Odorant binding protein
From Proteopedia
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
====''Bombyx mori'' BmorPBP (lets talk about sex..)==== | ====''Bombyx mori'' BmorPBP (lets talk about sex..)==== | ||
<StructureSection load='1ls8' size='340' side='right' caption='''Bombyx mori'' PBP -BmorPBP scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1ls8' size='340' side='right' caption='''Bombyx mori'' PBP -BmorPBP scene=''> | ||
| - | PBPs are specialized members of the insect odorant-binding protein (OBP) super-family. | + | Pheromone binding proteins (PBPs) are specialized members of the insect odorant-binding protein (OBP) super-family. |
The main purpse in the dult moth's short life is reproduction. In fact, the male and female moth invest all of theire energy and resourses hoping to reach to the ultimate goal- mating. This long journy begins when the female moth releases a sex pheromone, usualy in specific hours in the night <ref>doi: 10.1007/BF01946910</ref>. | The main purpse in the dult moth's short life is reproduction. In fact, the male and female moth invest all of theire energy and resourses hoping to reach to the ultimate goal- mating. This long journy begins when the female moth releases a sex pheromone, usualy in specific hours in the night <ref>doi: 10.1007/BF01946910</ref>. | ||
| - | BmorPBP was first identified in the ''B. mori'' male antennae by Krieger et al. in 1996 <ref>doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(95)00096-8</ref>, as the PBP of the first sex pheromone discovered ((E,Z)-10,12-hexadecadienol, or [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bombykol Bombykol]]). The male moth needs to detect minut amount of the pheromone, while following turbulent wind-born pheromone trail | + | BmorPBP was first identified in the ''B. mori'' male antennae by Krieger et al. in 1996 <ref>doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(95)00096-8</ref>, as the PBP of the first sex pheromone discovered ((E,Z)-10,12-hexadecadienol, or [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bombykol Bombykol]]). The male moth needs to detect minut amount of the pheromone in the air, while following turbulent wind-born pheromone trail and response fast (experimental evidence shows a response time of 0.5 seconds<ref>doi: 10.1038/293161a0</ref>). As the electrical signal transduction after the activation of the odorant receptor are too fast, Kaissling <ref name="Kaissling 2009">doi: 10.1007/s00359-009-0461-4</ref>have suggested that the |
====BmorPBP structure and function==== | ====BmorPBP structure and function==== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
====Protein conformations==== | ====Protein conformations==== | ||
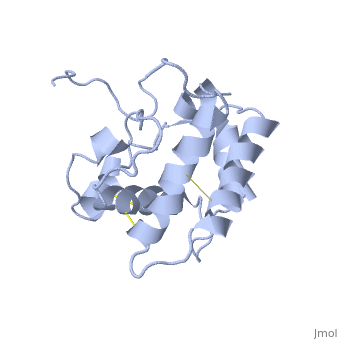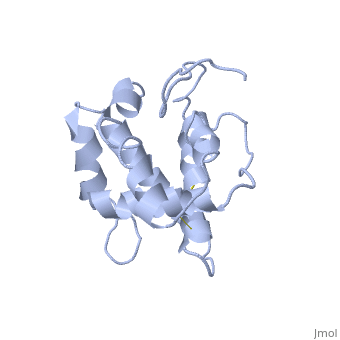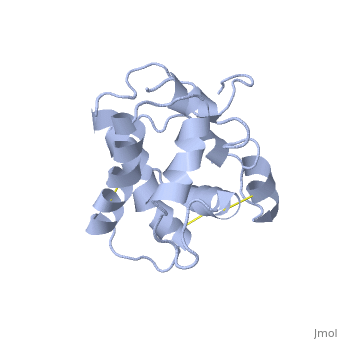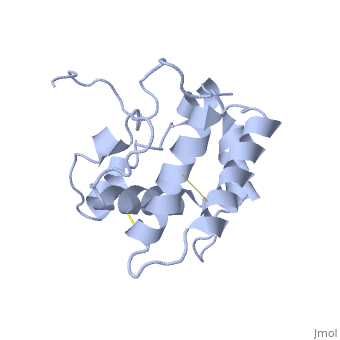
| - | BmorPBP has two conformations | + | BmorPBP has two conformations: The "open form" (A) and the "close form" (B)<ref>DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.43.30950</ref>. The bombykol and the alpha-helix loacated in the c-terminus of the protein compete for the binding site: when the c-terminus is inside the binding cavity it's in alpha helix shape, and the protien is in its "close form" (B), wherease in the "open form" (A) the c-terminus is outside of the protein and has no defined secondery sturcture. |
In a nuetral pH (6.5-7) the protein is in the "open form" (A), in which the | In a nuetral pH (6.5-7) the protein is in the "open form" (A), in which the | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
