Methionine synthase
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Methionine synthase
| |||||||||||
Structural highlights
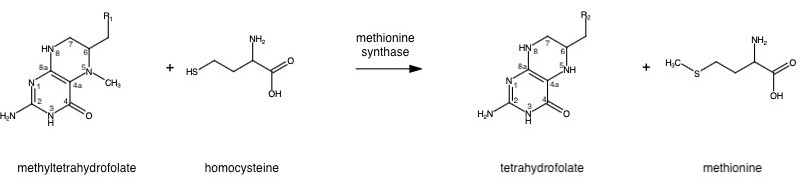
Methionine synthase (MetH) is a B12-dependent enzyme that methylates homocysteine to regenerate methionine. The has yet to be determined but we understand it contains 4 domains of B12 cobalamin (in pink), methyltetrahydrofolate (blue), homocysteine (yellow), and SAH (as part of the SAM cycle; in red). Each domain with an important function required for catalytic and reactivation cycles.
Vitamin B-12
Oxidation States of Cobalamin
Relevance
Methionine deficiency can result in diseases such as birth abnormalities.
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
References
- ↑ Barra L, Fontenelle C, Ermel G, Trautwetter A, Walker GC, Blanco C. Interrelations between glycine betaine catabolism and methionine biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 102F34. J Bacteriol. 2006 Oct;188(20):7195-204. doi: 10.1128/JB.00208-06. PMID:17015658 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00208-06
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Kia Yang, Karsten Theis, Michal Harel, Anna Postnikova, Michael O'Shaughnessy