User:Isabela de Aquino Zogbi/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[Image:Schema_of_the_human_dysferlin_domain_structures_(2).png]] | [[Image:Schema_of_the_human_dysferlin_domain_structures_(2).png]] | ||
| - | ====DysF Domain==== | ||
| - | One Dysf domain is inserted into the other Dysf domain forming an inner Dysf domain (not represented in the image below) and a two part outer Dysf domain (N-terminal DysFN and C-terminal DysFC), and it is woth mentioning that the Dysf domain is held together by arginine/ aromatic sidechain stacking. The crystal structure of the human dysferlin inner DysF domain with a resolution of 1.9 Ångstroms by X-Ray diffraction (2). | ||
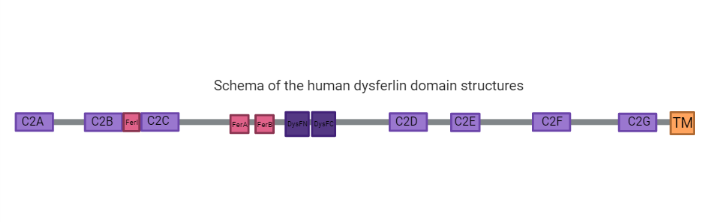
====C2 Domains==== | ====C2 Domains==== | ||
| - | C2 domains are independently membrane-binding modules of about 130 residues found in a large and diverse set of eukaryotic proteins that share a common overall fold: a single compact greek-key motif organized as an eight-stranded antiparallel β-sandwich consisting of a pair of four-stranded β-sheets (6, 7). | + | C2 domains are independently membrane-binding modules of about 130 residues found in a large and diverse set of eukaryotic proteins that share a common overall fold: a single compact greek-key motif organized as an eight-stranded antiparallel β-sandwich consisting of a pair of four-stranded β-sheets (6, 7). |
| + | ====Fer Domains==== | ||
| + | Ferlins proteins are characterized by ferlin-specific small 60-70 residue motifs with conserved secondary structure termed FerI, FerA and FerB (6). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====DysF Domain==== | ||
| + | One Dysf domain is inserted into the other Dysf domain forming an inner Dysf domain (not represented in the image below) and a two part outer Dysf domain (N-terminal DysFN and C-terminal DysFC), and it is woth mentioning that the Dysf domain is held together by arginine/ aromatic sidechain stacking. The crystal structure of the human dysferlin inner DysF domain with a resolution of 1.9 Ångstroms by X-Ray diffraction (2). | ||
===Function=== | ===Function=== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
====C2 Domains function==== | ====C2 Domains function==== | ||
| - | C2 domains are calcium sensitive phospholipid binding domains with an approximate length of 130 amino acids (5), while the function of the Dysf domain remains unclear (1;2). The presence of the C2 domains is common to ferlin-like proteins, in which only the C2A domain binds strongly to lipids in a calcium dependent way. The other domains have weaker bonds or are calcium independent. Also, C2A, E and F domains have shown a relevant function in the protein activity (5). | + | C2 domains are calcium sensitive phospholipid binding domains with an approximate length of 130 amino acids (5), while the function of the Dysf domain remains unclear (1;2). The presence of the C2 domains is common to ferlin-like proteins, in which only the C2A domain binds strongly to lipids in a calcium dependent way. The other domains have weaker bonds or are calcium independent. Also, C2A, E and F domains have shown a relevant function in the protein activity (5). In response to elevated calcium concentrations, these domains target a protein to a particular membrane compartment based upon preference for an organelle specific lipid headgroup. After binding, some C2 domains actively cluster lipids or bend the membrane, actively perturbing membrane structure in helping to facilitate cellular processes (8). |
Revision as of 04:39, 19 June 2022
Dysferlin
| |||||||||||