Ferredoxin
From Proteopedia
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
'''3D structure of acetylcholinesterase'''<br /> | '''3D structure of acetylcholinesterase'''<br /> | ||
The active site gorge has <scene name='Acetylcholinesterase/New_down_gorge/6'>two binding sites</scene>, a catalytic site (consisting of the catalytic triad together with Trp84 & Phe330) and a peripheral site (including Trp 279 & Tyr 121), which helps prebind the substrate and direct it toward the active site. The 3D structure showed not only that the active site was buried deep in the enzyme, but surprisingly, there were no negatively charged residues along this gorge, as was expected to help attract the positively charged ACh substrate, rather, instead, a series of aromatic residues that are highly conserved in all AChE sequences. See: [[AChE inhibitors and substrates]] | The active site gorge has <scene name='Acetylcholinesterase/New_down_gorge/6'>two binding sites</scene>, a catalytic site (consisting of the catalytic triad together with Trp84 & Phe330) and a peripheral site (including Trp 279 & Tyr 121), which helps prebind the substrate and direct it toward the active site. The 3D structure showed not only that the active site was buried deep in the enzyme, but surprisingly, there were no negatively charged residues along this gorge, as was expected to help attract the positively charged ACh substrate, rather, instead, a series of aromatic residues that are highly conserved in all AChE sequences. See: [[AChE inhibitors and substrates]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Selected 3D Structures of AChE == | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===Acetylcholinesterase - AChE native=== | ||
| - | [[3lii]] – hAChE - recombinant human <br /> | ||
| - | [[1ea5]], [[2ace]] – ''Tc''AChE – trigonal – ''Torpedo californica'' <br /> | ||
| - | [[2j3d]] – ''Tc''AChE – monoclinic <br /> | ||
| - | [[1w75]] – ''Tc''AChE – orthorhombic <br /> | ||
| - | [[1eea]] – ''Tc''AChE – cubic <br /> | ||
| - | [[2vt6]], [[2vt7]] – ''Tc''AChE – different dosage <br /> | ||
| - | [[1qid]] to [[1qim]] - ''Tc''AChE synchrotron radiation damage <br /> | ||
| - | [[1j06]], [[1maa]] – mAChE - mouse <br /> | ||
| - | [[1qo9]] – ''Dm''AChE - ''Drosophila'' <br /> | ||
| - | [[1c2o]], [[1c2b]] – electrophorus AChE – Electric eel <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===AChE active site inhibitors conjugating at the bottom of the active site gorge=== | ||
| - | [[2w9i]] – ''Tc''AChE + methylene blue <br /> | ||
| - | [[2wls]] – MosAChE + AMTS13 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2vq6]] – ''Tc''AChE + 2-PAM <br /> | ||
| - | [[2j3q]] – ''Tc''AChE + Thioflavin T <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ha0]] – mAChE + ketoamyltrimethylammonium <br /> | ||
| - | [[2h9y]] – mAChE + TMTFA <br /> | ||
| - | [[1gpk]], [[1gpn]], [[1vot]] – ''Tc''AChE + huperzine <br /> | ||
| - | [[1gqr]] – ''Tc''AChE + rivastigmine <br /> | ||
| - | [[1gqs]] – ''Tc''AChE + NAP <br /> | ||
| - | [[1e66]] – ''Tc''AChE + huprine <br /> | ||
| - | [[1dx4]], [[1qon]] – ''Dm''AChE + tacrine derivative <br /> | ||
| - | [[1oce]] – ''Tc''AChE + MF268 <br /> | ||
| - | [[1ax9]], [[1ack]] – ''Tc''AChE + edrophonium <br /> | ||
| - | [[1amn]] – ''Tc''AChE + TMTFA <br /> | ||
| - | [[1acj]] – ''Tc''AChE + tacrine <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===AChE peripheral site inhibitors conjugating at the surface of the protein=== | ||
| - | [[1ku6]] - mAChE + fasciculin 2 <br /> | ||
| - | [[1ku6]], [[1mah]] - mAChE + fasciculin 2 <br /> | ||
| - | [[1j07]] - mAChE + decidium <br /> | ||
| - | [[1n5m]] - mAChE + gallamine <br /> | ||
| - | [[1n5r]] - mAChE + propidium <br /> | ||
| - | [[1b41]], [[1f8u]] - hAChE + fasciculin 2 <br /> | ||
