Catalytic Subunit of T. Castaneum TERT Polymerase
From Proteopedia
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<scene name='Catalytic_Subunit_of_T._Castaneum_TERT_Polymerase/Val_342/1'>Active Site of the Enzyme</scene> | <scene name='Catalytic_Subunit_of_T._Castaneum_TERT_Polymerase/Val_342/1'>Active Site of the Enzyme</scene> | ||
| - | + | <scene name='Catalytic_Subunit_of_T._Castaneum_TERT_Polymerase/Positive_ionic_binding_pocket/1'>Positive Binding Pocket</scene> | |
Revision as of 21:19, 2 December 2012
|
Abstract
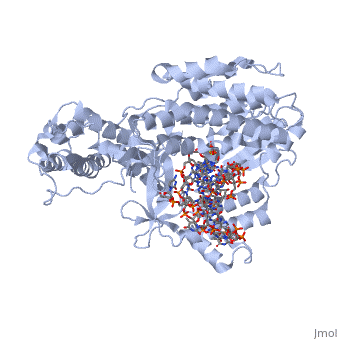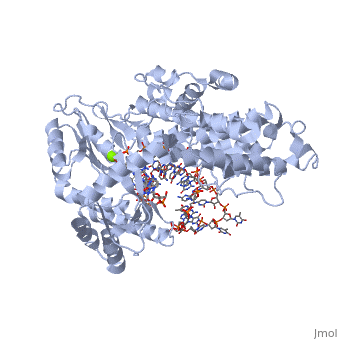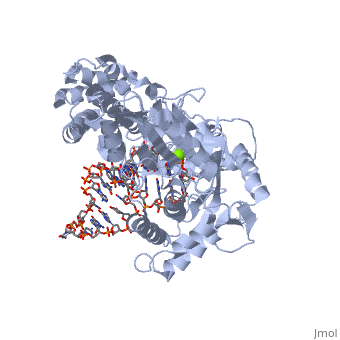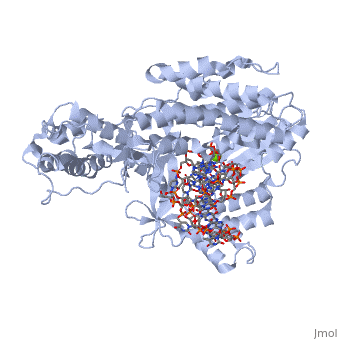
Telomerase is a specialized DNA polymerase that extends the 3' ends of eukaryotic linear chromosomes, a process required for genomic stability and cell viability. Here we present the crystal structure of the active Tribolium castaneum telomerase catalytic subunit, TERT, bound to an RNA-DNA hairpin designed to resemble the putative RNA-templating region and telomeric DNA. The RNA-DNA hybrid adopts a helical structure, docked in the interior cavity of the TERT ring. Contacts between the RNA template and motifs 2 and B' position the solvent-accessible RNA bases close to the enzyme active site for nucleotide binding and selectivity. Nucleic acid binding induces rigid TERT conformational changes to form a tight catalytic complex. Overall, TERT-RNA template and TERT-telomeric DNA associations are remarkably similar to those observed for retroviral reverse transcriptases, suggesting common mechanistic aspects of DNA replication between the two families of enzymes.
Differences Between Human Telomerase
</StructureSection>