User:Jamie Abbott/Sandbox2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
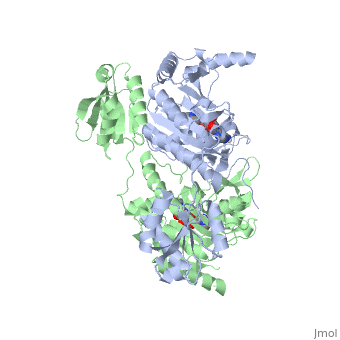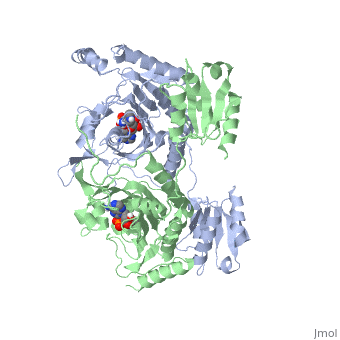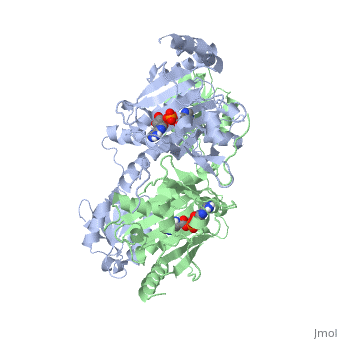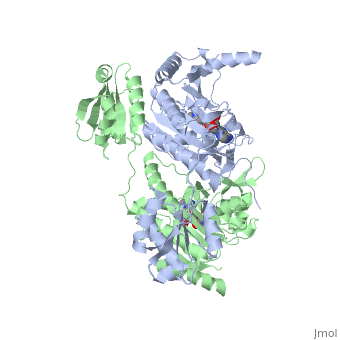
'''Function and Catalysis'''<StructureSection load='1KMM' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase (PDB entry [[1KMM]])' scene=''>Class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases aminoacylate the 3'OH of their cognate tRNAs. | '''Function and Catalysis'''<StructureSection load='1KMM' size='500' side='right' caption='Structure of Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase (PDB entry [[1KMM]])' scene=''>Class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases aminoacylate the 3'OH of their cognate tRNAs. | ||
| - | The active site to HisRS contains a histidine binding pocket composed of highly conserved residues found in distinct sequences motifs. First, the LV/AAGGGLDYY loop (or HisA loop) forms one wall of the binding pocket. This HisA loop is highly conserved and extends over a part of the active site.<ref=aaRSbook/>Francklyn, C., and Arnez, J.G. (2004) in ''Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases'' (Ibba, M.,Francklyn, C.,Cusack, S.. Eds.) [http://www.landesbioscience.com/books/iu/id/810/?nocache=145477703 Landes Publishing, Austin, TX]</ref> Second, the glycine-rich β-strand (sequence AGGRYDGL preceding motif III) comprises the histidine binding pocket floor and wall. Finally, conserved side chains that make direct contact with histidine are Glu83 and Gly127 (motif II), which contact the α-amino and α-carbonyl functional groups, respectively, and Glu131 (motif II) and Tyr264, which make hydrogen bonds to the Nδ and Nε, respectively, of the imidazole ring.<ref>aaRSbook</ref></StructureSection> | + | The active site to HisRS contains a histidine binding pocket composed of highly conserved residues found in distinct sequences motifs. First, the LV/AAGGGLDYY loop (or HisA loop) forms one wall of the binding pocket. This HisA loop is highly conserved and extends over a part of the active site.<ref name="aaRSbook"/>Francklyn, C., and Arnez, J.G. (2004) in ''Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases'' (Ibba, M.,Francklyn, C.,Cusack, S.. Eds.) [http://www.landesbioscience.com/books/iu/id/810/?nocache=145477703 Landes Publishing, Austin, TX]</ref> Second, the glycine-rich β-strand (sequence AGGRYDGL preceding motif III) comprises the histidine binding pocket floor and wall. Finally, conserved side chains that make direct contact with histidine are Glu83 and Gly127 (motif II), which contact the α-amino and α-carbonyl functional groups, respectively, and Glu131 (motif II) and Tyr264, which make hydrogen bonds to the Nδ and Nε, respectively, of the imidazole ring.<ref>aaRSbook</ref></StructureSection> |
<scene name='User:Jamie_Abbott/Sandbox2/Hisrsdimer/2'>Dimer</scene> | <scene name='User:Jamie_Abbott/Sandbox2/Hisrsdimer/2'>Dimer</scene> | ||
<scene name='User:Jamie_Abbott/Sandbox2/Hisrsdimer_to_monomer/2'>Monomer</scene> | <scene name='User:Jamie_Abbott/Sandbox2/Hisrsdimer_to_monomer/2'>Monomer</scene> | ||
Revision as of 20:22, 14 April 2012
Contents |
Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase
Histidyl tRNA Synthetase (HisRS) is a 94kD homodimer that belongs to the Class II of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRS). Class II enzymes have a composed of anti-parallel β-sheets and α-helices (residues 1-325).
Function and Catalysis
| |||||||||||