Journal:Acta Cryst F:S2053230X20010122
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:Tabg.png|thumb|350px|left|Sequence alignment of LRRs in TMK3. The boundary of each LRR is shown on its right. The conserved residues are shown with yellow background. The solid black star indicates the amino acids specific to plant LRR proteins.]] | [[Image:Tabg.png|thumb|350px|left|Sequence alignment of LRRs in TMK3. The boundary of each LRR is shown on its right. The conserved residues are shown with yellow background. The solid black star indicates the amino acids specific to plant LRR proteins.]] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
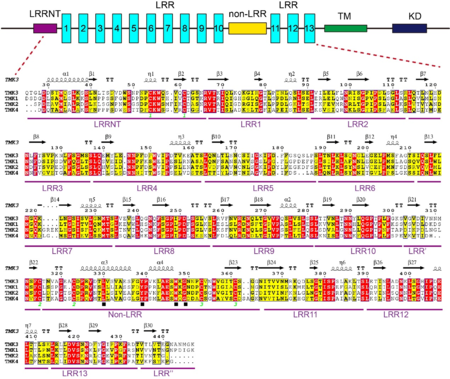
| - | The non-LRR has a Cys cluster with the pattern of ''Cx''<sub>''6-7''</sub>''Cx''<sub>''29-30''</sub>''Cx''<sub>''6-11''</sub>''C'' (Cys315-Cys323 and Cys353-Cys361) and a conserved motif of Lx8Yx7-8WxG ( | + | The non-LRR has a Cys cluster with the pattern of ''Cx''<sub>''6-7''</sub>''Cx''<sub>''29-30''</sub>''Cx''<sub>''6-11''</sub>''C'' (Cys315-Cys323 and Cys353-Cys361) and a conserved motif of Lx8Yx7-8WxG (see static image below) similar to Yx8KG found in many LRR- receptor-like kinases (Fritz-Laylin ''et al.,'' 2005<ref name="Fritz">PMID:15955925</ref>). |
| - | [[Image:Qw.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:Qw.png|thumb|450px|left|Sequence alignments of the ECDs of TMK3 and its homologs from Arabidopsis. Top: schematic representation of TMK3 protein. TM: transmembrane domain; KD: kinase domain; LRR: leucine-rich repeat. Bottom: Sequence alignment of the ECDs of TMK3 and its homologs from Arabidopsis. Conserved and similar residues are highlighted with red and yellow ground respectively. The solid black square indicates a conserved motif (Lx8Yx7-8WxG). Two cysteines that form a disulfide bond are labeled with the same number (in green) at bottom.]] |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
Most of LRR structures have caps, which shield the hydrophobic core of the first LRR unit at the N-terminus and the last unit at the C-terminus. In extracellular proteins or extracellular regions, the N-terminal and C-terminal caps frequently consist of Cys clusters including two or four Cys residues. The Cys clusters on the N- terminal and C-terminal sides of the LRR arcs are called LRRNT and LRRCT, respectively. Almost all known typical LRR structures include an LRRNT, some of which also have an LRRCT. TMK3-LRR belongs to the LRR subgroups that lacks LRRCT and possesses only an LRRNT (with Cx6C) characterized by a disulfide bond between Cys54 and Cys61. We have also observed five asparagine residues (N165, N170, N223, N286 and N448) modified by N-glycosylation (Figure 3C). | Most of LRR structures have caps, which shield the hydrophobic core of the first LRR unit at the N-terminus and the last unit at the C-terminus. In extracellular proteins or extracellular regions, the N-terminal and C-terminal caps frequently consist of Cys clusters including two or four Cys residues. The Cys clusters on the N- terminal and C-terminal sides of the LRR arcs are called LRRNT and LRRCT, respectively. Almost all known typical LRR structures include an LRRNT, some of which also have an LRRCT. TMK3-LRR belongs to the LRR subgroups that lacks LRRCT and possesses only an LRRNT (with Cx6C) characterized by a disulfide bond between Cys54 and Cys61. We have also observed five asparagine residues (N165, N170, N223, N286 and N448) modified by N-glycosylation (Figure 3C). | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 4 August 2020
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.