This tutorial is designed for High School (ages 14-19).
Purpose of the Tutorial
Throughout this tutorial we will be targeting basic chemistry topics. A scientific research article will be used to demonstrate key chemistry topics we will be discussing. These topics are vital to the understanding of more advanced chemistry. There are interactive molecules incorporated into the text to help your understanding.
The summary of the research article will be confusing; you are not expected to understand it completely to benefit from the tutorial. The research article is used as a reference to demonstrate the chemistry topics we will be discussing.
Summary: Scientific Research Artical
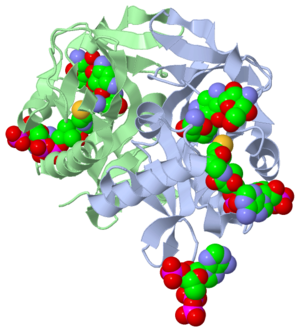
- The study where this molecule was obtained is named "Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Complex with Coenzyme A and Tobramycin". The study focused on AAC (2’)- Ic, also known as aminoglycoside 2’- N- acetyltransferase. The scientists in the study determined the crystal structure of AAC (2’)-Ic from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The specific fold of AAC (2’)-Ic is placed in the GNAT or GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase superfamily. Although the physiological function of AAC(2’)-Ic is not certain, the crystal structure determined by the scientists allowed them to hypothesize. Through the crystal structure, scientists determined that this enzyme might acetylate mycothiol, which is a key biosynthetic intermediate and the major reducing agent in mycobacterium. This enzyme is capable of acetylating aminoglycosides bearing a 2’ amino group. When this occurs the aminoglycoside antibiotic becomes inactive.
Objectives
By the end of this tutorial you should be able to:
1. Describe and provide examples of covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds
2. Understand and identify the importance of secondary structures
3. Understand and describe an active site
4. Describe what a ligand is
5. Understand and explain the importance of Tobramycin as an antibiotic
6. Describe the general function of CoA
7. Be able to classify amino acids and understand what the classification represents
Types of Bonds
There are three common types of bonds. These bonds include a hydrogen bond, covalent bond, or an ionic bond. The strongest bond is a covalent bond, followed by the ionic bond, which leaves the weakest bond to be the hydrogen bond.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds, the strongest type of bond, involve the sharing of electrons between two molecules/atoms. An example of a covalent bond is shown here. This is the amino acid Arginine. Amino Acids are discussed in a later section; this representation is only used to show a covalent bond. The Red molecule is Oxygen, the grey molecules are carbons and the blue molecules are nitrogen’s. All of these atoms are covalently bound. The carbons, nitrogen’s, and oxygen are all sharing electrons with their adjacent atoms. These bonds are very stable.
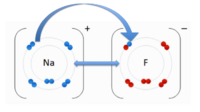
Ionic Bonds
An ionic bond is an attraction between two molecules of opposite charge. The opposite charges are positive (+) and negative (-). A positively charged atom is referred to as a cation, and a negatively charged atom is referred to as an anion. To the image to the right, you can see a negatively charged Fluorine (F) and the cation Sodium (Na). These two atoms are attracted to each other due to there opposite charges. The double-sided arrow between them is representation of there attractive force.
In this representation the pink depicts the negatively charged (anionic/acidic) portion of the molecule and the yellow represents the positively charged (cationic/basic) portion of the molecule. Through this representation you will notice that the charges are evenly distributed. They are evenly distributed because the positive and negative charges are attracted to one and other, while the positive-positive and negative-negative charges repel each other. The repulsion of common charges and the attraction of oppositely charged atoms/molecules is what causes them to distribute evenly.
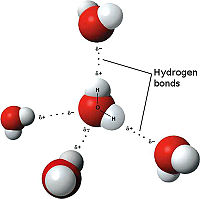
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen Bonds, the weakest of bonds, are attractive interactions between an electronegative atom and hydrogen. Electronegative atoms are atoms that have high electron density. They are strong atoms that pull electrons towards them from weaker/low electron density atoms, such as hydrogen. When the electronegative atom pulls the electrons, it leaves the other atom with a slightly positive charge. Water is the most common example of hydrogen bonding. The water molecule chemical formula is H2O. The highly electronegative oxygen pulls the hydrogen closer by attracting hydrogen’s electrons and allowing the formation of a water droplet. The electronegative atoms allow for the droplet to be held together instead of spreading. In this representation the hydrogen bonds are represented as yellow-dashed lines. The hydrogen bonds are important to the stability of the secondary structures.
