Xanthine Oxidoreductase
Xanthine oxidoreductase is actually considered to exist as two enzymes in one, one being xanthine oxidase and the other existing as xanthine dehydrogenase. When the enzyme was initially purified by scientists two different forms of the enzyme were found, where one uses nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and the other uses oxygen. The two forms were believed to exist as two different enzymes and were thus given two different names; however, upon further investigation into the amino acid sequence of the enzymes it was determined that the enzymes were actually the same. The two forms of the enzyme can differ in two ways:
1. Within the oxidoreductase enzyme there are multiple disulfide bridges. In the case that these bridges are left untouched the enzyme will then take on the characteristics to act as an oxidase, but in the event that these bridges are restricted the enzyme then acts as a dehydrogenase.
2. The oxidoreductase enzyme is permanently altered by proteases so that it will be constantly utilized in the oxidase form.
Mechanism of Action
Xanthine oxidase is characterized as a molybdenum containing enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of a sp2 hybrized carbon in a broad range of aromatic heterocycles and aldehydes. In eukaryotes xanthine oxidase exist as a with each monomer containing . The crystal structure of the bovine xanthine oxidase complex contains two active sites with varying intrinsic activity. The crystalline structure of a xanthine oxidase monomer offers a better view of the active molybdenum center, the ferredoxin iron sulfur, , clusters, and . The is thought to be composed of glutamine, glutamic acid, phenylalanine, arginine, and the molybdenum center. The substrate is believed to bind between the Phe 1009 and Phe 914.
Electron Extraction
One side of the xanthine oxidoreductase enzyme consists of an active site that includes a molybdenum atom which binds to a purine substrate and adds a hydroxyl group.
During this process . One of the final steps in the electron transfer funnels electrons to a FAD group. The opposing side then transfers the electrons to NAD or oxygen depending on the dehydrogenase or oxidase nature of the enzyme. The dehydrogenase form of the enzyme transfers these electrons to NAD, while the oxidase form blocks NAD through a loop of protein that covers the FAD molecule allowing smaller oxygen molecules to accept the electrons.
Metabolism
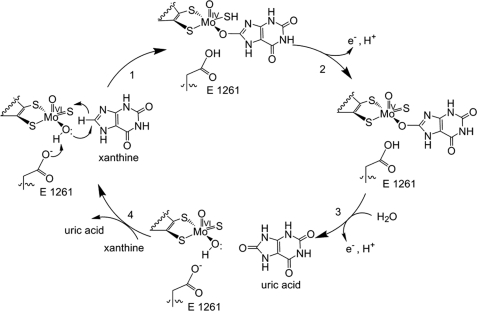
Following the intramolecular electron transfer that occurs within the enzyme, the enzyme is able to catalyze the reaction of purine degradation products to ultimately yield uric acid. The comprehensive catalytic activity of the enzyme consists of a redox reaction that includes a reduction reaction in which the substrate is oxidized by a hydroxylation at the molybdenum center and a oxidation reaction in which electrons are removed from the enzyme by it's FAD. During the reduction reaction the substrate is hydrolyzed (at a specific carbon) by a nucleophilic attack with the MO-OH group within the enzyme's metal center. While this nucleophilic attack is occurring, there is also an accompanying step taking place where the carbon being hydroxylized is transferring a hydride to a MO=S group. The bound substrate product is then expelled by solvent hydroxide to regenerate the original MO-OH ligand to be used for consecutive catalytic cycles. The oxidation reaction on the other hand consists of transporting electrons from the FAD center to a terminal electron acceptor such as NAD+ (dehydrogenase) or oxygen (oxidase)
Clinical Application
Xanthine oxidase act by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme, namely its purine metabolism activity. Inhibitors of the enzyme are commonly used in the treatment of hyperuricemia, and its corresponding medical conditions such as gout, by reducing the production of uric acid. Currently there is also investigation of the use of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. As previously mentioned xanthine oxidase plays an important role in purine degradation with the last step in this process resulting in the production of uric acid to be excreted from the body. This excretion; however, is not always an efficient process and there can be an abnormal accumulation of uric acid in the blood. This accumulation can come as a result of increased production by the way of a purine rich diet, decreased excretion by the way of drug interactions or genetics, or a combination of the two. The most common type of xanthine oxidase inhibitors are classified as purine analogues and consists of allopurinol and oxypurinol.