Copper Amine Oxidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Additional Resources == | == Additional Resources == | ||
| - | [http://www.google.ca/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=2&ved=0CB8QFjAB&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.jbc.org%2Fcontent%2F271%2F9%2F4718.full.pdf&rct=j&q=Topa%20quinone&ei=lb6UTZyZH8PdiAKF9t39CA&usg=AFQjCNFe66G0M8KGm8HD9rmSgzSyZwi9RQ&sig2=nwPWJNlka1WrmFatRPFH9Q&cad=rja The Biosynthesis of Topa Quinone Cofactor in Bacterial Amine Oxidases] | + | *[http://www.google.ca/url?sa=t&source=web&cd=2&ved=0CB8QFjAB&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.jbc.org%2Fcontent%2F271%2F9%2F4718.full.pdf&rct=j&q=Topa%20quinone&ei=lb6UTZyZH8PdiAKF9t39CA&usg=AFQjCNFe66G0M8KGm8HD9rmSgzSyZwi9RQ&sig2=nwPWJNlka1WrmFatRPFH9Q&cad=rja The Biosynthesis of Topa Quinone Cofactor in Bacterial Amine Oxidases] |
| - | + | *[http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2D1W Entry 2D1W in the RCSB Protein Data Bank] | |
| - | [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2D1W Entry 2D1W in the RCSB Protein Data Bank] | + | |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 20:30, 31 March 2011
| This Sandbox is Reserved from January 10, 2010, through April 10, 2011 for use in BCMB 307-Proteins course taught by Andrea Gorrell at the University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
Structure
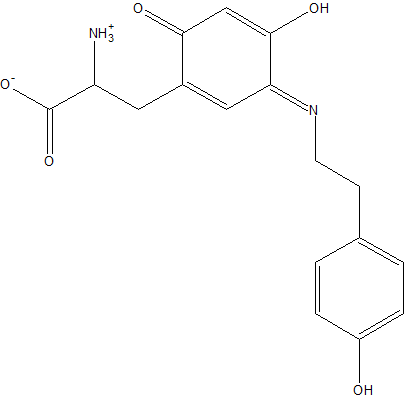
2d1w is a copper amine oxidase derived from Arthrobacter globiformis, and is classified as classified as EC 1.4.3.6 in the EC number classification of enzymes. It belongs to the larger class of oxidoreductases. The structure of this enzyme was determined by Murakawa et al. in 2005, by x-ray diffraction[1]. It consists of a disulfide-linked homodimer, with each subunit containing 638 residues. Each subunit also contains a copper ligand,, near the active site, which is coordinated by three histidine residues. Located near the Cu2+ ligand is a modified tyrosine residue, which is similar in structure to a cofactor in many other copper amine oxidases, topa quinone[2]. The active site of the enzyme is located near the center of the homodimer, which is connected to the outside of the enzyme by an extensively hydrated channel. It is suspected that the water helps to carry O2 to the active site[3].
Reaction
Overview
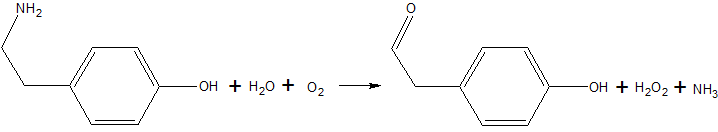
Copper amine oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of a primary amine to the corresponding aldehyde, yielding hydrogen peroxide and free ammonia. An example of this is the oxidation of tyramine:
Mechanism
Additional Resources
- The Biosynthesis of Topa Quinone Cofactor in Bacterial Amine Oxidases
- Entry 2D1W in the RCSB Protein Data Bank
References
- ↑ Murakawa T, Okajima T, Kuroda S, Nakamoto T, Taki M, Yamamoto Y, Hayashi H, Tanizawa K. Quantum mechanical hydrogen tunneling in bacterial copper amine oxidase reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Apr 7;342(2):414-23. Epub 2006 Feb 8. PMID:16487484 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.150
- ↑ Parsons MR, Convery MA, Wilmot CM, Yadav KD, Blakeley V, Corner AS, Phillips SE, McPherson MJ, Knowles PF. Crystal structure of a quinoenzyme: copper amine oxidase of Escherichia coli at 2 A resolution. Structure. 1995 Nov 15;3(11):1171-84. PMID:8591028
- ↑ Mure M, Mills SA, Klinman JP. Catalytic mechanism of the topa quinone containing copper amine oxidases. Biochemistry. 2002 Jul 30;41(30):9269-78. PMID:12135347
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Raymond Lyle, Alexander Berchansky, OCA, Jaime Prilusky