Secondary Structures
- Secondary structures are alpha helices and beta sheets, which help contribute to the stability of the molecule. The alpha helices are represented with pink arrows and the beta strands are represented with yellow arrows. This molecule has approximately four alpha helices and two beta strands when presented as a monomer. Since this structure is represented as a dimer you actually have eight alpha helices and four beta sheets. The concept of a dimer is explained in the "Ligands" section later on in the tutorial. Alpha helices rotate in a clockwise manner and are also oriented in a parallel formation. The parallel alpha helices are held together by hydrogen bond, which we discussed earlier. Beta sheets are often anti-parallel. The structure of the alpha and beta sheets in Tuberculosis/CoA/Tobramycin structure represents the GNAT fold. The folding of a protein is what gives the function. When a change occurs in the folding, a change in the function also takes place. The GNAT fold described in the study has a function of acetylation, which is the addition of an acyl group. The chemical formula of an acetyl group is COCH3. It is important to note that the discovery of the GNAT fold lead to the understanding of the major function.
Active Site
- The active site of a molecule can be described as a pocket where an interaction between substrates causes a physiological effect by causing a change in conformation. The conformation is referring to the orientation of the molecules involved in the structure. The conformation change can inhibit or activate the physiological effect. The active site is where the ligand is going to bind. (Ligands are discussed in detail later on in the “Ligands” section) The active site can either be inhibited or activated by ligands. Referring back to our article, the active site is where the substrate, in this case tobramycin, binds to CoA and the mycobacterium to cause an antibacterial effect. It the study described, this is where the acetylation of the tobramycin should be occurring. The acetylation of tobramycin would cause the tobramycin to be inactive, hence inhibiting the active site.
Ligand
- Ligands are molecules or complexes that are within the secondary structures that orient in such a way to contribute the function of the complex as a whole. Ligands can have binding sites on receptors, and when bound can trigger a physiological response. A ligand can be a competitive agonist, allosteric agonist, competitive antagonist, or an allosteric antagonist. An agonist is a ligand that causes a physiological response, activating the active site. An antagonist is a ligand that inhibits a physiological response, not allowing the active site to be activated.
- A ligand is competitive when it is binding to the same site as the physiological activator; hence it is competing for the same site. When a ligand binds to an allosteric site, the ligand is binding to the same receptor but it is not binding to the active site. The ligands present in the complex used by the research article are coenzyme A, Tobramycin and Phosphate-Adenosine-5'-Diphosphate.
Coenzyme A
- Coenzyme (CoA) is a coenzyme that synthesizes and oxidizes fatty acids. This process is essential for the utilization of fatty acids. Coenzyme A is used as a substrate in the citric acid cycle. The citric acid cycle is also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA). This process is important to the production of ATP, which is an energy source used by the body.
- The Protein’s in this molecule are represented as a dimer. A dimer is a chemical structure formed from two identical subunits. Some molecules are present as a dimer because it is more stable then the monomer. The dimer is constructed by connecting two subunits along their axis.
Tobramycin
- Tobramycin is an antibiotic part of the aminoglycoside family. Aminoglycosides produce antibacterial effects by inhibiting protein synthesis and compromising the cell wall structure. By inhibiting the protein synthesis of the bacteria, it does not allow the bacteria to replicate. The cell wall is an important structure to bacteria because it provides the structure and stability to the bacteria. By disrupting the cell wall, we are removing the stability of the bacteria and ultimately casing bacteria death.
Tobramycin targets a variety of bacteria, particularly gram(-) species. Just like all drugs there are side effects associated with tobramycin. Some of the more common side effects are ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Ototoxic is hearing loss and nephrotoxic is causing kidney damage. The kidney damage is due to Tobramycin reabsorption through the renal tubules. This basically means that tobramycin may be toxic to the kidneys. The toxicity is caused by the contact-time in the renal tubules where the drug is located.