Two theories have been propsed for the activation of the odorant receptors located on the dendrtirte membrane. One theory suggests that the pheromone-PBP complex is needed for the receptor activation, while the second theory argue that the pheromone itself is sufficient for the activation of the receptor. | Two theories have been propsed for the activation of the odorant receptors located on the dendrtirte membrane. One theory suggests that the pheromone-PBP complex is needed for the receptor activation, while the second theory argue that the pheromone itself is sufficient for the activation of the receptor. | ||
| - | [[Image:Nmodel.png|thumb|upright=1.5|The events prior the neuron exsitation, according to "N model" suggested by Kaissling (2009)<ref | + | [[Image:Nmodel.png|thumb|upright=1.5|The events prior the neuron exsitation, according to "N model" suggested by Kaissling (2009)<ref name="Kaissling 2009" />]] |
*'''Activation by the pheromone alone''' | *'''Activation by the pheromone alone''' | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
| - | The surface of the dendrite is negatively charged <ref>DOI: 10.1016/0040-8166(84)90004-1</ref>, which cause the accumulation of positively charged kations near the membrane surface (20-50 nm), thereby inducing a low pH environment near the dendrite membrane | + | The surface of the dendrite is negatively charged <ref>DOI: 10.1016/0040-8166(84)90004-1</ref>, which cause the accumulation of positively charged kations near the membrane surface (20-50 nm), thereby inducing a low pH environment near the dendrite membrane <ref name="Kaissling 2009" />. |
Revision as of 10:49, 11 January 2015
Contents |
Introduction
Odorant-binding protein (OBP) are soluble proteins which involve in the processes of odorant detection in the olfactory sensilla.
The first OBP that was identified is Bovine odorant binding protein, that was isolated from a cow's mucus ref. Though functunaly same, vertebrates and insects OBP have different origin and stucture. OBPs are important for insect olfaction. For instance, OBP76a (LUSH) in the fly Drosophila melanogaster is required for the detection of the pheromone vaccenyl acetate [Ha and Smith, 2006; Xu et al., 2005] and has been proven to adopt a conformation that activates the odorant receptor [Laughlin et al., 2008].
OBP in insects
OBP Function
Despite five decades of intensive research, the exact roles of OBP and the mechanism by which the odorant receptor (OR) is activated are still in dispute [1][2].
A few functions have been suggested for OBP: 1. Solubelizing the odorant molecule and its transportation in the sensillar lymph.
2. Protecting the odorant molecule from the odorant degrading enzymes, in the sensillar lymph.
3. Activating of the odorant receptor on the dendrite membrane, by the odorant-OBP complex.
4. Mediating the deactivation of the odorant molecule after the activation of the receptor.
5. An organic anion (the protein has 9 negative charges).
Of all, the first role of OBP as an odorant solubilizer and carrier is generally accepted.
In order to explain the structure and function of these fascinating proteins, this page will further focus on a particular OBP - the well investigated Bombyx mori PBP: BmorPBP.
Bombyx mori BmorPBP (lets talk about sex..)
| |||||||||||
See also
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Nurit Eliash, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky