User:Rana Saad/The human GABAb receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
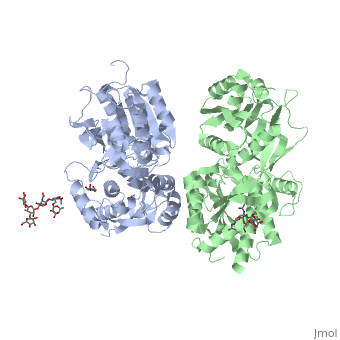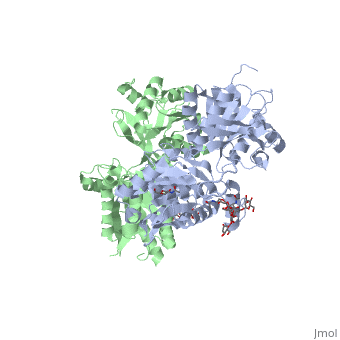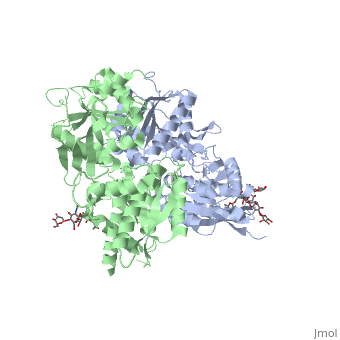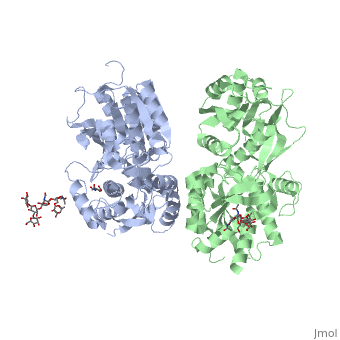
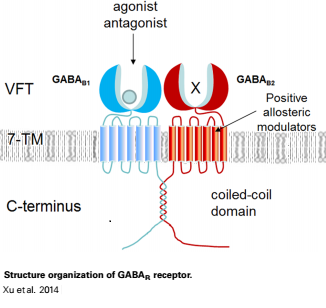
Mammalian GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is a class C [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/G_protein-coupled_receptor#3D_Structures_of_G_protein-coupled_receptors G-protein coupled receptor]<ref>PMID:23237917</ref>. Its structure is similar to [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor|metabotropic glutamate receptors]] (mGluR) ligand binding domain. GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is central to inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain and so is considered a good candidate for treatments against alcoholism, stress and number of brain diseases<ref>PMID:19913201</ref>. | Mammalian GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is a class C [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/G_protein-coupled_receptor#3D_Structures_of_G_protein-coupled_receptors G-protein coupled receptor]<ref>PMID:23237917</ref>. Its structure is similar to [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor|metabotropic glutamate receptors]] (mGluR) ligand binding domain. GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is central to inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain and so is considered a good candidate for treatments against alcoholism, stress and number of brain diseases<ref>PMID:19913201</ref>. | ||
[[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|thumb|200px]] | [[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|thumb|200px]] | ||
| - | |||
=='''''Structure'''''== | =='''''Structure'''''== | ||
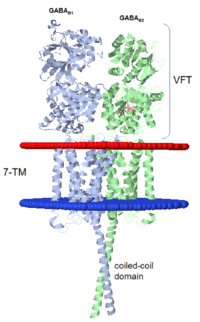
| - | GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of GABA<sub>B1</sub> (GBR1) and GABA<sub>B2</sub> (GBR2). GBR1 is responsible for ligand-binding. GBR2, on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunits. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of only a few obligate receptor | + | GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of GABA<sub>B1</sub> (GBR1) and GABA<sub>B2</sub> (GBR2). GBR1 is responsible for ligand-binding. GBR2, on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunits. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of only a few obligate receptor heterodimer currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete receptor, but the extracellular and intracellular domains of it . |
===GBR1 and GBR2 subunits structure=== | ===GBR1 and GBR2 subunits structure=== | ||
| - | Each subunit is a domain of seven-transmembrane helixes, composed of a large extracellular domain - venus flytrap (VFT), | + | Each subunit is a domain of seven-transmembrane helixes, composed of a large extracellular domain - venus flytrap (VFT), it is called like this because it is like the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venus_flytrap venus flytrap] while binding agonist and antagonist. |
VFT contains two lobe-shaped domains: LB1 and LB2, which are connected by three short loops. | VFT contains two lobe-shaped domains: LB1 and LB2, which are connected by three short loops. | ||
LB1 and LB2 are <scene name='70/701448/Gbr2_subunit/1'>αβ-folds composed of central β sheet flanked by an α helix</scene><ref>PMID:24305054</ref>. | LB1 and LB2 are <scene name='70/701448/Gbr2_subunit/1'>αβ-folds composed of central β sheet flanked by an α helix</scene><ref>PMID:24305054</ref>. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
