Background
Metabolic Role
Component of Endocannabinoid System
Structure
Catalytic triad
MGL has a classic catalytic triad that contains Ser-His-Asp. This triad has a natural attraction to Endocannabinoids, specifically 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG). 2-AG contributes to brain signals (neurons) to suppress the pain pathways when a patient is feeling depressed or suffering from any type of pain.
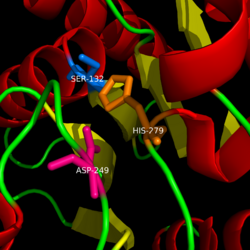
Catalytic Triad of MGL structure
Binding
Inhibition
Research on MGL is being geared towards inhibiting 2-AG from binding to the catalytic triad and being hydrolyzed. The binding of 2-AG to the catalytic triad can not be inhibited, but it can be extracted before being hydrolyzed. MPD (2-methyl-pentane-2,4-diol)is located at the end of the tunnel where the catalytic triad is at and the tunnel is filled with MPD molecules. MPD being in the same vicinity will extract 2-AG from the triad and the MPD molecule will sit in there in place of 2-AG. This natural inhibition phenomenon is known as interfacial activation.
Ligand Binding Site
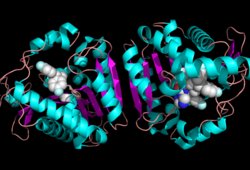
Ligand within the Overall Structure of MGL
Overall Reaction
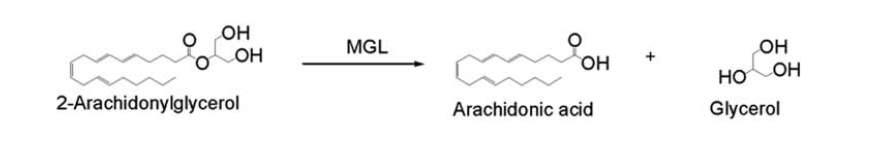
Literature
Additional Resources
Serine hydrolases
References
External links