Poli 3-hydroxyalcanoates (PHA) are the main components of the cytoplasmatic inclusions, called PHA granules. They serve as carbon and energy reserves in many species of procariotes. PHA polymers can be made from different sized monomers, ranging from 4 to 14 carbon atoms. They are typically synthetized when there is an unbalanced distribution of nutrients in the medium, mainly an abundance of carbon sources coupled with the lack of another essential component. Among the existing PHAs, the most common are the poli-3-hydroxybutirate (PHB) polymers. [1]. PHBs are specially relevant due to their properties that resemble conventional plastics, such as polypropylene. Since they are biopolymers made from renewable, biodegrabable and compatible source materials, PHBs present themselves as an industrial alternative to petrol-based plastics.[2][3]
The polymerization of PHA monomers is performed by the PHA sintase/polymerase (phaC) enzyme. At first, two acetyl-CoA molecules are condensed into one acetoacetyl-CoA by a β-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, and then reduced to (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA by the acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Finally, phaC polymerizes the (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA molecules into the PHA polymer.[4]
Currently, there are four known classes of phaC, that are distinguished by their primary structure, substrate specificity and subunits composition [5][6]. Despite vast diversity, only the catalytic domain of the PhaCcn-CAT from Ralstonia eutropha H16 (syn. Cupriavidus necator) and the USM2 PhaCcs-CAT from the Chromobacterium sp., both being class 1 phaCs.[6]
Class 1
Overview
The class 1 phaCs synthetize preferentially short chain PHAs, with 3 to 5 carbon monomers, and are composed by a single enzymatic unit, with molecular mass ranging from 63 to 73 kDA.[6][7]
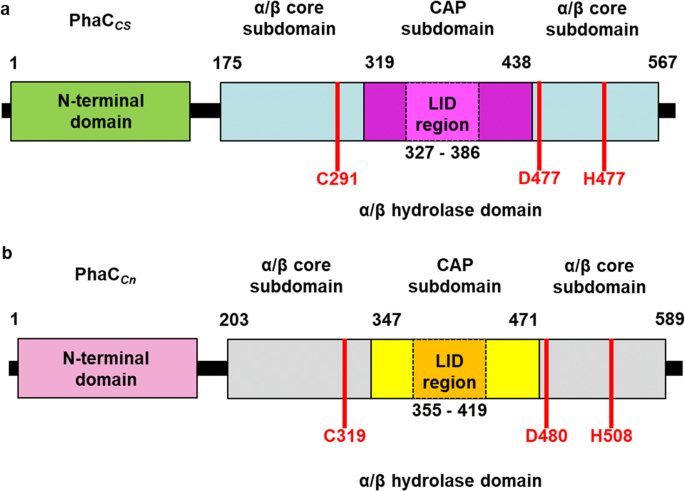
Thanks to the X-ray cristallography data from PhaCcn-CAT and PhaCcs-CAT, it was possible to categorize the class 1 phaCs in based on their molecular organization, made of two domains: The N-terminal domain and the . The C-terminal domain carries the (Cys-Asp-His) located deep within the hydrophobic , that in the closed conformation is partially covered by the Cap .[6][7]
Structure from two class 1 phaCs (PhaCcn-CAT and PhaCcs-CAT). Image obtained from Chek et., al 2018.[7]
N-terminal domain
The N-terminal domain has no defined function, and attempts to perform X-ray cristallography of this region have not been sucessful. Many studies have gathered evidence of possible roles that the N-terminal domain performs, such as: enzymatic activity efficiency, binding to PHA granules, substrate specificity, phaC expression, interaction with other PHA-related proteins and dimers formation and estabilization. Still, elucidation of its exact catalytic mechanism remains necessary.[6]
C-terminal domain
Contrary to the flexible N-terminal domain, the is relatively stable, making its crytalization process easier. Because of this, it was possible to obtain the C-terminal domain structure from PhaCcn-CAT and PhaCcs-CAT through X-ray cristallography, with resolution of 1.8 Å and 1.48 Å, respectively. The C-terminal domain has the (Cys-Asp-His), the substrate entrance and the product egress tunnel.[6]
