Monoamine oxidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
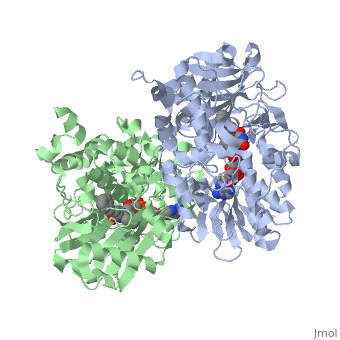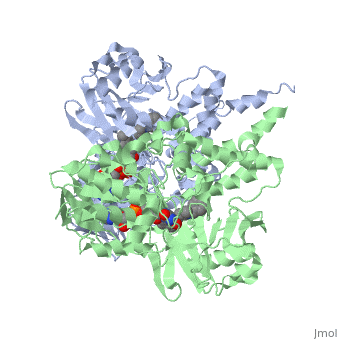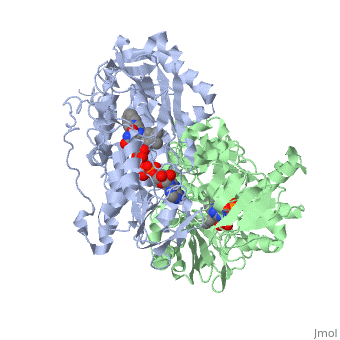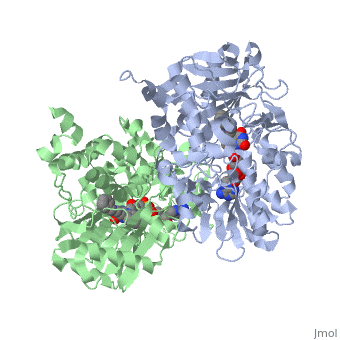
{{STRUCTURE_1gos| PDB=1gos | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right| CAPTION=Human MAO-B dimer complex with FAD and phenyl-propenylidine derivative, [[1gos]] }} | {{STRUCTURE_1gos| PDB=1gos | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right| CAPTION=Human MAO-B dimer complex with FAD and phenyl-propenylidine derivative, [[1gos]] }} | ||
| - | + | == Function == | |
| - | '''Monoamine oxidas'''e (MAO) are enzymes which catalyze the oxidation of monoamines. MAO contains FAD as co-factor.<br /> | + | '''Monoamine oxidas'''e (MAO) are enzymes which catalyze the oxidation of monoamines<ref>PMID:15279561</ref>. MAO contains FAD as co-factor.<br /> |
* '''MAO-A''' and '''MAO-C''' are human enzymes which oxidize adrenaline, noradrenaline, serotonin and dopamine.<br /> | * '''MAO-A''' and '''MAO-C''' are human enzymes which oxidize adrenaline, noradrenaline, serotonin and dopamine.<br /> | ||
| - | * '''MAO-B''' is a human enzyme which oxidizes benzylamine and phenylethylamine. For details on MAO-B see [[Monoamine oxidase b]]. | + | * '''MAO-B''' is a human enzyme which oxidizes benzylamine and phenylethylamine. For details on MAO-B see [[Monoamine oxidase b]].<br /> |
| + | * '''MAO-N''' is a ''Aspergillus niger'' enzyme which oxidizes primary amines<ref>PMID:18951902</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | Elevated levels of MAO-A in the brain are measured during depression<ref>PMID:17088501</ref>. MAO inhibitors were the first anti-depression drugs developed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | MAO-B active site is composed of 2 cavities: the substrate cavity in front of the FAD and the entrance cavity. Safinamide - a drug tested for Parkinson's disease<ref>PMID:17030736</ref> - occupies both cavities<ref>PMID:17915852</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of monoamine oxidase == | ==3D structures of monoamine oxidase == | ||
| Line 33: | Line 42: | ||
**[[2vvl]], [[2vvm]], [[3zdn]] – MAO-N (mutant) + FAD – ''Aspergillus niger'' | **[[2vvl]], [[2vvm]], [[3zdn]] – MAO-N (mutant) + FAD – ''Aspergillus niger'' | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 08:08, 1 May 2016
| |||||||||
| Human MAO-B dimer complex with FAD and phenyl-propenylidine derivative, 1gos | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Monoamine oxidase, with EC number 1.4.3.4 | ||||||||
| Related: | 1h8r | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Contents |
Function
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) are enzymes which catalyze the oxidation of monoamines[1]. MAO contains FAD as co-factor.
- MAO-A and MAO-C are human enzymes which oxidize adrenaline, noradrenaline, serotonin and dopamine.
- MAO-B is a human enzyme which oxidizes benzylamine and phenylethylamine. For details on MAO-B see Monoamine oxidase b.
- MAO-N is a Aspergillus niger enzyme which oxidizes primary amines[2].
Relevance
Elevated levels of MAO-A in the brain are measured during depression[3]. MAO inhibitors were the first anti-depression drugs developed.
Structural highlights
MAO-B active site is composed of 2 cavities: the substrate cavity in front of the FAD and the entrance cavity. Safinamide - a drug tested for Parkinson's disease[4] - occupies both cavities[5].
</StructureSection>
3D structures of monoamine oxidase
Updated on 01-May-2016
References
- ↑ Tipton KF, Boyce S, O'Sullivan J, Davey GP, Healy J. Monoamine oxidases: certainties and uncertainties. Curr Med Chem. 2004 Aug;11(15):1965-82. PMID:15279561
- ↑ Atkin KE, Reiss R, Koehler V, Bailey KR, Hart S, Turkenburg JP, Turner NJ, Brzozowski AM, Grogan G. The structure of monoamine oxidase from Aspergillus niger provides a molecular context for improvements in activity obtained by directed evolution. J Mol Biol. 2008 Dec 31;384(5):1218-31. Epub 2008 Oct 14. PMID:18951902 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.090
- ↑ Meyer JH, Ginovart N, Boovariwala A, Sagrati S, Hussey D, Garcia A, Young T, Praschak-Rieder N, Wilson AA, Houle S. Elevated monoamine oxidase a levels in the brain: an explanation for the monoamine imbalance of major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Nov;63(11):1209-16. PMID:17088501 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.63.11.1209
- ↑ Caccia C, Maj R, Calabresi M, Maestroni S, Faravelli L, Curatolo L, Salvati P, Fariello RG. Safinamide: from molecular targets to a new anti-Parkinson drug. Neurology. 2006 Oct 10;67(7 Suppl 2):S18-23. PMID:17030736
- ↑ Binda C, Wang J, Pisani L, Caccia C, Carotti A, Salvati P, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A. Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: safinamide and coumarin analogs. J Med Chem. 2007 Nov 15;50(23):5848-52. Epub 2007 Oct 4. PMID:17915852 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm070677y