User:Ann Taylor/Sandbox Adenosine Deaminase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{STRUCTURE_2ada| PDB=2ada | SCENE= }} | ||
| + | ===ADENOSINE DEAMINASE=== | ||
| - | Adenosine deaminase is involved in the degradation of purine nucleotides. It is especially active in lympocytes, and mutation of adenosine deaminase results in severe immunodeficiency. Adenosine deaminase contains an eight stranded parallel alpha/beta barrel with the active site in a deep pocket at the beta-barrel COOH-terminal end. | + | |
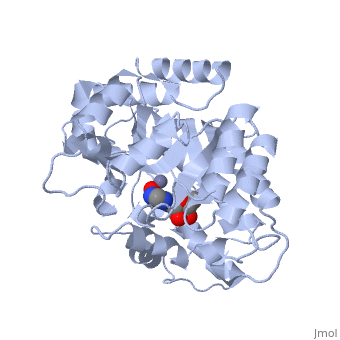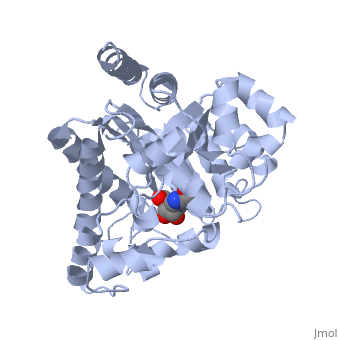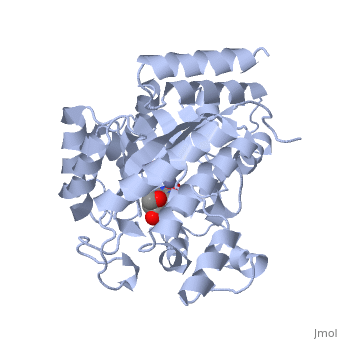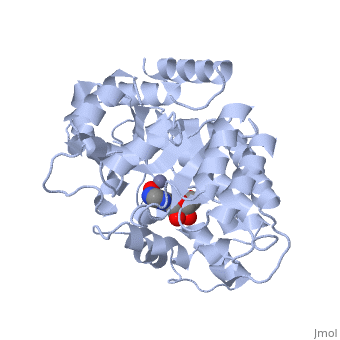
| + | Adenosine deaminase is involved in the degradation of purine nucleotides. It is especially active in lympocytes, and mutation of adenosine deaminase results in severe immunodeficiency. Adenosine deaminase contains an eight stranded parallel alpha/beta barrel with the active site in a deep pocket at the beta-barrel COOH-terminal end. <ref>PMID:1925539 </ref> The active site contains a zinc cofactor, which coordinates to the 6-hydroxyl of the transition state analogue, 6-hydroxyl, 1,6-dihydropurine ribonucleoside. The zinc is coordinated to three histidine residues and an aspartic acid residue. | ||
The transition state analogue held in place mostly by polar interactions. The ribose group is close to the opening of the pocket, with the purine portion deeper in the pocket, close to the zinc. Nine hydrogen bonds stabilize the transition state-enzyme complex. | The transition state analogue held in place mostly by polar interactions. The ribose group is close to the opening of the pocket, with the purine portion deeper in the pocket, close to the zinc. Nine hydrogen bonds stabilize the transition state-enzyme complex. | ||
Revision as of 15:03, 26 September 2013
| |||||||||
| 2ada, resolution 2.40Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Adenosine deaminase, with EC number 3.5.4.4 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
ADENOSINE DEAMINASE
Adenosine deaminase is involved in the degradation of purine nucleotides. It is especially active in lympocytes, and mutation of adenosine deaminase results in severe immunodeficiency. Adenosine deaminase contains an eight stranded parallel alpha/beta barrel with the active site in a deep pocket at the beta-barrel COOH-terminal end. [1] The active site contains a zinc cofactor, which coordinates to the 6-hydroxyl of the transition state analogue, 6-hydroxyl, 1,6-dihydropurine ribonucleoside. The zinc is coordinated to three histidine residues and an aspartic acid residue.
The transition state analogue held in place mostly by polar interactions. The ribose group is close to the opening of the pocket, with the purine portion deeper in the pocket, close to the zinc. Nine hydrogen bonds stabilize the transition state-enzyme complex.