The overall form of a phaC protein is that of a typical protein from the α/β-hydrolase-fold, with the C-terminal domain made of an α/β-hydrolase core and a Cap , corresponding to the Thr347-Pro471 residues in PhaCcn-CAT, and Thr319-Pro438 residues in PhaCcs-CAT. It is in the α/β-hydrolase subdomain that the entrance tunnel, the catalytic site and the product egress tunnel are located. This region seems to be preserved in phaCs.[6]
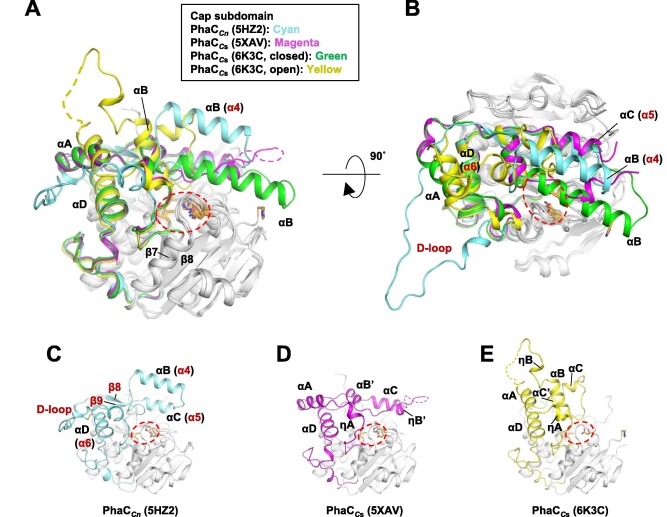
Regarding the Cap , the LID region is extremely dynamic and flexible, having an open or closed conformation based on structural changes. Because of this, the Cap subdomain, specially the LID region, is not as conserverd in the phaCs as the α/β-hydrolase subdomain. The Cap subdomain is located after the β7 sheet, and connects with the β8 sheet from the α/β-hydrolase core. In PhaCcn-CAT, the Cap subdomain is formed by three α-helixes (α4, α5 and α6) and two β-sheets (β8 and β9). Meanwhile, PhaCcs-CAT has six α-helixes (αA, αB, αC, αD, ηA and ηB').[6]. The Cap subdomain is paramount in the phaC dimer formation and regulation of substrate entry and product release, due to the dynamic and flexible properties, specially of the LID region.[6]
Video produced by Chek et al., 2020, showing the phaC conformational change.[8]
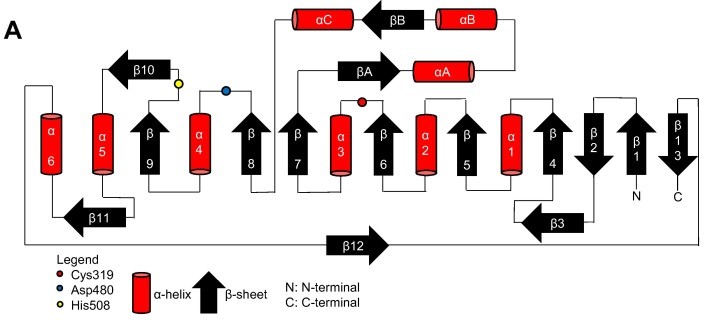
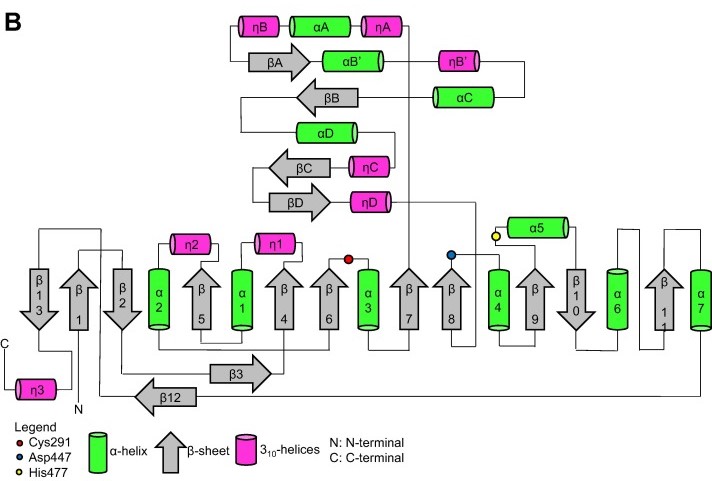
Secondary structure
Topology diagram for the catalytic domain of the PhaCcn-CAT monomer. Image obtained from Neoh et al., 2022.[6]
Topology diagram for the catalytic domain of the PhaCcs-CAT monomer. Image obtained from Neoh et al., 2022.[6]
Terciary structure
Terciary structure of PhaCcn-CAT and PhaCcs-CAT, with the Cap subdomain highlighted. Image obtained from Neoh et al., 2022.[6]
Quaternary structure
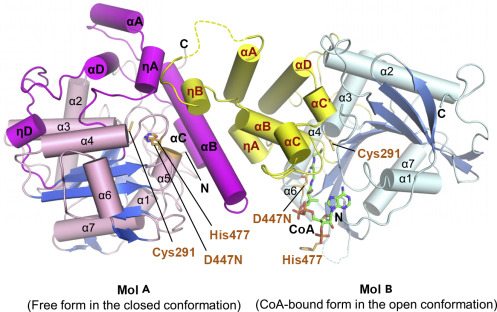
The co-crystal of a PhaCcs-CAT with CoA reveals the complex structure of an asymmetric dimer, with two protomers in different forms. The closed form is CoA-free, and the open form is CoA-bound. In the open form, the CoA molecule is accommodated in the active site cleft, created by dynamic conformational transitions in the Cap and local conformational shifts in the α/β-hydrolase core . One protomer was in the closed conformation (free form), while the other protomer was bound to CoA in an open conformation. Observations were made that the free form is important for stabilizing the form bound to CoA.[6][8]
In general, monomeric and dimeric forms exist in equilibrium, but it is generally understood that PhaC is active in its dimeric form, which is essential for the functionality of PHA synthase. This active form (dimeric form) can be induced in the presence of substrates.[6]
The Cap and mainly its LID region are important in the dimerization of PhaC, as they mediate the movement of the protomer, regulating the shift between the closed-closed form (homodimer) and the open-closed form (heterodimer).[6]
