User:Eduardo Soares/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
Highlight representation of the the <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">c-di-GMP</scene> and <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein, putting in evidence the alpha helix. | Highlight representation of the the <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">c-di-GMP</scene> and <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein, putting in evidence the alpha helix. | ||
| + | ===The Crystal Structure of the Protein of VCA0042 from Vibrio cholerae O1 ([[1yln]])=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='1yln/Pilz_start/1'>PilZ</scene> | ||
| + | |||
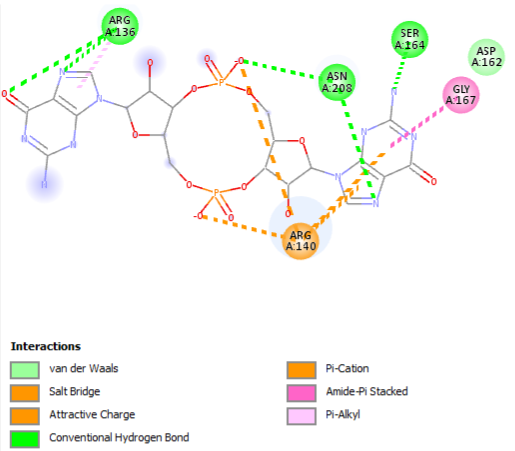
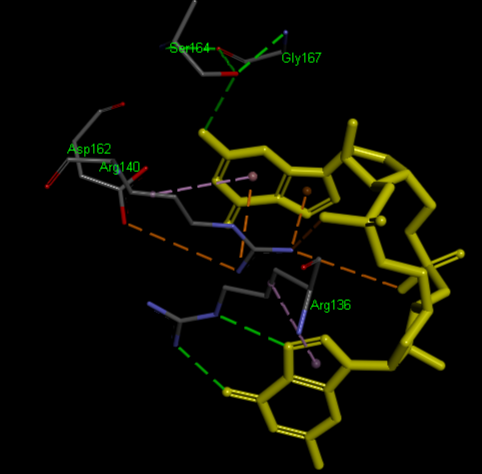
| + | <scene name='1yln/Pilz_binding/2'>Binding site</scene> (R136, R140, D162, S164, G167) | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 11:27, 26 June 2023
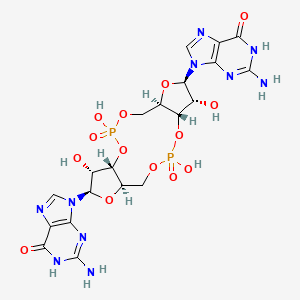
VCA0042/plzD complexed with c-di-GMP
Introduction
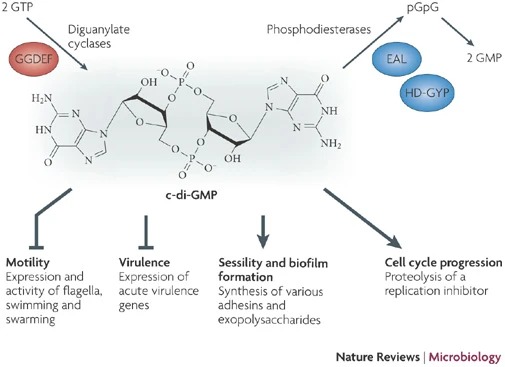
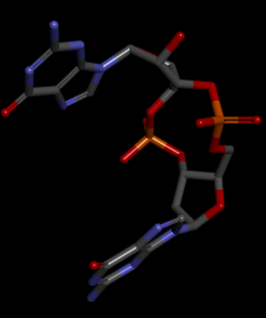
The PDB code 2RDE represents a PilZ protein complexed with cyclic diguanylate monophosphate (c-di-GMP) in Vibrio cholera there is a molecular interaction involved in the regulation of bacterial biofilm formation and motility. The complex is formed by the binding of the small signaling molecule c-di-GMP to a protein domain known as PilZ. This interaction plays a crucial role in bacterial physiology and is implicated in various cellular processes. [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.
- ↑ Pecina, Anna, et al. The Stand-Alone PilZ-Domain Protein MotL Specifically Regulates the Activity of the Secondary Lateral Flagellar System in Shewanella putrefaciens. Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 12, 2021. Frontiers, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.668892.
- ↑ Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.
- ↑ Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.
- ↑ Hengge, R. Principles of c-di-GMP signalling in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 7, 263–273 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2109
- ↑ Purificação, Aline Dias da, et al. The World of Cyclic Dinucleotides in Bacterial Behavior. Molecules, vol. 25, n. 10, Janeiro de 2020, p. 2462. www.mdpi.com, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102462.
- ↑ Purificação, Aline Dias da, et al. The World of Cyclic Dinucleotides in Bacterial Behavior. Molecules, vol. 25, n. 10, Janeiro de 2020, p. 2462. www.mdpi.com, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102462.
- ↑ Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.