SARS-CoV-2 protein N
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='84/842060/Sars-cov-2_protein_n/2' caption=''> | |
| - | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='84/842060/Sars-cov-2_protein_n/ | + | |
{{Theoretical_model}} | {{Theoretical_model}} | ||
{{Template:ModelConfidence}} | {{Template:ModelConfidence}} | ||
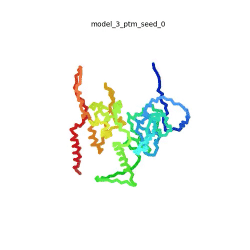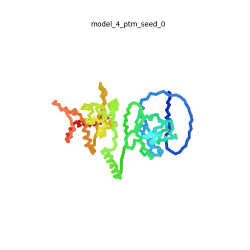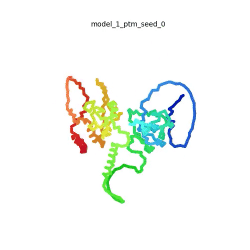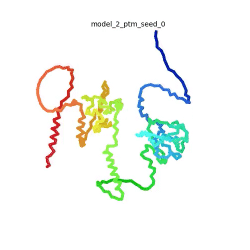
| - | To the right is an '''[[AlphaFold]]2''' 3D model of SARS CoV-2 Protein N (UniProt ID: | + | To the right is an '''[[AlphaFold]]2''' 3D model of SARS CoV-2 Protein N (length=419 amino acids, [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P0DTC9 UniProt ID: P0DTC9]) color coded by the pLDDT scores. It corresponds to the highest ranked model in terms of the pLDDT confidence scores, ''i.e.'', model 5<ref name="MIT_ColabFold"> MIT ColabFold https://colab.research.google.com/github/sokrypton/ColabFold/blob/main/beta/AlphaFold2_advanced.ipynb </ref>. |
| + | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The primary function of the Nucleocapsid protein (N-protein) is to package the viral genome into a helical ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that protects the genomic RNA, and bind it tightly during the virus’s journey to a new host<ref name="Chang"> PMID:24418573 </ref>. N-proteins are necessary for viral RNA transcription and replication and are also regulating these processes. The packaging of the RNA into the RNP complex is a fundamental part of the RNA assembly in infected cells. N-proteins are also involved in the replication cycle and have influence on the hosts cellular response to viral infection<ref name="Chang"/>. | The primary function of the Nucleocapsid protein (N-protein) is to package the viral genome into a helical ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that protects the genomic RNA, and bind it tightly during the virus’s journey to a new host<ref name="Chang"> PMID:24418573 </ref>. N-proteins are necessary for viral RNA transcription and replication and are also regulating these processes. The packaging of the RNA into the RNP complex is a fundamental part of the RNA assembly in infected cells. N-proteins are also involved in the replication cycle and have influence on the hosts cellular response to viral infection<ref name="Chang"/>. | ||
== Structure description == | == Structure description == | ||
| - | [[Image:SARSCoV2_protein_N_250.gif|250px|left|thumb|'''Morph''' of the top 5 ranked [[AlphaFold]]2 models of '''SARS-CoV-2 Protein N''', ''rainbow'' color coded N-C<ref name="MIT_ColabFold"/>.]]<br />The N-protein consists of 419 amino acids and can be divided into two folded domains and three disordered regions. The three disordered regions dynamically change their conformation and are very flexible (see '''morph''' of the top 5 ranked AlphaFold2 models, to the left, that gives a feel for the flexibility of these domains). This flexibility allows them to rotate and enable the binding to macromolecules like RNA. The two folded domains on the other hand are well structured and have thus been modelled using X-Ray diffraction<ref name="Kang"> PMID: 32363136 </ref> and NMR. <ref name="Savastano">PMID: 32363136 </ref><ref name="Cubuk">PMID:33782395</ref>. | + | [[Image:SARSCoV2_protein_N_250.gif|250px|left|thumb|'''Morph''' of the top 5 ranked [[AlphaFold]]2 models of '''SARS-CoV-2 Protein N''', ''rainbow'' color coded N-C (blue to red)<ref name="MIT_ColabFold"/>.]]<br />The N-protein consists of 419 amino acids and can be divided into two folded domains and three disordered regions. The three disordered regions dynamically change their conformation and are very flexible (see '''morph''' of the top 5 ranked AlphaFold2 models, to the left, that gives a feel for the flexibility of these domains). This flexibility allows them to rotate and enable the binding to macromolecules like RNA. The two folded domains on the other hand are well structured and have thus been modelled using X-Ray diffraction<ref name="Kang"> PMID: 32363136 </ref> and NMR. <ref name="Savastano">PMID: 32363136 </ref><ref name="Cubuk">PMID:33782395</ref>. |
=== N-terminal flexible arm === | === N-terminal flexible arm === | ||
The N-terminal flexible arm is one of the disordered regions, but with parts of transient helicity. Its conformation is significantly affected by the neighbouring folded RNA binding domain (RBD), which reduces the accessible space of the flexible arm and hence supports an expanded configuration of this domain. Interactions with the RBD through fuzzy interactions cause kinetic traps for certain transient configurations. Furthermore, some attractive and repulsive interactions with the RBD are supported by the arginine-rich region (residues 31 - 41) and by residue Phe 17 of the NTD. The arginine-rich motif was found to form a transient alpha helix (H2)<ref name="Cubuk"/>. | The N-terminal flexible arm is one of the disordered regions, but with parts of transient helicity. Its conformation is significantly affected by the neighbouring folded RNA binding domain (RBD), which reduces the accessible space of the flexible arm and hence supports an expanded configuration of this domain. Interactions with the RBD through fuzzy interactions cause kinetic traps for certain transient configurations. Furthermore, some attractive and repulsive interactions with the RBD are supported by the arginine-rich region (residues 31 - 41) and by residue Phe 17 of the NTD. The arginine-rich motif was found to form a transient alpha helix (H2)<ref name="Cubuk"/>. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| - | [[Coronavirus_Disease 2019 (COVID-19)]] | + | [[Coronavirus_Disease 2019 (COVID-19)]]<br> |
| - | + | [[SARS-CoV-2_virus_proteins]]<br> | |
| + | [[COVID-19 AlphaFold2 Models]] | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||