User:Michael Kerins/Bovine Odorant Binding Protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''''Bovine Odorant Binding Protein''''' | '''''Bovine Odorant Binding Protein''''' | ||
---- | ---- | ||
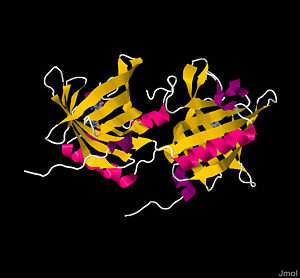
| - | [[Image:1GT1.jpg|300px|left|thumb| Crystal structure of Bovine Odorant Binding Protein]] [[Image:cow.jpg|300px|right|thumb| Cow]] Bovine | + | [[Image:1GT1.jpg|300px|left|thumb| Crystal structure of Bovine Odorant Binding Protein]] [[Image:cow.jpg|300px|right|thumb| Cow]] Bovine odorant binding protein, '''bOBP''', is a 19 kDa protein found in the nasal mucosa of the ungulate subfamily ''Bovinae''. It is crucial to eliciting a "sense of smell." Although the exact function oBP is not known (in reality, it likely has several functions), the traditional role ascribed to bOBP is to aid in the transport of volatile odorants from the air to an odorant receptor, and to aid in crossing the aqueous mucus layer. To perform this feat, bOBP utilizes two |
---- | ---- | ||
| + | <scene name='User:Michael_Kerins/Bovine_Odorant_Binding_Protein/Homodimer/2'>bOBP backbone in blue</scene> | ||
=='''Introduction'''== | =='''Introduction'''== | ||
Revision as of 16:42, 9 April 2011
Bovine Odorant Binding Protein
Bovine odorant binding protein, bOBP, is a 19 kDa protein found in the nasal mucosa of the ungulate subfamily Bovinae. It is crucial to eliciting a "sense of smell." Although the exact function oBP is not known (in reality, it likely has several functions), the traditional role ascribed to bOBP is to aid in the transport of volatile odorants from the air to an odorant receptor, and to aid in crossing the aqueous mucus layer. To perform this feat, bOBP utilizes two
Contents |
Introduction
The need to smell
Test
Test
Test
Test
Test
Structure
What are the basic parameters of bOBP?
bOBP is a homodimer of two virtually symmetrical subunits held together noncovalently.
|