Carboxypeptidase A
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==Important Tyr248 Residue== | ==Important Tyr248 Residue== | ||
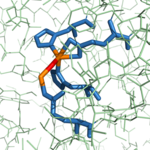
| - | 1CPX’s most interesting distinction from other CPA proteins is that its crystallographic data revealed a different conformation of the Tyr248 residue [[Image:1CPX-Tyr248.png|thumb|Figure 2: Important Tyr248 residue of 1CPX pointing toward the hydrophobic binding pocket.]] <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. Previous literature has suggested that the conserved Tyrosine residue among CPA proteins has been involved in an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_catalysis#Induced_fit induced fit mechanism] because <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_5cpa/1'>Tyr248 typically has been found pointing outward toward solution</scene> when a substrate is not bound to the enzyme (see [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPA3 3CPA]) <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. However, 1CPX's crystallographic data shows <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_1cpx/1'>Tyr248 pointing toward the active site</scene> without a substrate bound. Therefore, this denies the previously proposed induced fit mechanism for CPA proteins and suggests that Tyr 248 is a ligand to the catalytic Zinc in 1CPX <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. Moreover, this data supports that this is the <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_1cpx/1'>native conformation of Tyr248 in solution</scene> because none of the residues in the protein’s active site interact in the crystallographic packing <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. Not only does Tyr248 point toward the active site, but in doing so, <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_pointing_toward/2'>Tyr248 caps the hydrophobic binding pocket</scene> with its interactions with Ile247 and a hydrogen bond <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. | + | 1CPX’s most interesting distinction from other CPA proteins is that its crystallographic data revealed a different conformation of the Tyr248 residue [[Image:1CPX-Tyr248.png|thumb|Figure 2: Important Tyr248 residue of 1CPX pointing toward the hydrophobic binding pocket.]] <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. Previous literature has suggested that the conserved Tyrosine residue among CPA proteins has been involved in an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_catalysis#Induced_fit induced fit mechanism] because <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_5cpa/1'>Tyr248 typically has been found pointing outward toward solution</scene> when a substrate is not bound to the enzyme (see [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPA3 3CPA]) <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. However, 1CPX's crystallographic data shows <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_1cpx/1'>Tyr248 pointing toward the active site</scene> without a substrate bound. Therefore, this denies the previously proposed induced fit mechanism for CPA proteins and suggests that Tyr 248 is a ligand to the catalytic Zinc in 1CPX <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. Moreover, this data supports that this is the <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_1cpx/1'>native conformation of Tyr248 in solution</scene> because none of the residues in the protein’s active site interact in the crystallographic packing <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. Not only does Tyr248 point toward the active site, but in doing so, <scene name='69/694222/Tyr248_pointing_toward/2'>Tyr248 caps the hydrophobic binding pocket</scene> (blue) with its interactions with Ile247 and a hydrogen bond <ref name="CPA1">Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. ''Biochemistry''. 37(47):16555-16564. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/bi981678i DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i]</ref>. This point of view is able to clearly show how Tyr248 is thought to be a ligand with the catalytic Zinc. |
== Mechanism of Action == | == Mechanism of Action == | ||
Revision as of 20:58, 2 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Carboxypeptidase A in Bos taurus
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 Bukrinsky JT, Bjerrum MJ, Kadziola A. 1998. Native carboxypeptidase A in a new crystal environment reveals a different conformation of the important tyrosine 248. Biochemistry. 37(47):16555-16564. DOI: 10.1021/bi981678i
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Christianson DW, Lipscomb WN. 1989. Carboxypeptidase A. Acc. Chem. Res. 22:62-69.
- ↑ Suh J, Cho W, Chung S. 1985. Carboxypeptidase A-catalyzed hydrolysis of α-(acylamino)cinnamoyl derivatives of L-β-phenyllactate and L-phenylalaninate: evidence for acyl-enzyme intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107:4530-4535. DOI: 10.1021/ja00301a025
- ↑ Geoghegan, KF, Galdes, A, Martinelli, RA, Holmquist, B, Auld, DS, Vallee, BL. 1983. Cryospectroscopy of intermediates in the mechanism of carboxypeptidase A. Biochem. 22(9):2255-2262. DOI: 10.1021/bi00278a031
- ↑ Kaplan, AP, Bartlett, PA. 1991. Synthesis and evaluation of an inhibitor of carboxypeptidase A with a Ki value in the femtomolar range. Biochem. 30(33):8165-8170. PMID: 1868091
- ↑ Worthington, K., Worthington, V. 1993. Worthington Enzyme Manual: Enzymes and Related Biochemicals. Freehold (NJ): Worthington Biochemical Corporation; [2011; accessed March 28, 2017]. Carboxypeptidase A. http://www.worthington-biochem.com/COA/
- ↑ Pitout, MJ, Nel, W. 1969. The inhibitory effect of ochratoxin a on bovine carboxypeptidase a in vitro. Biochem. Pharma. 18(8):1837-1843. DOI: 0.1016/0006-2952(69)90279-2
- ↑ Normant, E, Martres, MP, Schwartz, JC, Gros, C. 1995. Purification, cDNA cloning, functional expression, and characterization of a 26-kDa endogenous mammalian carboxypeptidase inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 92(26):12225-12229. PMCID: PMC40329
Student Contributors
- Thomas Baldwin
- Michael Melbardis
- Clay Schnell
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michael Melbardis, Douglas Schnell, Thomas Baldwin, Geoffrey C. Hoops, Michal Harel