| - | [[1fss]] - TcAChE + fasciculin 2 <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===AChE bis inhibitors spanning the active site gorge=== | ||
| - | [[3i6m]] – ''Tc''AChE + N-piperidinopropyl galanthamine <br /> | ||
| - | [[3i6z]] - ''Tc''AChE + saccharinohexyl galanthamine <br /> | ||
| - | [[1zgb]], [[1zgc]] – ''Tc''AChE + tacrine (10) hupyridone <br /> | ||
| - | [[2w6c]] – ''Tc''AChE + bis-(-)-nor-meptazinol <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ckm]], [[2cmf]] – ''Tc''AChE + bis-tacrine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2cek]] – ''Tc''AChE + N-[8-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-ylthio)octyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-amine <br /> | ||
| - | [[1ut6]] - ''Tc''AChE + N-9-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridinyl)-1,8-diaminooctane <br /> | ||
| - | [[1odc]] - ''Tc''AChE + N-4-quinolyl-N-9-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridinyl)-1,8-diaminooctane <br /> | ||
| - | [[1w4l]], [[1w6r]], [[1w76]], [[1dx6]], [[1qti]] - TcAChE + galanthamine and derivative <br /> | ||
| - | [[1q83]], [[1q84]] - mAChE + TZ2PA6 <br /> | ||
| - | [[1h22]], [[1h23]] – ''Tc''AChE + bis-hupyridone <br /> | ||
| - | [[1hbj]] – ''Tc''AChE + quinoline derivativev <br /> | ||
| - | [[1e3q]] – ''Tc''AChE + bw284c51 <br /> | ||
| - | [[1eve]] – ''Tc''AChE + e2020 <br /> | ||
| - | [[1acl]] – ''Tc''AChE + decamethonium <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ===AChE organophosphate inhibitors causing irreversible inhibition=== | ||
| - | [[2wu3]] – mAChE + fenamiphos and HI-6 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2wu4]] – mAChE + fenamiphos and ortho-7 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jgf]] - mAChE + fenamiphos <br /> | ||
| - | [[2wfz]], [[2wg0]], [[1som]] - ''Tc''AChE + soman <br /> | ||
| - | [[2wg1]] - ''Tc''AChE + soman + 2-PAM <br /> | ||
| - | [[2whp]], [[2whq]], [[2whr]] – mAChE + sarin and HI-6 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jgg]] - mAChE + sarin <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jgl]] - mAChE + VX and sarin <br /> | ||
| - | [[1cfj]] - ''Tc''AChE + sarin, GB <br /> | ||
| - | [[3dl4]], [[3dl7]] – mAChE + tabun <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jey]] – mAChE + HLO-7 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2c0p]], [[2c0q]] - mAChE + tabun <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jez]] - mAChE + tabun + HLO-7 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jf0]] - mAChE + tabun + Ortho-7 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jgh]] - mAChE + VX <br /> | ||
| - | [[1vxo]], [[1vxr]] - ''Tc''AChE + VX <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jgi]], [[2jgm]] - mAChE + DFP <br /> | ||
| - | [[1dfp]] - ''Tc''AChE + DFP <br /> | ||
| - | [[2jgj]], [[2jgk]], [[2jge]] - mAChE + methamidophos <br /> | ||
| - | [[2gyu]] - mAChE + HI-6 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2gyv]] - mAChE + Ortho-7 <br /> | ||
| - | [[2gyw]] - mAChE + obidoxime <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===AChE substrate analogues mimicking the binding of the substrate acetylcholine=== | ||
| - | [[2ha4]] – mAChE (mutant) + acetylcholine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2vja]], [[2vjb]], [[2vjc]], [[2vjd]], [[2cf5]] – ''Tc''AChE + 4-oxo-N,N,N-trimethylpentanaminium <br /> | ||
| - | [[2v96]], [[2v97]], [[2v98]], [[2v99]] – ''Tc''AChE + 1-(2-nitrophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl-arsenocholine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ha2]] – mAChE + succinylcholine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ha3]] - mAChE + choline <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ha5]] – mAChE (mutant) + acetylthiocholine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ha6]] – mAChE (mutant) + succinylthiocholine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ha7]] – mAChE (mutant) + butyrylthiocholine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2ch4]], [[2c58]] – ''Tc''AChE + acetylthiocholine <br /> | ||
