
| | + | == Function == |
| | + | '''Xylosidase''' (XYL) catalyzes the hydrolysis of α- or β-glycosidic linkages. |
| | | | |
| - | '''Xylosidase''' (XYL) catalyzes the hydrolysis of α- or β-glycosidic linkages. Β-XYL catalyzes the endo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or endo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage. Α-XYL catalyzes the exo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or exo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage from the non-reducing termini of xylans. XYL catalyzes the conversion of cellulose and hemicellulose xylan to xylose. | + | *'''α-XYL''' catalyzes the exo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or exo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage from the non-reducing termini of xylans<ref>PMID:10801892</ref>. XYL catalyzes the conversion of cellulose and hemicellulose xylan to xylose. |
| | + | *'''β-XYL''' catalyzes the endo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or endo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage<ref>PMID:15283123</ref>. |
| | + | *'''α-XYL family 31''' catalyzes the hydrolysis of α-xylosyl from isoprimeverose<ref>PMID:35441671</ref>. |
| | + | *'''β-XYL family 3''' catalyzes the endo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or endo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage<ref>PMID:35120929</ref>. |
| | + | *'''β-XYL family 43''' and '''β-XYL family 52''' degrade xylooligosaccharides<ref>PMID:26494804</ref>, <ref>PMID:12738774</ref>. |
| | + | *'''β-XYL family 120''' degrades xylobiose and xylotriose<ref>PMID:31698702</ref>. |
| | + | *'''β-XYL/glucosidase''' bifunctional enzyme active on beta-xylosides and beta-glucosides. |
| | | | |
| | + | == Structural highlights == |
| | + | The <scene name='55/551220/Cv/5'>active site of α-xylosidase contains the xyloglucan and nucleophilic water</scene><ref>PMID:21426303</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='55/551220/Cv/6'>Ni/Cl complex</scene>. |
| | == 3D Structures of xylosidase == | | == 3D Structures of xylosidase == |
| | + | [[Xylosidase 3D structures]] |
| | | | |
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}}
| + | ==References== |
| - | | + | <references /> |
| - | '''α-xylosidase family 31'''
| + | </StructureSection> |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[2xvg]], [[2xvk]] – CjXYL – ''Cellvibrio japonicus'' <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[2xvl]] – CjXYL + xylobiose <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[1xsi]], [[1xsj]], [[1we5]] – EcXYL – Escherichia coli<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1xsk]] – EcXYL + intermediate<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''β-xylosidase'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[1yrz]] – XYL – ''Bacillus halodurans'' <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[1yif]] – XYL – ''Bacillus subtilis'' <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[3c2u]] – XYL + propane derivative – ''Selenomonas ruminantium'' <BR />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''β-xylosidase family 39'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[1px8]], [[1uhv]] – TsXYL – ''Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum'' <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[4ekj]] – XYL – Caulobacter vibrioides<BR />
| + | |
| - | [[2bs9]], [[1w91]] – BsXYL – ''Bacillus stearothermophilus'' <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[2bfg]] – BsXYL + xylobiose <BR />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''β-xylosidase family 43'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[1y7b]], [[1yi7]], [[3k1u]] – CaXYL – ''Clostridium acetobutylicum'' <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[3qed]], [[3qee]] – CjXYL <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[2exh]] – BsXYL <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[2exi]] – BsXYL (mutant) <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[2exj]] – BsXYL + xylobiose <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[2exk]] – BsXYL (mutant) + xylobiose <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[3qef]] – CaXYL (mutant) + arabinofuranose <BR />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | '''β-xylosidase family 120'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[3vst]] – TsXYL <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[3vsv]] – TsXYL + xylose <BR />
| + | |
| - | [[3vsu]] – TsXYL + xylobiose <BR />
| + | |
| | [[Category:Topic Page]] | | [[Category:Topic Page]] |
|
Function
Xylosidase (XYL) catalyzes the hydrolysis of α- or β-glycosidic linkages.
- α-XYL catalyzes the exo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or exo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage from the non-reducing termini of xylans[1]. XYL catalyzes the conversion of cellulose and hemicellulose xylan to xylose.
- β-XYL catalyzes the endo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or endo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage[2].
- α-XYL family 31 catalyzes the hydrolysis of α-xylosyl from isoprimeverose[3].
- β-XYL family 3 catalyzes the endo-hydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glycosidic or endo-hydrolysis of 1,3-β-D-glycosidic linkage[4].
- β-XYL family 43 and β-XYL family 52 degrade xylooligosaccharides[5], [6].
- β-XYL family 120 degrades xylobiose and xylotriose[7].
- β-XYL/glucosidase bifunctional enzyme active on beta-xylosides and beta-glucosides.
Structural highlights
The [8]. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. .
3D Structures of xylosidase
Xylosidase 3D structures
References
- ↑ Moracci M, Cobucci Ponzano B, Trincone A, Fusco S, De Rosa M, van Der Oost J, Sensen CW, Charlebois RL, Rossi M. Identification and molecular characterization of the first alpha -xylosidase from an archaeon. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22082-9. PMID:10801892 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M910392199
- ↑ Martinez GA, Chaves AR, Civello PM. beta-xylosidase activity and expression of a beta-xylosidase gene during strawberry fruit ripening. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2004 Feb;42(2):89-96. PMID:15283123 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2003.12.001
- ↑ Nakamichi Y, Matsuzawa T, Watanabe M, Yaoi K. Crystal structure of glycoside hydrolase family 31 α-xylosidase from a soil metagenome. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2022 Jun 25;86(7):855-864. PMID:35441671 doi:10.1093/bbb/zbac058
- ↑ Kojima K, Sunagawa N, Mikkelsen NE, Hansson H, Karkehabadi S, Samejima M, Sandgren M, Igarashi K. Comparison of Glycoside Hydrolase family 3 beta-xylosidases from basidiomycetes and ascomycetes reveals evolutionarily distinct xylan degradation systems. J Biol Chem. 2022 Feb 1:101670. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101670. PMID:35120929 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101670
- ↑ Falck P, Linares-Pastén JA, Adlercreutz P, Karlsson EN. Characterization of a family 43 β-xylosidase from the xylooligosaccharide utilizing putative probiotic Weissella sp. strain 92. Glycobiology. 2016 Feb;26(2):193-202. PMID:26494804 doi:10.1093/glycob/cwv092
- ↑ Bravman T, Belakhov V, Solomon D, Shoham G, Henrissat B, Baasov T, Shoham Y. Identification of the catalytic residues in family 52 glycoside hydrolase, a beta-xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T-6. J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 18;278(29):26742-9. PMID:12738774 doi:10.1074/jbc.M304144200
- ↑ Rohman A, Dijkstra BW, Puspaningsih NNT. β-Xylosidases: Structural Diversity, Catalytic Mechanism, and Inhibition by Monosaccharides. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 6;20(22):5524. PMID:31698702 doi:10.3390/ijms20225524
- ↑ Larsbrink J, Izumi A, Ibatullin F, Nakhai A, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ, Brumer H. Structural and enzymatic characterisation of a Glycoside Hydrolase Family 31 alphaxylosidase from Cellvibrio japonicus involved in xyloglucan saccharification. Biochem J. 2011 Mar 22. PMID:21426303 doi:10.1042/BJ20110299
|