All of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agonist agonists] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_antagonist antagonists] bind the extracellular VFT module situated at the crevice between the LB1 and LB2 domains of the GBR1 subunit. | All of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agonist agonists] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_antagonist antagonists] bind the extracellular VFT module situated at the crevice between the LB1 and LB2 domains of the GBR1 subunit. | ||
| - | + | Both lobes LB1 and LB2 resdues of GBR1 interact with the GABA<sub>B</sub> agonsits such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-Aminobutyric_acid GABA],[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baclofen baclofen]. as a results of this interacting '''closed conformation''' will be stabilized when <scene name='70/701448/Gaba_ligand/4'> GBR1 subunit bound to GABA</scene> or <scene name='70/701448/Baclofen/3'>bound to baclofen</scene> and other agonists. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Both lobes LB1 and LB2 resdues of GBR1 interact with the GABA<sub>B</sub> agonsits such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma-Aminobutyric_acid GABA],[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baclofen baclofen]. as a results of this interacting '''closed conformation''' will be stabilized when <scene name='70/701448/Gaba_ligand/4'> GBR1 | + | |
| - | ===Antgonist-induced heterodimer interface=== | ||
GABA<sub>B</sub> Antgonists such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saclofen saclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-46381.html CGP46381], [http://www.hellobio.com/phaclofen.html?picat=&q=phaclofen phaclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-35348.html?picat=&q=CGP+35348 CGP35348] and [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-54626-hydrochloride.html?picat=&q=CGP+54626 CGP54626], mostly intercat with LB1 resduses of GBR1. both ends of the antagonist bind the LB1, which produce '''open confirmation''' of GBR1. | GABA<sub>B</sub> Antgonists such as: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saclofen saclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-46381.html CGP46381], [http://www.hellobio.com/phaclofen.html?picat=&q=phaclofen phaclofen], [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-35348.html?picat=&q=CGP+35348 CGP35348] and [http://www.hellobio.com/cgp-54626-hydrochloride.html?picat=&q=CGP+54626 CGP54626], mostly intercat with LB1 resduses of GBR1. both ends of the antagonist bind the LB1, which produce '''open confirmation''' of GBR1. | ||
it is very easy to notice the '''open confirmation''' when : | it is very easy to notice the '''open confirmation''' when : | ||
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Saclofen_ant/2'>GBR1 | + | <scene name='70/701448/Saclofen_ant/2'>GBR1 subunit bound to saclofen</scene>. |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Cgp46381_ant/2'>GBR1 | + | <scene name='70/701448/Cgp46381_ant/2'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP46381</scene>. |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Phaclofen_ant/1'>GBR1 | + | <scene name='70/701448/Phaclofen_ant/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to phaclofen</scene>. |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_cg835348/1'>GBR1 | + | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_cg835348/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP35348</scene>. |
| - | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 | + | <scene name='70/701448/Ant_CGP54626/1'>GBR1 subunit bound to CGP54626</scene>. |
=='''''Dimerization motif'''''== | =='''''Dimerization motif'''''== | ||
Revision as of 16:51, 8 July 2015
| |||||||||||