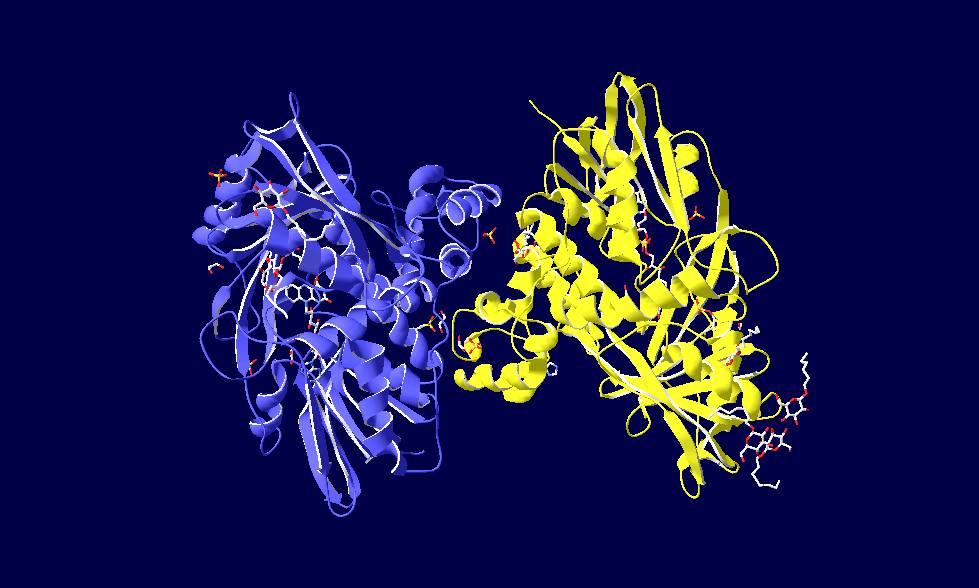
Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
From Proteopedia
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| - | Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GlpD) is an oxidoreductase enzyme which catalyze the reaction of transfer of electrons between molecules. GlpD is a membrane associated enzyme that is involved in glycerol metabolism, ubiquinone and glyceroneogenesis in E. coli. In Ecoli, many newly discovered structures of GlpD are being used to transfer electrons into the respiratory pathway and also for the metabolism of glycerol into its precursors for other pathways. The GlpD enzyme contains a | + | Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GlpD) is an oxidoreductase enzyme which catalyze the reaction of transfer of electrons between molecules. GlpD is a membrane associated enzyme that is involved in glycerol metabolism, ubiquinone and glyceroneogenesis in E. coli. In Ecoli, many newly discovered structures of GlpD are being used to transfer electrons into the respiratory pathway and also for the metabolism of glycerol into its precursors for other pathways. The GlpD enzyme contains a flavin active site which plays a major role in the respiratory electron transport chain and in cellular energy requirements. |
===Structure=== | ===Structure=== | ||
Revision as of 13:48, 26 March 2010
Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
Contents |
Introduction
Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GlpD) is an oxidoreductase enzyme which catalyze the reaction of transfer of electrons between molecules. GlpD is a membrane associated enzyme that is involved in glycerol metabolism, ubiquinone and glyceroneogenesis in E. coli. In Ecoli, many newly discovered structures of GlpD are being used to transfer electrons into the respiratory pathway and also for the metabolism of glycerol into its precursors for other pathways. The GlpD enzyme contains a flavin active site which plays a major role in the respiratory electron transport chain and in cellular energy requirements.
Structure
Function
Metabolism
Diseases
| Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox until after April 23, 2010. Sandboxes 151-200 are reserved until then for use by the Chemistry 307 class at UNBC taught by Prof. Andrea Gorrell. |
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Indu Toora, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Andrea Gorrell, Andrew Rebeyka, Jaime Prilusky