Structure of the PhaCcs-CAT heterodimer formed by the free and CoA-bound forms. Image obtained from Chek et., al 2020.[8]
Class 2
Among the 4 classes of phaC, the are the only that synthetize preferentially medium chain PHA, with 6 to 14 carbon monomers. Just like the class 1, they are also formed by a single enzymatic subunit, however, its molecular mass is, in general, higher than class 1 phaC, with approximately 62 kDa. It is suggested that the class 2 molecules also have two domains. [7]
Class 3
produce preferentially short chain PHAs, with 3 to 5 carbon monomers. However, differently from classes 1 and 2, , and has a smaller molecular mass ranging from 40 to 53 kDa.[7][9]
Class 4
Just like class 3, and , and has a smaller molecular mass than the other classes. The class 4 phaC also produce preferentially short chain PHAs, with 3 to 5 carbon monomers.[6]
References
- ↑ BARBOSA, Heloiza Ramos; GOMEZ, José Gregório Cabrera; TORRES, Bayardo Baptista. Microbiologia básic - bacteriologia: bacteriologia. 2. ed. São Paulo: Editora Atheneu, 2018. 336 p.
- ↑ BYROM, D.. Polymer synthesis by micro- organisms: technology and economics. Tibtech, [s. l], v. 5, p. 246-250, set. 1987.
- ↑ MADISON, Lara L.; HUISMAN, Gjalt W.. Metabolic Engineering of Poly(3-Hydroxyalkanoates): From DNA to Plastic. Microbiology And Molecular Biology Reviews, Massachusetts, v. 1, n. 63, p. 21-53, mar. 1999.
- ↑ Reddy, C.S.K, et al. “Polyhydroxyalkanoates: An Overview.” Bioresource Technology, vol. 87, no. 2, Apr. 2003, pp. 137–146, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960852402002122, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(02)00212-2.
- ↑ REHM, Bernd H. A. “Polyester Synthases: Natural Catalysts for Plastics.” Biochemical Journal, vol. 376, no. 1, 15 Nov. 2003, pp. 15–33, https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20031254.
- ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 Zher Neoh, Soon, et al. “Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase (PhaC): The Key Enzyme for Biopolyester Synthesis.” Current Research in Biotechnology, vol. 4, 2022, pp. 87–101, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbiot.2022.01.002.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Chek, Min Fey, et al. “PHA Synthase (PhaC): Interpreting the Functions of Bioplastic-Producing Enzyme from a Structural Perspective.” Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, vol. 103, no. 3, 3 Dec. 2018, pp. 1131–1141, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9538-8. Accessed 14 May 2023.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 CHEK, Min Fey; KIM, Sun-Yong; MORI, Tomoyuki; TAN, Hua Tiang; SUDESH, Kumar; HAKOSHIMA, Toshio. Asymmetric Open-Closed Dimer Mechanism of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase PhaC. Iscience, [S.L.], v. 23, n. 5, p. 101084, maio 2020. Elsevier BV. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101084.
- ↑ Jia, Kaimin, et al. “Study of Class I and Class III Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Synthases with Substrates Containing a Modified Side Chain.” Biomacromolecules, vol. 17, no. 4, 22 Mar. 2016, pp. 1477–1485, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00082.





