1c5k
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /><applet load="1c5k" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1c5k, resolution 2.Å" /> '''THE STRUCTURE OF TOLB,...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1c5k.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1c5k" size=" | + | [[Image:1c5k.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1c5k" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
caption="1c5k, resolution 2.Å" /> | caption="1c5k, resolution 2.Å" /> | ||
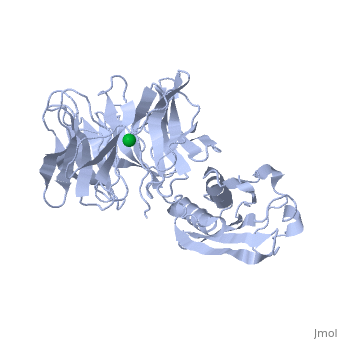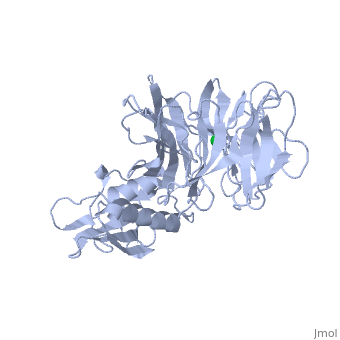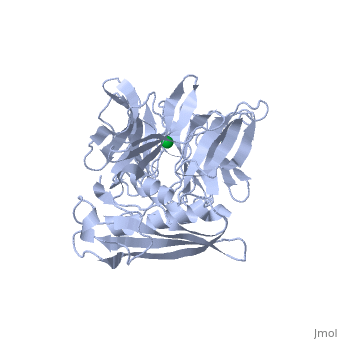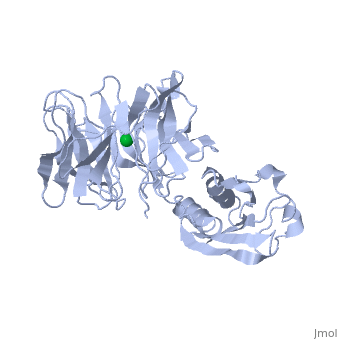
'''THE STRUCTURE OF TOLB, AN ESSENTIAL COMPONENT OF THE TOL-DEPENDENT TRANSLOCATION SYSTEM AND ITS INTERACTIONS WITH THE TRANSLOCATION DOMAIN OF COLICIN E9'''<br /> | '''THE STRUCTURE OF TOLB, AN ESSENTIAL COMPONENT OF THE TOL-DEPENDENT TRANSLOCATION SYSTEM AND ITS INTERACTIONS WITH THE TRANSLOCATION DOMAIN OF COLICIN E9'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | BACKGROUND: E colicin proteins have three functional domains, each of | + | BACKGROUND: E colicin proteins have three functional domains, each of which is implicated in one of the stages of killing Escherichia coli cells: receptor binding, translocation and cytotoxicity. The central (R) domain is responsible for receptor-binding activity whereas the N-terminal (T) domain mediates translocation, the process by which the C-terminal cytotoxic domain is transported from the receptor to the site of its cytotoxicity. The translocation of enzymatic E colicins like colicin E9 is dependent upon TolB but the details of the process are not known. RESULTS: We have demonstrated a protein-protein interaction between the T domain of colicin E9 and TolB, an essential component of the tol-dependent translocation system in E. coli, using the yeast two-hybrid system. The crystal structure of TolB, a procaryotic tryptophan-aspartate (WD) repeat protein, reveals an N-terminal alpha + beta domain based on a five-stranded mixed beta sheet and a C-terminal six-bladed beta-propeller domain. CONCLUSIONS: The results suggest that the TolB-box residues of the T domain of colicin E9 interact with the beta-propeller domain of TolB. The protein-protein interactions of other beta-propeller-containing proteins, the yeast yPrp4 protein and G proteins, are mediated by the loops or outer sheets of the propeller blades. The determination of the three-dimensional structure of the T domain-TolB complex and the isolation of mutations in TolB that abolish the interaction with the T domain will reveal fine details of the protein-protein interaction of TolB and the T domain of E colicins. |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1C5K is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli] with YB as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1C5K is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli] with <scene name='pdbligand=YB:'>YB</scene> as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1C5K OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[Category: Bamford, V.]] | [[Category: Bamford, V.]] | ||
[[Category: Carr, S.]] | [[Category: Carr, S.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Hemmings, A | + | [[Category: Hemmings, A M.]] |
[[Category: James, R.]] | [[Category: James, R.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Penfold, C | + | [[Category: Penfold, C N.]] |
[[Category: YB]] | [[Category: YB]] | ||
[[Category: beta propellor]] | [[Category: beta propellor]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Category: protein-protein interactions]] | [[Category: protein-protein interactions]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 12:02:36 2008'' |
Revision as of 10:02, 21 February 2008
|
THE STRUCTURE OF TOLB, AN ESSENTIAL COMPONENT OF THE TOL-DEPENDENT TRANSLOCATION SYSTEM AND ITS INTERACTIONS WITH THE TRANSLOCATION DOMAIN OF COLICIN E9
Overview
BACKGROUND: E colicin proteins have three functional domains, each of which is implicated in one of the stages of killing Escherichia coli cells: receptor binding, translocation and cytotoxicity. The central (R) domain is responsible for receptor-binding activity whereas the N-terminal (T) domain mediates translocation, the process by which the C-terminal cytotoxic domain is transported from the receptor to the site of its cytotoxicity. The translocation of enzymatic E colicins like colicin E9 is dependent upon TolB but the details of the process are not known. RESULTS: We have demonstrated a protein-protein interaction between the T domain of colicin E9 and TolB, an essential component of the tol-dependent translocation system in E. coli, using the yeast two-hybrid system. The crystal structure of TolB, a procaryotic tryptophan-aspartate (WD) repeat protein, reveals an N-terminal alpha + beta domain based on a five-stranded mixed beta sheet and a C-terminal six-bladed beta-propeller domain. CONCLUSIONS: The results suggest that the TolB-box residues of the T domain of colicin E9 interact with the beta-propeller domain of TolB. The protein-protein interactions of other beta-propeller-containing proteins, the yeast yPrp4 protein and G proteins, are mediated by the loops or outer sheets of the propeller blades. The determination of the three-dimensional structure of the T domain-TolB complex and the isolation of mutations in TolB that abolish the interaction with the T domain will reveal fine details of the protein-protein interaction of TolB and the T domain of E colicins.
About this Structure
1C5K is a Single protein structure of sequence from Escherichia coli with as ligand. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
The structure of TolB, an essential component of the tol-dependent translocation system, and its protein-protein interaction with the translocation domain of colicin E9., Carr S, Penfold CN, Bamford V, James R, Hemmings AM, Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):57-66. PMID:10673426
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 12:02:36 2008