User:Isabela de Aquino Zogbi/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Structure and Function == | == Structure and Function == | ||
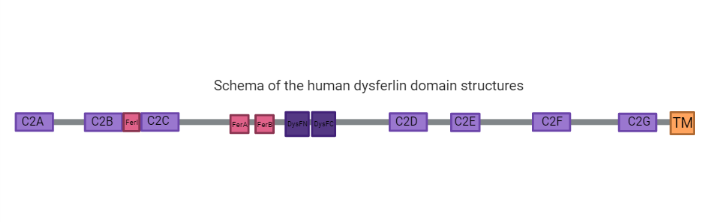
| - | <scene name='91/915204/Secondary_structure_dysf/4'>Dysferlin</scene> has seven tandem C2 domains (<scene name='91/915204/C2adomain/1'>C2A</scene>, B, D, E and G), three Fer domains (FerA, FerB and FerI) which are short conserved regions found only in the ferlin protein family and are not yet shown to be folded domains (2), two <scene name='91/915204/Inner_dysf/1'>Dysf domains</scene> and a C-terminal transmembrane domain | + | ===Structure=== |
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='91/915204/Secondary_structure_dysf/4'>Dysferlin</scene> has seven tandem C2 domains (<scene name='91/915204/C2adomain/1'>C2A</scene>, B, D, E and G), three Fer domains (FerA, FerB and FerI) which are short conserved regions found only in the ferlin protein family and are not yet shown to be folded domains (2), two <scene name='91/915204/Inner_dysf/1'>Dysf domains</scene> and a C-terminal transmembrane domain with a helix embedded in a patching vesicle. One Dysf domain is inserted into the other Dysf domain forming an inner Dysf domain (not represented in the image below) and a two part outer Dysf domain (N terminal DysFN and C terminal DysFC), and it is woth mentioning that the Dysf domain is held together by arginine/ aromatic sidechain stacking. | ||
[[Image:Schema_of_the_human_dysferlin_domain_structures_(2).png]] | [[Image:Schema_of_the_human_dysferlin_domain_structures_(2).png]] | ||
| - | Many dysferlinopathy causing mutations fall in the DysF domains (2). | + | ===Function=== |
| + | Many dysferlinopathy causing mutations fall in the DysF domains (2). It's important to notice that dysferlin function is linked with calcium-activated membrane repair caused by fusing aggregated intracellular vesicles with the sarcolemma at the site of injury(2). | ||
| + | |||
| + | C2 domains are calcium sensitive phospholipid binding domains with an approximate length of 130 amino acids (5), while the function of the Dysf domain remains unclear (1;2). The presence of the C2 domains is common to ferlin-like proteins, in which only the C2A domain binds strongly to lipids in a calcium dependent way. The other domains have weaker bonds or are calcium independent. Also, C2A, E and F domains have shown a relevant function in the protein activity (5). | ||
It has been shown that dysferlin deficiency delays myoblast (undifferentiated mononuclear muscle cells) fusion/maturation in vitro, suggesting that dysferlin may also participate in muscle differentiation and regeneration process (3). | It has been shown that dysferlin deficiency delays myoblast (undifferentiated mononuclear muscle cells) fusion/maturation in vitro, suggesting that dysferlin may also participate in muscle differentiation and regeneration process (3). | ||
Revision as of 22:10, 18 June 2022
| |||||||||||