Journal:JBSD:1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
'''Dynamics of conserved water mediated salt bridge in hIMPDH simulated structures''' | '''Dynamics of conserved water mediated salt bridge in hIMPDH simulated structures''' | ||
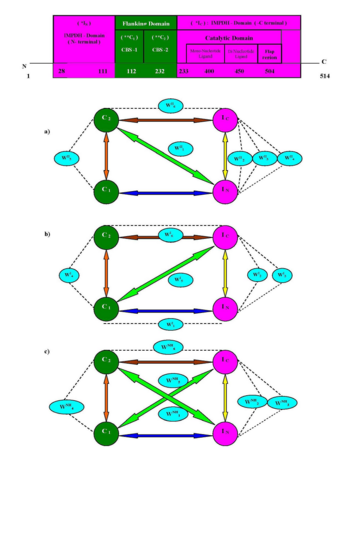
| - | The six conserved hydrophilic sites which are stabilized the salt bridges (evolved during molecular simulation) in IMPDH seem very interesting and it shade some new light for the development of forthcoming science on IMPDH enzyme. The hydrophilic centers WII2, WII3 and WII4 of hIMPDH-II, WI2 and WI3 of hIMPDH-I, and WNH2, WNH3 of nhIMPDH-II structure are responsible for intra domain (IN --- IC) association, domain recognition through water mediated salt bridge. During dynamics, WII5, WI4 and WNH4 of 1B3O, <scene name='Journal:JBSD:1/Cv/6'>1JCN</scene> and 1JR1 are solely involved in (C1 -- C2) intra domain recognition and gear the conformational orientation of flanking CBS domains. Another important structural role of WII1 and WNH1 are to stabilize the isoform-specific inter-domain (IN --- C2) in type –II IMPDH (1B3O and 1JR1) structures or to connect the two terminal domains via water mediated salt bridge. Possibly the sequence dissimilarity (~ 15 % between type 1 and II) and structural topology of enzyme may control the dynamic behavior of water molecules in inter-domain clefts. Moreover, this inherent flexibility of water molecules in the hIMPDH-II simulated structure may influence the biochemical activities in CML cancer cells. The work put forward some light on the binding propensity of CBS domain with catalytic domains (IN and IC) via interaction of conserved water mediated salt bridges (WII1 and WII6 in 1B3O, WI1, WI5 and WI6 in 1JCN, WNH1, WNH2, WNH3, WNH5 and WNH6 in 1JR1) and their exclusive participation in recognition process. | + | The six conserved hydrophilic sites which are stabilized the salt bridges (evolved during molecular simulation) in IMPDH seem very interesting and it shade some new light for the development of forthcoming science on IMPDH enzyme. The hydrophilic centers WII2, WII3 and WII4 of hIMPDH-II, WI2 and WI3 of hIMPDH-I, and WNH2, WNH3 of nhIMPDH-II structure are responsible for intra domain (IN --- IC) association, domain recognition through water mediated salt bridge. During dynamics, WII5, WI4 and WNH4 of 1B3O, <scene name='Journal:JBSD:1/Cv/6'>1JCN</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBSD:1/Cv/9'>1JR1</scene> are solely involved in (C1 -- C2) intra domain recognition and gear the conformational orientation of flanking CBS domains. Another important structural role of WII1 and WNH1 are to stabilize the isoform-specific inter-domain (IN --- C2) in type –II IMPDH (1B3O and 1JR1) structures or to connect the two terminal domains via water mediated salt bridge. Possibly the sequence dissimilarity (~ 15 % between type 1 and II) and structural topology of enzyme may control the dynamic behavior of water molecules in inter-domain clefts. Moreover, this inherent flexibility of water molecules in the hIMPDH-II simulated structure may influence the biochemical activities in CML cancer cells. The work put forward some light on the binding propensity of CBS domain with catalytic domains (IN and IC) via interaction of conserved water mediated salt bridges (WII1 and WII6 in 1B3O, WI1, WI5 and WI6 in 1JCN, WNH1, WNH2, WNH3, WNH5 and WNH6 in 1JR1) and their exclusive participation in recognition process. |
During dynamics charges over the oxygen atom of water molecules are varied in the Lys --- Asp / Lys --- Glu salt bridges. Some charges on Lys (-Nz) are transferred to acidic oxygen of Asp / Glu residues and vise versa. However, in water mediated Arg --- Asp interaction, some charges are observed to flow from the basic nitrogen center to acidic oxygen atoms and the charges over water oxygen is also varied. During dynamics, the flow of charges through water molecules in Lys to Asp /Glu residues are observed to be bidirectional, whereas in case of Arg to Asp, it is unidirectional. | During dynamics charges over the oxygen atom of water molecules are varied in the Lys --- Asp / Lys --- Glu salt bridges. Some charges on Lys (-Nz) are transferred to acidic oxygen of Asp / Glu residues and vise versa. However, in water mediated Arg --- Asp interaction, some charges are observed to flow from the basic nitrogen center to acidic oxygen atoms and the charges over water oxygen is also varied. During dynamics, the flow of charges through water molecules in Lys to Asp /Glu residues are observed to be bidirectional, whereas in case of Arg to Asp, it is unidirectional. | ||
Revision as of 13:14, 18 July 2012
| |||||||||||
- ↑ REF
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.