| - | [[2c5g]] – ''Tc''AChE + thiocholine <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===Others...=== | ||
| - | [[2j4f]] – ''Tc''AChE + Hg <br /> | ||
| - | [[1vzj]] – ''Tc''AChE tetramerization domain <br /> | ||
| - | [[1jjb]] – ''Tc''AChE + PEG <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | More structures can be obtained by searching for | ||
| - | [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Special:Search?search=AChE&fulltext=AChE AChE] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | [[Category: catalytic triad]] | ||
| - | [[Category: cholinesterase]] | ||
| - | [[Category: cholinesterases]] | ||
| - | [[Category: acetylcholine]] | ||
| - | [[Category: cation-pi]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Alzheimers]] | ||
| - | [[Category: nerve gasses]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==External Links == | ||
| - | [http://www.messiah.edu/departments/chemistry/molscilab/jtat_080120/acetylcholinesterase/contents/contents.htm Acetylcholinesterase Tutorial] by Karl Oberholser, Messiah College | ||
| - | |||
| - | [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/pdb54_1.html PDB Molecule of the Month - Acetylcholinesterase] | ||
| - | |||
| - | [http://www.weizmann.ac.il/sb/faculty_pages/Sussman/movies/Radiation_Damage Movies: X-ray Damage in ACh] & [http://www.weizmann.ac.il/sb/faculty_pages/Sussman/movies/richardnew.mpg Nature's Vacuum Cleaner] by R. Gillilan, Cornell Univ | ||
Revision as of 07:15, 27 May 2010
|
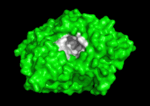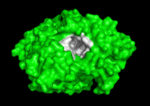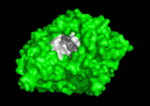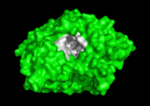
3D structure of acetylcholinesterase
Ferredoxin (Fd) is found in chloroplasts which mediates electron transfer and contains an iron-sulfur cluster. It is involved in the photosynthesis process where its iron atoms accept or discharge electrons when they are being oxidized or reduced. The iron-sulfur cluster can contain 2Fe-2S and is termed plant-like or 3Fe-4S or 4Fe-4S clusters. Adrenodoxin (ADR) is a ferredoxin containing a 2Fe-2S group involved in electron transfer from NADPH+ to a cytochrome P-450 in the adrenal gland. Putidaredoxin (PUT) and terpredoxin (TER) are involved in the same reaction in bacteria and contain a 2Fe-2S group.
Contents |
2Fe-2S containing ferredoxins
3hui – Fd – Rhodopseudomonas palustris
2kaj, 1dox, 1doy – SyFd +Ga – Synechocystis – NMR
1off – SyFd
3gce – Fd – Nocardioides aromaticivorans
2e4p, 2e4q - Fd – Pseudomonas sp.
2q3w, 1vm9 - PmFd (mutant) – Pseudomonas mendocina
2i7f - Fd – Rhodobacter capsulatus
1rfk - Fd – Cyanobacterium masticogladus laminosus
1vck - Fd – Pseudomonas resinovorans
1wri, 1frr - Fd – Equisetum arvense
1sjg - PmFd– NMR
1iue - Fd– Plasmodium falciparum
1m2a –AeFd – Aquifex aeolicus
1m2b, 1m2d, 1f37, 1f5b, 1f5c – AeFd (mutant)
1l5p – Fd – Trichomonas vaginalis
1i7h - Fd – Escherichia coli
1czp, 1qt9, 1frd, 1fxa - aFd– anabaena
1j7a, 1j7b, 1j7c , 1qoa, 1qob, 1qof, 1qog- aFd (mutant)
1e0z – Fd – Halobacterium salinarium
1pfd – Fd – Petroselinum crispum – NMR
1a70 - Fd (mutant) – Spinacia oleracea
1awd - Fd – Chlorella fusca
2cjn, 2cjo, 1roe – SyFd – NMR
1rof – SyFd – Synechococcus elongates
1doi - Fd – Haloarcula marismortui
4fxc – Fd – Spirulina platensis
1fxi – Fd – Aphanothece sacrum
3dqy, 2qpz - Fd – Pseudomonas putida
4Fe-4S containing ferredoxins
3eun – AvFd – Allochromatium vinosum
3exy - AvFd (mutant)
2vkr - Fd+Zn – Acidianus ambivalens
2z8q - PfFd (mutant) – Pyrococcus furiosus
2fgo - Fd– Pseudomonas aeruginosa
