User:Gourinchas Geoffrey/Sandbox 205
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
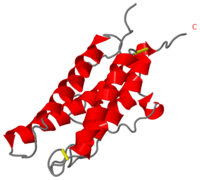
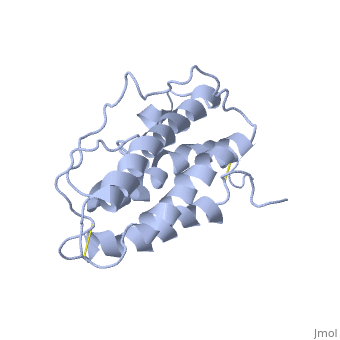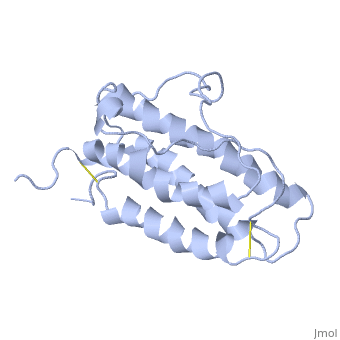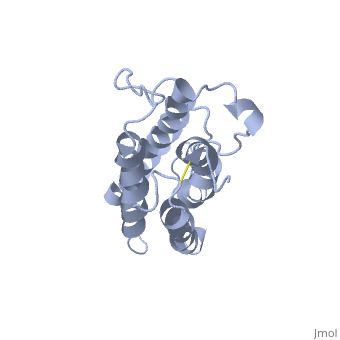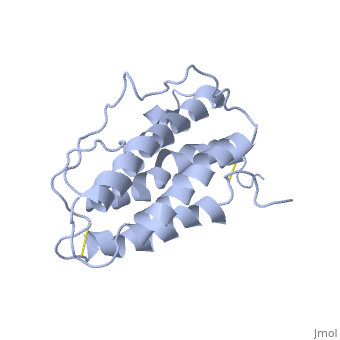
It is composed to 4 alpha-helix: αA, αB, αC and αD which are associated the some in front of the others. | It is composed to 4 alpha-helix: αA, αB, αC and αD which are associated the some in front of the others. | ||
| - | αA et αD are held together by a disulfide bond between <scene name='User:Gourinchas_Geoffrey/Sandbox_205/ | + | αA et αD are held together by a disulfide bond between <scene name='User:Gourinchas_Geoffrey/Sandbox_205/Cysteine_7_n2/1'>Cysteine 7</scene> and <scene name='User:Gourinchas_Geoffrey/Sandbox_205/Cysteine_161_n2/1'>Cysteine 161</scene>. |
αB et αC are held together by a short loop. | αB et αC are held together by a short loop. | ||
The molecule of Erythropoietin have two opposite binding sites with his receptor. The first site include segments of αA, αB and αD and a part of the loop which connects αA and αB. This site include a hydrophobic center which interact with the receptor. | The molecule of Erythropoietin have two opposite binding sites with his receptor. The first site include segments of αA, αB and αD and a part of the loop which connects αA and αB. This site include a hydrophobic center which interact with the receptor. | ||
| - | The Phenylalanine 93 of the receptor is critical important for binding of Erythropoietin to his receptor thanks to hydrogen bonds with residues | + | The Phenylalanine 93 of the receptor is critical important for binding of Erythropoietin to his receptor thanks to hydrogen bonds with residues <scene name='User:Gourinchas_Geoffrey/Sandbox_205/Threonine_44/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> and <scene name='User:Gourinchas_Geoffrey/Sandbox_205/Asparagine_147/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> of Erythropoietin. </StructureSection> |
Revision as of 21:43, 27 November 2011
HUMAN ERYTHROPOIETIN
|
Erythropoietin is a glycoprotein hormone which is involved in Erythropoiesis, which is the red blood cells production. It allows the differenciation of the erythrocyte precursors in the bone marrow.
Structure
| |||||||||||