Structure
Moxifloxacin is a synthetic antimicrobial fluoroquinolone with the molecular formula C21H24FN3O4. It has an average molecular weight of 401.438 g/mol [1]. Fluoroquinolones are organic compounds categorized as a quinoline, aromatic ring with a substituted carboxyl group at one or more positions, as well as a fluoride as a central part of the compound (2). The compound is able to accept eight hydrogen bonds and donate two [1]. The structure of the drug can also be found as a form of a monohydrochloride salt (2).
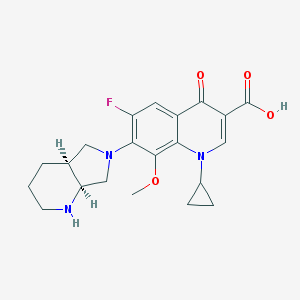 [2]
[2]
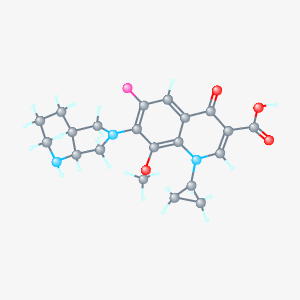 [3]
[3]
Function
Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that also acts as an antibacterial compound [1]. The drug is typically taken in 400mg tablets for five days and ranging up to fourteen days. When dealing with more severe infections, moxifloxacin is administered in 400mg through intravenous injections (3). Moxifloxacin is active against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria with an increased affinity for gram-positive bacteria, such as the multidrug-resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae (3). Other examples of infections for which moxifloxacin is prescribed include bronchitis, sinusitis, skin or soft tissue infection, anthrax prophylaxis, and tuberculosis (4). The function of moxifloxacin is inhibited by the consumption of cations, but the precise mechanism is unknown. One possible explanation for the decreased function of moxifloxacin in the presence of cations is the binding of cations to the compound causing chelation and therefore a decreased amount of drug available to interact with the bacteria. Alternatively, the presence of cations may interact with the drug’s target, DNA , which decreases its effectiveness [4].
Mechanism
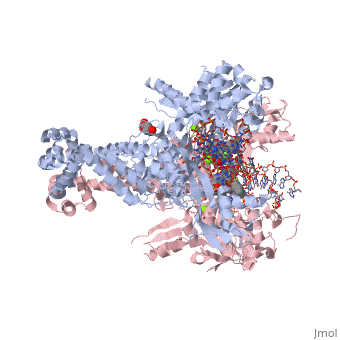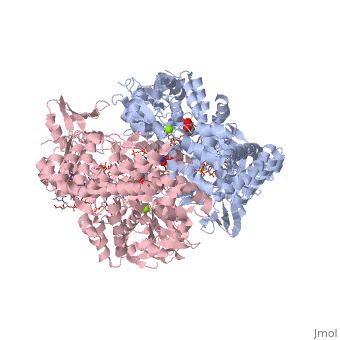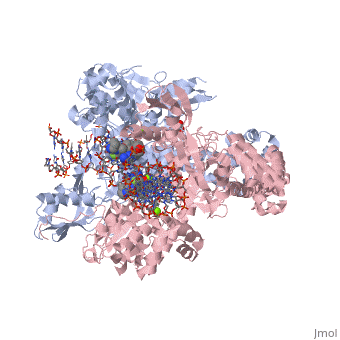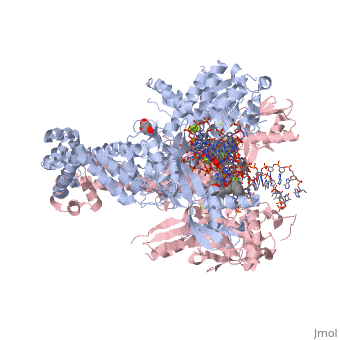
Moxifloxacin is an antibiotic that works by inhibiting the function of two bacterial enzymes, topoisomerase II (DNA Gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, both of which are necessary for bacterial DNA replication. (6) DNA Gyrase works by inducing supercoils in DNA, and by unwinding DNA during replication, thus relieving torsional stress as helicase separates the double strand. [4] Topoisomerase IV causes decatenation, the unlinking of strands of tangled DNA, a function also necessary for DNA replication. (8) Moxifloxacin is taken up by human phagocytic leukocytes, such as neutrophils and macrophages, where it remains active against obligate intracellular bacterial pathogens. (9) Moxifloxacin, like other quinolones, may be able to enter bacterial cells through porins, which are small beta-barrel channels through their membranes. (10) Moxifloxacin can then bind directly to its target, topoisomerase. Topoisomerases work by binding to a segment, called a G segment, and simultaneously binding a second DNA segment called the T segment. Topoisomerase cleaves the G segment, passes the T segment through the cleaved G segment, and then ligates the G segment back together. Topoisomerases require a magnesium ion for the cleavage of the G segment. Moxifloxacin prevents the action of topoisomerases by coordinating two bonds to a serine and a glutamic acid present on the enzyme using the and associated water molecules. By this mechanism, Moxifloxacin is able to modulate the activity of the bacterial topoisomerase. (11)
Human uses of Moxiflacin
Moxifloxacin is an artificial antibacterial agent that is designed for oral and intravenous administration. It belongs to the category of drugs called fluoroquinolone antibiotics that is used to stop the growth of bacteria by inhibiting bacterial topoisomerase enzymes. While humans produce these same enzymes, human topoisomerase do not have the serine and glutamic acid residues needed for the action of the drug (11). It is prescribed to treat various numbers of infections that are caused by gram-positive and gram negative bacteria, which results in a number of diseases such as acute flare-ups of chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, acute bacterial infection of the sinuses, complicated intra-abdominal infections and pelvic inflammatory disease(1). Moxifloxacin has been recently found to have another great advantage that includes treatment of dermatologic pathogens on the skin. It has a resistance towards pathogens that occur due to wounds caused by human and animal bite. Moxifloxacin can be used for a number of treatments; however, its use should be carefully administered in serious infections because it can lead to serious side effects, (2) such as acute allergic reactions, diarrhea, and connective tissue problems, muscle pain, depression, agitation, renal problems and confusion (4). Therefore, it should be used exclusively for infections that cannot be treated with alternate safer antibiotics.