1iqz, 1ir0 - BtFd – Bacillus thermoproteolyticus
1rgv - Fd – Thauera aromatica
1dax, 1dfd – DaFd – Desulfovibrio africanus – NMR
1fxr - DaFd
1vjw – Fd – Thermotoga maritima
3Fe-4S containing ferredoxins
2v2k – Fd – Mycobacterium smegmatis
1wtf - BtFd (mutant)
1sj1 - PfFd
1fxd - DgFd – Desulfovibrio gigas
1f2g – DgFd – NMR
1xer - Fd – Sulfolobus tokodaii
4Fe-4S+3Fe-4S containing ferredoxins
1gao, 6fdr, 7fd1, 7fdr, 1axq, 6fd1, 1frh, 1fri,1frj, 1frk, 1frl, 1frm, 1fda, 1fdb, 1fdd, 5fd1, 1fer – AvFd – Azotobacter vinelandii
1pc4, 1pc5, 1g6b, 1g3o, 1ff2, 1b0v, 1d3w, 1b0t, 1a6l, 1ftc, 1frx, 2fd2, 1fd2 - AvFd (mutant)
1h98 – Fd – Thermus thermophilus
1a8p, 1bd6 - BsFd – Bacillus schlegelii – NMR
4Fe-4S+4Fe-4S containing ferredoxins
1dur – Fd – Peptoniphilus asaccarolyticus
1bwe, 1bqx - BsFd (mutant) – NMR
2fdn, 1fca , 1fdn- Fd – Clostridium acidi-urici
1blu - Fd – Chromatium vinosum
1clf – Fd – Clostridium pasteurianum – NMR
Adrenoredoxin
jqr – ADR Fd domain (mutant)+cytochrome c (mutant) – yeast – NMR
2bt6 – cADR1 modified – cow
1l6u, 1l6v – cADR1 – NMR
1e6e – cADR (mutant)+ADR reductase
1cje, 1ayf - cADR
Putidaredoxin
1yji, 1yjj, 1pdx – PpPUT – Pseudomonas putida – NMR
3lb8 – PpPUT (mutant)+PUT reductase
1xln, 1xlo, 1xlp, 1xlq, 1r7s, 1oqq, 1oqr - PpPUT (mutant)
1gpx, 1put- PpPUT (mutant) - NMR
Terpredoxin
1b9r – TER – Pseudomonas - NMR
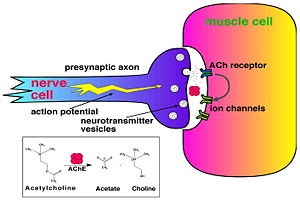
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is key enzyme in the nervous system of animals. By rapid hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (ACh), AChE terminates neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses. It is a very fast enzyme, especially for a serine hydrolase, functioning at a rate approaching that of a diffusion-controlled reaction. AChE inhibitors are among the key drugs approved by the FDA for management of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The powerful toxicity of organophosphorus (OP) poisons is attributed primarily to their potent AChE inhibitors.
The 3D structure of Torpedo californica AChE (TcAChE) (Sussman et al. & Silman (1991)) opened up new horizons in research on an enzyme that had already been the subject of intensive investigation. The unanticipated structure of this extremely rapid enzyme, in which the active site was found to be buried at the bottom of a , lined by aromatic residues, led to a revision of the views then held concerning substrate traffic, recognition, and hydrolysis (Botti et al. Sussman & Silman (1999)). To understand how those aromatic residues behave with the enzyme, see Flexibility of aromatic residues in acetylcholinesterase.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a debilitating brain disease that occurs in around 10% of the elderly and, as yet, there is no known cure. At present, the most widely used treatments consist are medications that attempt to increase the brain’s levels of ACh, whose levels decrease with onset of disease. These drugs work by interfering with AChE. Thus drugs that are mild inhibitors of AChE, like Tacrine, E2020 (Aricept) and the Traditonal Chinese Medicine (TCM) Huperzine appear to retard symptoms of AD.
|
The active site gorge has , a catalytic site (consisting of the catalytic triad together with Trp84 & Phe330) and a peripheral site (including Trp 279 & Tyr 121), which helps prebind the substrate and direct it toward the active site. The 3D structure showed not only that the active site was buried deep in the enzyme, but surprisingly, there were no negatively charged residues along this gorge, as was expected to help attract the positively charged ACh substrate, rather, instead, a series of aromatic residues that are highly conserved in all AChE sequences. See: AChE inhibitors and substrates
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky, Eran Hodis, Wayne Decatur, David Canner