Sandbox Reserved 715
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
;'''''Thermotoga maritima'' β-fructosidase (invertase)''' | ;'''''Thermotoga maritima'' β-fructosidase (invertase)''' | ||
| - | [[Image:1uyp asr r 500.jpg | 200 px |left]] | + | [[Image:1uyp asr r 500.jpg | 200 px |left|thumb|EC 3.2.1.26.]] |
Revision as of 00:36, 31 December 2012
Please, do not delete or modify any text or image. Thank you.
- Thermotoga maritima β-fructosidase (invertase)
Contents |
Introduction
The β-fructosidase (β-D-fructofuranosidase EC 3. 2. 1. 26.) of the thermophilic baterium Thermotoga maritima is an enzyme which hydrolyzes sucrose to release fructose and glucose. 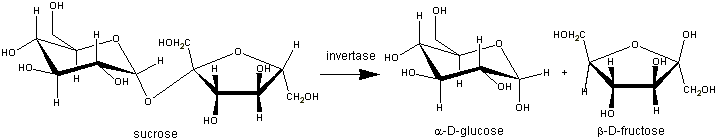
This enzyme achieves the hydrolysis with a retention molecular mechanism. Actually, the invertase hydrolyses the D-sucrose to form the D-fructose and the D-glucose. So, the substrate anomeric configuration is conserved in products. The β-fructosidase belongs to the GH32 (Glycoside hydrolysases 32) according to the sequence-based classification of glycoside hydrolysases.
Glycoside Hydrolases and the GH32 family
The Glycoside Hydrolysases
The glycoside hydrolases (GH) constitute a widespread enzyme group presenting a huge variety of protein folds and substrate specificities. They share a common feature which are two important amino acid residues. These two amino acid residues constitute the catalytic machinery accountable to the glycosidic bond cleavage. And they have been identified as an aspartate situated near the N-terminus and acting as the nucleophile, and a glutamate acting as the general acide/base.
The GH32 Family
The GH32 family includes over 370 members from plants, fungi and bacteria. This family contains not only invertases but other fructofuranosidases like insulinase, transfructosidase or inulinase.
Structure
Active site
The β-sandwich
Applications
|