Tobramycin trade name is Tobrex. A trade name is another name for tobramycin. It is a pregnancy category D. Pregnancy categories are assigned to all drugs. They are used to classify how likely the drug is to cause harm to the fetus. The pregnancy categories are A, B, C, D, and X. Pregnancy category A causes no harm to the fetus and pregnancy category X indefinitely causes harm to the fetus. Since Tobramycin is a pregnancy category D, this is not an optimal choice for a pregnant patient.
Tobramycin can be given intravenously, intramuscularly, as an inhalation or ophthalmicly. Intravenously is an IV route of administration where the drug is administered directly to the vasculature or blood vessels. Intramuscular is a shot that penetrates your muscle. A common example of an intramuscular administration would be a flu shot. Inhalation is a route of administration where the lungs are the targets. An example of this would be an inhaler used in asthmatics. Ophthalmic administration is where the drug is administered to the eye; an example would be an eye drop.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 common amino acids. The basic structure of an amino acid is an amine group (-NH2), a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) and a functional group specific to each amino acid. The functional group determines how the amino acid is categorized. They are categorized as polar, non-polar, acidic or basic. Amino acids are commonly referred to using their three-letter abbreviation. I have provided the three-letter abbreviations along side the amino acids in their category list.
An amino acid is considered polar when the charges electronegativity between atoms in the functional group are extremely different. For example, water is considered polar. This is because the electronegativity of oxygen is extremely high and the electronegativity of hydrogen is extremely low. The opposing electronegativity is making water polar. In contrast, non-polar is when the electronegativity of the atoms in the functional group are similar. An amino acid is considered polar when it has an acidic functional group, such as a carboxylic acid (pH~1-6). In correlation, a basic amino acid has a basic functional group, such as an amine group (pH~8-14). An amino acid is neutral when it has a functional group that displays a pH close to physiological pH (~7). A list of the most common amino acids and their categories are as follows for your reference.
Neutral Amino Acids:
Alanine (ala)
Asparagine (asn)
Cysteine (cyc)
Glutamine (gln)
Glycine (gly)
Isoleucine (ile)
Leucine (leu)
Methionine (met)
Phenylalanine (phe)
Proline (pro)
Serine (ser)
Threonine (thr)
Tryptophan (trp)
Tyrosine (tyr)
Valine (val)
Acidic amino acids:
Aspartic acid (asp) Glutamic acid (glu)
Basic Amino acids:
Arginine (arg)Histidine (his) Lysine (lys)
Polar Amino acids:
Arginine (arg) Asparagine (asn) Aspartic acid (asp)Cysteine (cyc) Glutamic Acid (glu) Glutamine (gln) Histidine (his) Lysine (lys) Serine (ser) Threonine (thr) Tryptophan (trp) Tyrosine (tyr)
Non-polar amino acids:
Alanine (ala) Glycine (gly) Isoleucine (ile) Leucine (leu) Methionine (met) Phenylalanine (phe) Proline (pro) Valine (val)
There are 8 different amino acids present in the research article main compound.
CoA Amino Acids
Coenzyme A (CoA) has seven amino acids bound to it. The amino acids consist of two arginine, one glycine, and four valine’s.
Arginine is a basic amino acid and is a nonessential A nonessential amino acid is an amino acid that can be synthesized by the body, so it is not essential that you obtain the amino acid form another source. Glycine is a non-polar, basic amino acid. It is also the smallest common amino acid. The functional group attached is hydrogen. Valine is also categorized as a nonpolar, basic amino acid. Valine is nonpolar and basic because the functional group consists of two methyl groups.
CoA and Arg124
CoA and Gly92
CoA and Val96
CoA and Val86
CoA and Val94
CoA and Val84
Tobramycin Amino Acids
Tobramycin has four amino acids bound to it. There are two aspartic acid, a serine, and a tryptophan.
Asp35
Trp181
Ser117
Asp152
PAP Amino Acids
PAP has four amino acids bound to it. There are two histidine’s and a tryptophan.
His54
Trp90
His55
<Vetting, M. W., et al. "Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Complex with Coenzyme A and Tobramycin." RCSB Protien DataBase. N.p., 28 Aug.2002. Web. 13 July 2011. <http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1M4D>.>
Maňas, Michal, trans. "File:3D model hydrogen bonds in water.jpg." Wikimedia Commons. Wikimedia Commons, 3 Dec. 2007. Web. 31 Oct. 2012. <http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:3D_model_hydrogen_bonds_in_water.jpg>.
http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/561aminostructure.html