Image:Gabab.xu2014.png
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
No higher resolution available.
Gabab.xu2014.png (326 × 308 pixel, file size: 50 KB, MIME type: image/png)
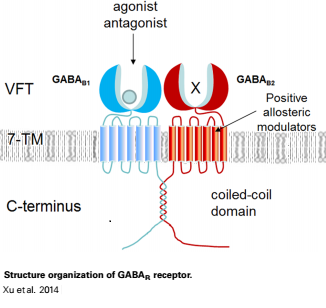
(Structure organization of GABAB receptor. GABAB receptor forms heterodimer composed by GABAB1 and GABAB2. GABAB1 is responsible for ligand binding in N-terminal VFT domain, whereas the VFT of GABAB2 fails to bind any known ligand (Xu et al.2014).) |
(Structure organization of GABAB receptor. GABAB receptor forms heterodimer composed by GABAB1 and GABAB2. GABAB1 is responsible for ligand binding in N-terminal VFT domain, whereas the VFT of GABAB2 fails to bind any known ligand (Xu et al.2014).) |
Current revision
Summary
Structure organization of GABAB receptor. GABAB receptor forms heterodimer composed by GABAB1 and GABAB2. GABAB1 is responsible for ligand binding in N-terminal VFT domain, whereas the VFT of GABAB2 fails to bind any known ligand (Xu et al.2014).
Licensing
{{subst:Non-commercial from license selector}}
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | User | Dimensions | File size | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (current) | 06:55, 18 May 2015 | Rana Saad (Talk | contribs) | 326×308 | 50 KB | Structure organization of GABAB receptor. GABAB receptor forms heterodimer composed by GABAB1 and GABAB2. GABAB1 is responsible for ligand binding in N-terminal VFT domain, whereas the VFT of GABAB2 fails to bind any known ligand (Xu et al.2014). |
- Edit this file using an external application
See the setup instructions for more information.
Links
The following pages link to this file:
