Group:MUZIC:Telethonin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Also known as T-Cap or Titin Cap protein. | Also known as T-Cap or Titin Cap protein. | ||
| - | It is a small protein of 19kDa, 167 amino acids. | + | It is a small protein of 19kDa, 167 amino acids. It is predominantly expressed in striated muscle. It is a structural protein of the muscle; it is associated to the Z-disc in the sarcomere. It acts as multifunctional protein linking titin and other proteins implicated in sarcomere structure and signalling pathways. |
| + | |||
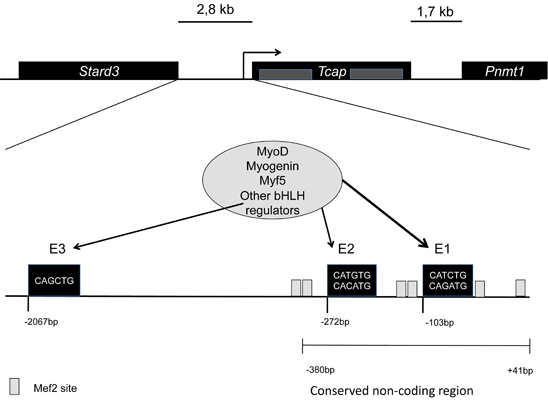
== Gene regulation and expression == | == Gene regulation and expression == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
At the transcriptional level it is thought that there is only one isoform of Tcap, and it is one of the most abundant transcripts in skeletal muscle <ref>PMID:9350988</ref>. It does not have different levels of expression in different types of skeletal muscle; levels of expression of ''Tcap'' are lower in neonatal compared to adult striated muscle. The transcript is accumulated in a linear pattern similar to that of the myosin heavy chain <ref>PMID: 10208846</ref>. In these same studies it was reported that denervation leads to decrease in the expression of Tcap, suggesting that locomotor activity is a potential regulator of its maintenance. | At the transcriptional level it is thought that there is only one isoform of Tcap, and it is one of the most abundant transcripts in skeletal muscle <ref>PMID:9350988</ref>. It does not have different levels of expression in different types of skeletal muscle; levels of expression of ''Tcap'' are lower in neonatal compared to adult striated muscle. The transcript is accumulated in a linear pattern similar to that of the myosin heavy chain <ref>PMID: 10208846</ref>. In these same studies it was reported that denervation leads to decrease in the expression of Tcap, suggesting that locomotor activity is a potential regulator of its maintenance. | ||
| - | == | + | == “Tcap” gene product, the protein Telethonin == |
| - | Telethonin protein is found mostly in skeletal and cardiac muscle. It is one of the major components of the sarcomere, it is localized to the Z-disc. | + | |
| + | Telethonin protein is found mostly in skeletal and cardiac muscle. It is one of the major components of the sarcomere, it is localized to the Z-disc. It was also reported a nuclear localization.<ref>PMID:12379311 </ref> <ref>PMID:16678796 </ref> | ||
Studies on telethonin structure by Zou et al. <ref>PMID:16407954</ref> report that it is made up of five stranded antiparallel β-sheets extended by two wing-shaped β-hairpin motifs (A-B, C-D). These two motifs are related by an approximate two-fold symmetry, which generates an almost perfect palindromic arrangement. | Studies on telethonin structure by Zou et al. <ref>PMID:16407954</ref> report that it is made up of five stranded antiparallel β-sheets extended by two wing-shaped β-hairpin motifs (A-B, C-D). These two motifs are related by an approximate two-fold symmetry, which generates an almost perfect palindromic arrangement. | ||
The structure of telethonin was determined using X-ray crystallography <ref>PMID:12446666</ref>,<ref>PMID:16407954</ref> . The shape and architecture of the complex of titin/telethonin was studied by small-angle- X-ray scattering (SAXS) and then compared to the crystallographic models. They also used in-vitro experiments to follow the formation of the complex in non-myogenic Cos1 cells, in order to understand if the assemblage is possible <ref>PMID:16713295</ref> | The structure of telethonin was determined using X-ray crystallography <ref>PMID:12446666</ref>,<ref>PMID:16407954</ref> . The shape and architecture of the complex of titin/telethonin was studied by small-angle- X-ray scattering (SAXS) and then compared to the crystallographic models. They also used in-vitro experiments to follow the formation of the complex in non-myogenic Cos1 cells, in order to understand if the assemblage is possible <ref>PMID:16713295</ref> | ||
