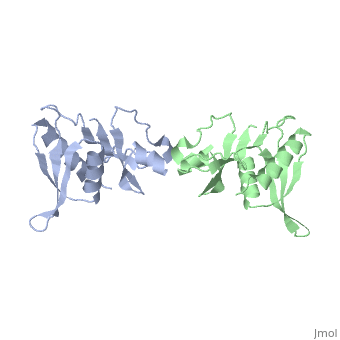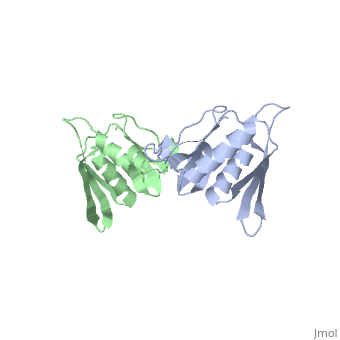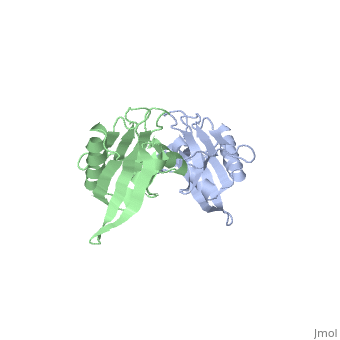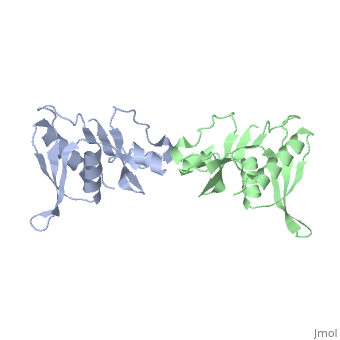1sei
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /><applet load="1sei" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1sei, resolution 1.9Å" /> '''STRUCTURE OF 30S RIBO...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1sei.jpg|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1sei" size=" | + | [[Image:1sei.jpg|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1sei" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
caption="1sei, resolution 1.9Å" /> | caption="1sei, resolution 1.9Å" /> | ||
'''STRUCTURE OF 30S RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN S8'''<br /> | '''STRUCTURE OF 30S RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN S8'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | BACKGROUND. Prokaryotic ribosomal protein S8 is an important RNA-binding | + | BACKGROUND. Prokaryotic ribosomal protein S8 is an important RNA-binding protein that occupies a central position within the small ribosomal subunit. It interacts extensively with 16S rRNA and is crucial for the correct folding of the central domain of the rRNA. S8 also controls the synthesis of several ribosomal proteins by binding to mRNA. It binds specifically to very similar sites in the two RNA molecules. RESULTS. S8 is divided into two tightly associated domains and contains three regions that are proposed to interact with other ribosomal components: two potential RNA-binding sites, and a hydrophobic patch that may interact with a complementary hydrophobic region of S5. The N-terminal domain fold is found in several proteins including two that bind double-stranded DNA. CONCLUSIONS. These multiple RNA-binding sites are consistent with the role of S8 in organizing the central domain and agree with the latest models of the 16S RNA which show that the S8 location coincides with a region of complicated nucleic-acid structure. The presence in a wide variety of proteins of a region homologous to the N-terminal domain supports the idea that ribosomal proteins must represent some of the earliest protein molecules. |
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1SEI is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geobacillus_stearothermophilus Geobacillus stearothermophilus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1SEI is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geobacillus_stearothermophilus Geobacillus stearothermophilus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1SEI OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[Category: Davies, C.]] | [[Category: Davies, C.]] | ||
[[Category: Ramakrishnan, V.]] | [[Category: Ramakrishnan, V.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: White, S | + | [[Category: White, S W.]] |
[[Category: prokaryotic]] | [[Category: prokaryotic]] | ||
[[Category: ribosomal protein]] | [[Category: ribosomal protein]] | ||
[[Category: rrna-binding]] | [[Category: rrna-binding]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 15:00:46 2008'' |
Revision as of 13:00, 21 February 2008
|
STRUCTURE OF 30S RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN S8
Overview
BACKGROUND. Prokaryotic ribosomal protein S8 is an important RNA-binding protein that occupies a central position within the small ribosomal subunit. It interacts extensively with 16S rRNA and is crucial for the correct folding of the central domain of the rRNA. S8 also controls the synthesis of several ribosomal proteins by binding to mRNA. It binds specifically to very similar sites in the two RNA molecules. RESULTS. S8 is divided into two tightly associated domains and contains three regions that are proposed to interact with other ribosomal components: two potential RNA-binding sites, and a hydrophobic patch that may interact with a complementary hydrophobic region of S5. The N-terminal domain fold is found in several proteins including two that bind double-stranded DNA. CONCLUSIONS. These multiple RNA-binding sites are consistent with the role of S8 in organizing the central domain and agree with the latest models of the 16S RNA which show that the S8 location coincides with a region of complicated nucleic-acid structure. The presence in a wide variety of proteins of a region homologous to the N-terminal domain supports the idea that ribosomal proteins must represent some of the earliest protein molecules.
About this Structure
1SEI is a Single protein structure of sequence from Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Structural evidence for specific S8-RNA and S8-protein interactions within the 30S ribosomal subunit: ribosomal protein S8 from Bacillus stearothermophilus at 1.9 A resolution., Davies C, Ramakrishnan V, White SW, Structure. 1996 Sep 15;4(9):1093-104. PMID:8805594
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 15:00:46 2008