This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Calcium-free Calmodulin
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== '''Calcium-free Calmodulin''' == | == '''Calcium-free Calmodulin''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{STRUCTURE_1cfc| PDB=1cfc | SCENE=Sandbox_190/1cfc/1 }} | ||
==='''General Information'''=== | ==='''General Information'''=== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 9: | ||
Calmodulin is a molecule that has been studied extensively in its functions within the cell, and has an important role in relaying Ca2+ signals within the cytosol. <ref name="1CRT">Hoeflich, K.P., & Ikura, M.. Calmodulin in action: diversity in target recognition and activation mechanisms, Cell. 2002 108:739-742</ref> It does this by binding to Ca2+, undergoing a conformational change, and may interact with various proteins within the cell.<ref name="1CRT"/><ref name="4CRT">PMID: 7552748</ref><ref name="3CRT">PMID: 3145979</ref> Once bound to a target protein, it undergoes a further conformational change and may activate certain systems. For example, there is a Ca2+ pump in the plasma membrane pump that is activated by the binding of Ca2+-bound calmodulin, and then uses ATP to drive the Ca2+ out of the cell. <ref name="6CRT">PMID: 12838335</ref> | Calmodulin is a molecule that has been studied extensively in its functions within the cell, and has an important role in relaying Ca2+ signals within the cytosol. <ref name="1CRT">Hoeflich, K.P., & Ikura, M.. Calmodulin in action: diversity in target recognition and activation mechanisms, Cell. 2002 108:739-742</ref> It does this by binding to Ca2+, undergoing a conformational change, and may interact with various proteins within the cell.<ref name="1CRT"/><ref name="4CRT">PMID: 7552748</ref><ref name="3CRT">PMID: 3145979</ref> Once bound to a target protein, it undergoes a further conformational change and may activate certain systems. For example, there is a Ca2+ pump in the plasma membrane pump that is activated by the binding of Ca2+-bound calmodulin, and then uses ATP to drive the Ca2+ out of the cell. <ref name="6CRT">PMID: 12838335</ref> | ||
| - | [[Image:3cln.png|left|200px]] | ||
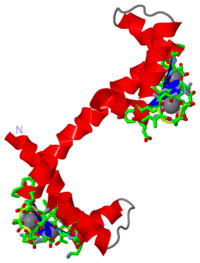
==='''Calcium-bound Calmodulin'''=== | ==='''Calcium-bound Calmodulin'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:3cln.png|thumb|200px]] | ||
The structure of calcium-bound calmodulin had previously been discovered using x-ray crystallography <ref name="3CRT"/>. It was then theorized that knowledge of the structure of calcium-free calmodulin would give greater insight into the function of the protein. Attempts were made to crystallize the calcium-free (or apo) form, but to no avail, thus it was | The structure of calcium-bound calmodulin had previously been discovered using x-ray crystallography <ref name="3CRT"/>. It was then theorized that knowledge of the structure of calcium-free calmodulin would give greater insight into the function of the protein. Attempts were made to crystallize the calcium-free (or apo) form, but to no avail, thus it was | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:calmodulin.png|left|200px]] |
| - | + | ||
<scene name='Sandbox_190/1cfc/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | <scene name='Sandbox_190/1cfc/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
Revision as of 06:21, 1 April 2010
Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox until after April 23, 2010. Sandboxes 151-200 are reserved until then for use by the Chemistry 307 class at UNBC taught by Prof. [[User:Andrea Gorrell|Andrea Chris Truscott
Calcium-free Calmodulin
General InformationCalmodulin is a molecule that has been studied extensively in its functions within the cell, and has an important role in relaying Ca2+ signals within the cytosol. [1] It does this by binding to Ca2+, undergoing a conformational change, and may interact with various proteins within the cell.[1][2][3] Once bound to a target protein, it undergoes a further conformational change and may activate certain systems. For example, there is a Ca2+ pump in the plasma membrane pump that is activated by the binding of Ca2+-bound calmodulin, and then uses ATP to drive the Ca2+ out of the cell. [4] Calcium-bound CalmodulinThe structure of calcium-bound calmodulin had previously been discovered using x-ray crystallography [3]. It was then theorized that knowledge of the structure of calcium-free calmodulin would give greater insight into the function of the protein. Attempts were made to crystallize the calcium-free (or apo) form, but to no avail, thus it was
References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Christopher Truscott, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, Andrea Gorrell