| - | This symmetry of telethonin permits its interaction with titin. Both are assembled in an antiparallel <scene name='User:Marcia_Ivonne_Pena_Paz/workbench/Telethonin/Telethonin-titin/1'>sandwich 2:1</scene> (titin:telethonin). Titin N-terminal domains Z1 and Z2 interact with the | + | This symmetry of telethonin permits its interaction with titin. Both are assembled in an antiparallel <scene name='User:Marcia_Ivonne_Pena_Paz/workbench/Telethonin/Telethonin-titin/1'>sandwich 2:1</scene> (titin:telethonin). Titin N-terminal domains Z1 and Z2 (two Ig like repeats) interact with the C-terminal region of telethonin (residues 1-53). Telethonin mediates in the antiparallel assembly of the two Z1Z2domains. |
| + | |||
| + | In early differentiating myocytes titin C-terminal and telethonin co-localize and titin kinase is close to telethonin C-terminal, and it is phosphorylated. This phosphorylation is involved in the reorganization of the cytoskeleton during myofibrillogenesis. <ref>PMID: 9804419 </ref> This co-localization is not seen in adult myofibrils, titin kinase is reported to localize in the M-band <ref>PMID: 9804419</ref>; It was also informed that telethonin interacts with other proteins including: Potassium channel β-subunit of the slow activating component of the delayed rectifier potassium current (IKs) channel (minK) <ref>PMID: 11697903</ref>, ankyrin1, and Z-disc proteins FATZ,/Myozenin-1/ Calsarcin-3 <ref>PMID: 11842093</ref>, and Ankrd2.<ref>PMID:15136035</ref> | ||
| - | In early differentiating myocytes titin C-terminal and telethonin co-localize and titin kinase is close to telethonin C-terminal, and it is phosphorylated. This phosphorylation is involved in the reorganization of the cytoskeleton during myofibrillogenesis. <ref>PMID: 9804419 </ref> This co-localization is not seen in adult myofibrils, titin kinase is reported to localize in the M-band <ref>PMID: 9804419</ref>; It was also informed that telethonin interacts with other proteins including: Potassium channel subunit minK/isk <ref>PMID: 11697903</ref>, ankyrin1, and Z-disc proteins FATZ, Calsarcin-3 <ref>PMID: 11842093</ref>, Ankrd2,<ref>PMID:15136035</ref> and MLP. <ref>PMID: 12507422</ref> | ||
| - | + | Telethonin interacts with minK’s cytoplasmic domain. MinK binds specifically to the sixteen C-terminal residues of telethonin. This suggest a that minK, telethonin ant titin form a complex that links myofibrils to the sarcolemma. Phosphorilation of telethonin in Ser157 is a negative regulation for this interaction. This interaction occurs in cardiac myofibrils, it has been reported that minK is not expressed in skeletal muscle.<ref>PMID: 11697903</ref>, | |
| - | + | ||
| + | Telethonin interacts with FATZ/Myozenin-1/Calsarcin-3 N-terminal between residues 78-125. It might be an association as mechanosensing and stretch-associated signalling machinery. <ref>PMID: 11842093</ref> | ||
The interaction between Ankrd2 and telethonin has been proposed as a sensor of muscle stress/stretch and a starting point for the transmission of the mechanical signal to the nucleus regulating gene expression. <ref>PMID: 15136035</ref> | The interaction between Ankrd2 and telethonin has been proposed as a sensor of muscle stress/stretch and a starting point for the transmission of the mechanical signal to the nucleus regulating gene expression. <ref>PMID: 15136035</ref> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
Telethonin is also involved in signalling processes that regulate muscle development. A feed back loop is formed with MRFs (MyoD, myogenin, Myf5) regulating Tcap gene expression; telethonin interacts with myostatin, inhibiting it. So it regulates MyoD through the Myostatin – Smad3 pathway. <ref>PMID:18440815</ref>. | Telethonin is also involved in signalling processes that regulate muscle development. A feed back loop is formed with MRFs (MyoD, myogenin, Myf5) regulating Tcap gene expression; telethonin interacts with myostatin, inhibiting it. So it regulates MyoD through the Myostatin – Smad3 pathway. <ref>PMID:18440815</ref>. | ||
| - | + | There is an interaction with MDM2 N-terminal. MDM2 is capable of redirecting telethonin to the nucleus. Telethonin is inhibited by MDM2 in a dose dependent manner. In cells MDM2 is involved in the regulation of proteasomal turnover of telethonin. <ref>PMID:16678796 </ref> | |
== Pathologies associated with telethonin == | == Pathologies associated with telethonin == | ||
Revision as of 09:11, 16 August 2011
Telethonin
| |||||||||||