Avelox (moxifloxacin)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
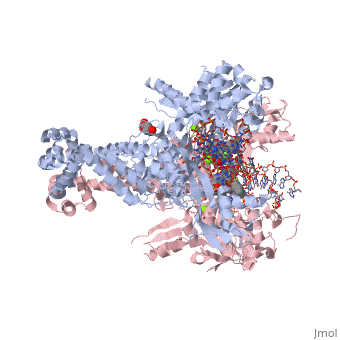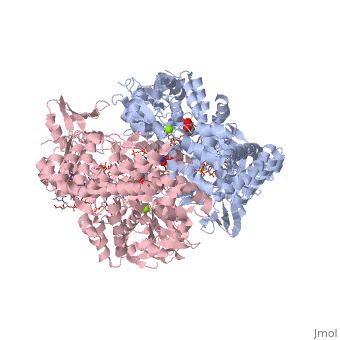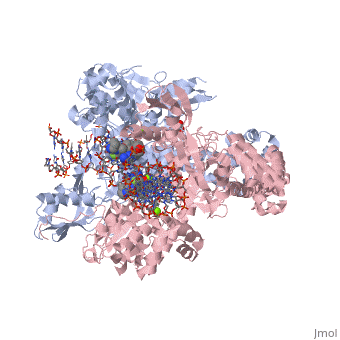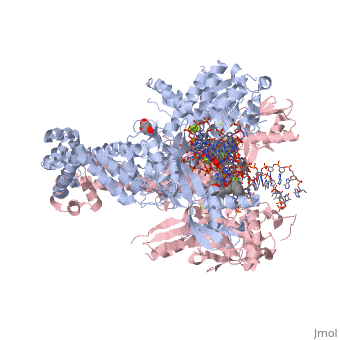
<StructureSection load='2xkk' size='340' side='right' caption='Crystal structure of Moxifloxacin, DNA and Acinetobacter baumannii Topoisomerase IV' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2xkk' size='340' side='right' caption='Crystal structure of Moxifloxacin, DNA and Acinetobacter baumannii Topoisomerase IV' scene=''> | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | <scene name='75/756549/Moxifloxacin/1'>Moxifloxacin</scene> is a synthetic antimicrobial fluoroquinolone with the molecular formula C<sub>21</sub>H<sub>24</sub>FN<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>. It has an average molecular weight of 401.438 g/mol '''<ref name="pubchem"> https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/moxifloxacin#section=2D-Structure </ref>'''. Fluoroquinolones are organic compounds categorized as a quinoline, aromatic ring with a substituted carboxyl group at one or more positions, | + | <scene name='75/756549/Moxifloxacin/1'>Moxifloxacin</scene> is a synthetic antimicrobial fluoroquinolone with the molecular formula C<sub>21</sub>H<sub>24</sub>FN<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>. It has an average molecular weight of 401.438 g/mol '''<ref name="pubchem"> https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/moxifloxacin#section=2D-Structure </ref>'''. Fluoroquinolones are organic compounds categorized as a quinoline, or an aromatic ring with a substituted carboxyl group at one or more positions, with a fluoride component as a central part of the compound '''<ref name="drugsdetails"> https://drugsdetails.com/moxifloxacin/#Pharmacophore_structure_Information_about_the_chemical_structure_of_the_drug</ref>'''. The compound is able to accept eight hydrogen bonds and donate two '''<ref name="pubchem" />'''. The structure of the drug can also be found in the form of a monohydrochloride salt <ref name=" drugsdetails " />. |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 00:22, 20 April 2017
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/moxifloxacin#section=2D-Structure
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 https://drugsdetails.com/moxifloxacin/#Pharmacophore_structure_Information_about_the_chemical_structure_of_the_drug
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 https://livertox.nlm.nih.gov//Moxifloxacin.htm
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 https://www.drugs.com/avelox.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7868402
- ↑ https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00218
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21703/
- ↑ https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/44/10/4528/2516939/How-topoisomerase-IV-can-efficiently-unknot-and
- ↑ http://aac.asm.org/content/43/1/12.full
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2696358/
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 http://vanderbilt.edu/vicb/DiscoveriesArchives/combatting_antibiotic_drug_resistance.html
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/moxifloxacin#section=Chemical-and-Physical-Properties