Antizyme Inhibitor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load="3BTN.pdb" size="400" color="white" frame="true" align="right" scene='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi/1' spinBox="true" > | ||
[[Image:AziFig.PNG|left|300px]] | [[Image:AziFig.PNG|left|300px]] | ||
| - | + | ==Antizyme Inhibitor== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
{{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_18369191}} | {{ABSTRACT_PUBMED_18369191}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | <StructureSection load="3BTN.pdb" size="500" color="white" frame="true" align="right" scene='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi/1' spinBox="true" > | ||
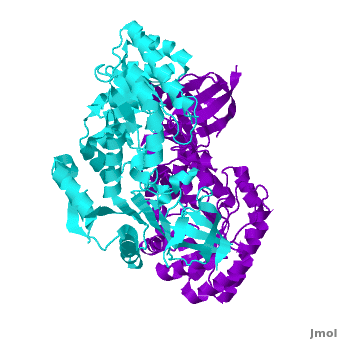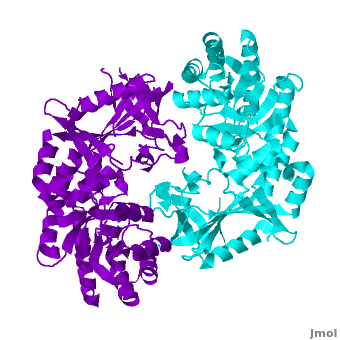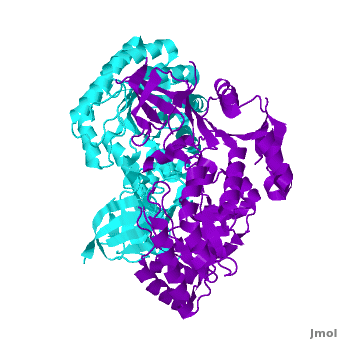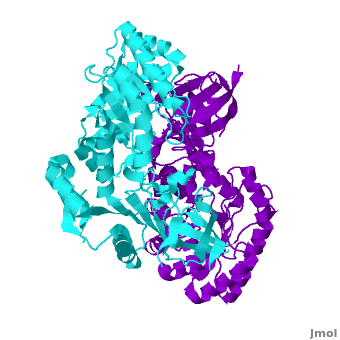
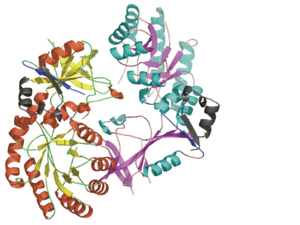
Each <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Monomer/5'>monomer</scene> consists of two domains: a <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Monomer/6'>TIM-like</scene> α/β-barrel [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TIM_barrel] domain (residues 45–280) and a modified <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Monomer/7'>Greek key</scene> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greek_key] β-sheet domain (residues 8–44 and 281–435). <font color='red'><b>Helices</b></font> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix] are colored in <font color='red'><b>red</b></font> and <font color='black'><b>β sheets</b></font> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet] in <font color='black'><b>yellow</b></font>. | Each <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Monomer/5'>monomer</scene> consists of two domains: a <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Monomer/6'>TIM-like</scene> α/β-barrel [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TIM_barrel] domain (residues 45–280) and a modified <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Monomer/7'>Greek key</scene> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greek_key] β-sheet domain (residues 8–44 and 281–435). <font color='red'><b>Helices</b></font> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix] are colored in <font color='red'><b>red</b></font> and <font color='black'><b>β sheets</b></font> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet] in <font color='black'><b>yellow</b></font>. | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
A sequence alignment and structural comparison of mouse AzI crystallographic dimer to mouse, human, and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trypanosome trypanosome] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ornithine_decarboxylase ODC] (mODC, hODC, and tODC, respectively) show high sequence identity (~50%) and structural similarity between AzI and ODC monomers (RMSD values of 1.85 Å, 1.6 Å, and 1.5 Å, respectively). The <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc/10'>structural comparison</scene> of mouse AzI crystallographic dimer (mAzI, <font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font> and <font color='blueviolet'><b>blueviolet</b></font>) to mODC (PDB code [[7odc]], (<font color='red'><b>red</b></font> and <font color='lime'><b>lime</b></font>) is shown. Superposition of the <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc/11'>interface</scene> of mAzI and mODC showing the inter-subunit variable loops (AzI residues 355–362 and 387–401). <font color='black'><b>AzI loops</b></font> are in <font color='black'><b>black</b></font>, and <font color='black'><b>ODC loops</b></font> are in <font color='black'><b>yellow</b></font>. | A sequence alignment and structural comparison of mouse AzI crystallographic dimer to mouse, human, and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trypanosome trypanosome] [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ornithine_decarboxylase ODC] (mODC, hODC, and tODC, respectively) show high sequence identity (~50%) and structural similarity between AzI and ODC monomers (RMSD values of 1.85 Å, 1.6 Å, and 1.5 Å, respectively). The <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc/10'>structural comparison</scene> of mouse AzI crystallographic dimer (mAzI, <font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font> and <font color='blueviolet'><b>blueviolet</b></font>) to mODC (PDB code [[7odc]], (<font color='red'><b>red</b></font> and <font color='lime'><b>lime</b></font>) is shown. Superposition of the <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc/11'>interface</scene> of mAzI and mODC showing the inter-subunit variable loops (AzI residues 355–362 and 387–401). <font color='black'><b>AzI loops</b></font> are in <font color='black'><b>black</b></font>, and <font color='black'><b>ODC loops</b></font> are in <font color='black'><b>yellow</b></font>. | ||
The two AzI monomers (<font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font>, <font color='blueviolet'><b>blueviolet</b></font>) have only <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc1/1'>43 contacting residues</scene> (< 3.5 Å apart), while there are more contacts between the two monomers of hODC, <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc1/2'>mODC</scene> (<font color='red'><b>red</b></font>, <font color='lime'><b>lime</b></font>), and tODC (74, 83 and 69, respectively). Moreover, the surface area buried by the two mODC monomers is significantly larger than the one buried by the AzI monomers. These features explain a very weak crystallographic AzI dimer. | The two AzI monomers (<font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font>, <font color='blueviolet'><b>blueviolet</b></font>) have only <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc1/1'>43 contacting residues</scene> (< 3.5 Å apart), while there are more contacts between the two monomers of hODC, <scene name='Antizyme_Inhibitor/Azi_odc1/2'>mODC</scene> (<font color='red'><b>red</b></font>, <font color='lime'><b>lime</b></font>), and tODC (74, 83 and 69, respectively). Moreover, the surface area buried by the two mODC monomers is significantly larger than the one buried by the AzI monomers. These features explain a very weak crystallographic AzI dimer. | ||
Revision as of 12:17, 11 June 2012
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Antizyme Inhibitor
3btn – AzI – mouse
1zo0 – AzI – rat - NMR
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Cancer
Reference
Shira Albeck, Orly Dym, Tamar Unger, Zohar Snapir, Zippy Bercovich and Chaim Kahana. Crystallographic and biochemical studies revealing the structural basis for antizyme inhibitor function. Protein Sci. 2008 May; 17(5): 793-802. Epub 2008 Mar 27.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Dinesh Kulhary, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky, Orly Dym