Aminopeptidase
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| - | + | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='VH9.pdb' size='500' side='right' scene='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/1' caption=''> | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
== Aminopeptidase from ''Aeromonas proteolytica''<ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-012-0873-4</ref> == | == Aminopeptidase from ''Aeromonas proteolytica''<ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-012-0873-4</ref> == | ||
| - | + | ||
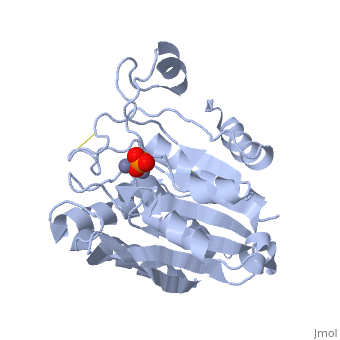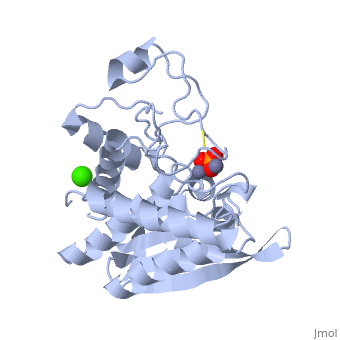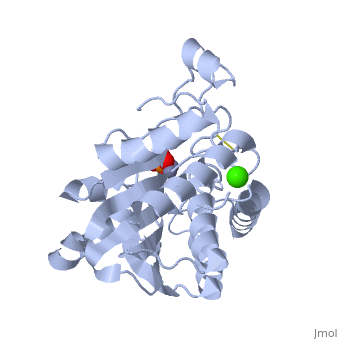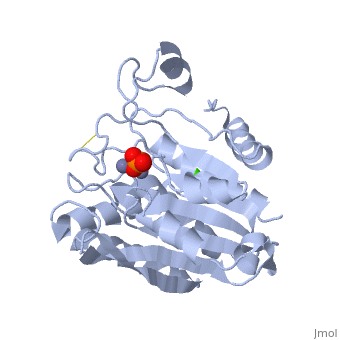
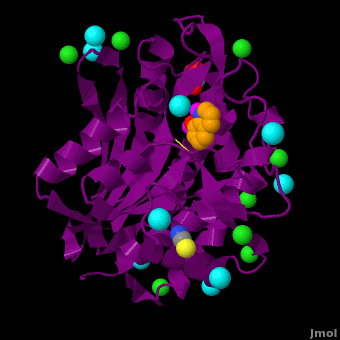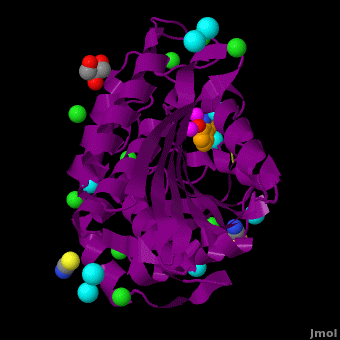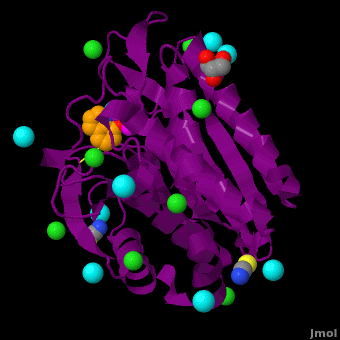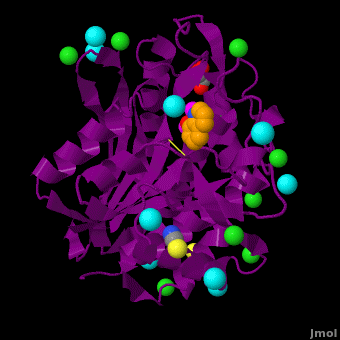
The selective inhibition of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/2'>aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica (AAP)</scene>, a <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/3'>dinuclear Zn2+</scene> hydrolase, by <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/10'>8-quinolinol (8-hydroxyquinoline, 8-HQ)</scene> derivatives is reported. Based on our findings about 8-HQ-based Zn<sup>2+</sup> fluorophores, it was hypothesized that 8-HQ derivatives have the potential to function as specific inhibitors of Zn<sup>2+</sup> enzymes, especially dinuclear Zn<sup>2+</sup> hydrolases. Inhibitory assays of 8-HQ derivatives against AAP disclosed that the 8-HQ and 5-substituted 8-HQ′s are competitive inhibitors for AAP with inhibition constants (''K''i) of 0.16—29 μM at pH 8.0. <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/11'>X-ray crystal structure analysis of an AAP with 8-HQ complex</scene> (1.3 Å resolution) as well as fluorescence titrations of these drugs with AAP confirmed that <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/13'>8-hydroxyquinoline binds to AAP in the 'Pyr-out' mode</scene>, in which the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/15'>hydroxide anion of 8-HQ bridges two Zn2+ (Zn1 and Zn2)</scene> in the active site of AAP and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/17'>nitrogen atom of 8-HQ coordinates to Zn1</scene> (PDB code: [[3vh9]]). <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/18'>Overlap of active site</scene> of <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">free AAP (colored green)</span> containing Zn<sup>2+</sup>-bound <font color='red'><b>water molecule (H2O or OH-; red sphere)</b></font> ([[1rtq]]) bridging two Zn<sup>2+</sup> and <font color='darkmagenta'><b>AAP–8-HQ complex (darkmagenta,</b></font> [[3vh9]]). <font color='magenta'><b>Two Zn<sup>2+</sup> are depicted as magenta spheres</b></font>. | The selective inhibition of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/2'>aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica (AAP)</scene>, a <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/3'>dinuclear Zn2+</scene> hydrolase, by <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/10'>8-quinolinol (8-hydroxyquinoline, 8-HQ)</scene> derivatives is reported. Based on our findings about 8-HQ-based Zn<sup>2+</sup> fluorophores, it was hypothesized that 8-HQ derivatives have the potential to function as specific inhibitors of Zn<sup>2+</sup> enzymes, especially dinuclear Zn<sup>2+</sup> hydrolases. Inhibitory assays of 8-HQ derivatives against AAP disclosed that the 8-HQ and 5-substituted 8-HQ′s are competitive inhibitors for AAP with inhibition constants (''K''i) of 0.16—29 μM at pH 8.0. <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/11'>X-ray crystal structure analysis of an AAP with 8-HQ complex</scene> (1.3 Å resolution) as well as fluorescence titrations of these drugs with AAP confirmed that <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/13'>8-hydroxyquinoline binds to AAP in the 'Pyr-out' mode</scene>, in which the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/15'>hydroxide anion of 8-HQ bridges two Zn2+ (Zn1 and Zn2)</scene> in the active site of AAP and the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/17'>nitrogen atom of 8-HQ coordinates to Zn1</scene> (PDB code: [[3vh9]]). <scene name='Journal:JBIC:15/Cv/18'>Overlap of active site</scene> of <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">free AAP (colored green)</span> containing Zn<sup>2+</sup>-bound <font color='red'><b>water molecule (H2O or OH-; red sphere)</b></font> ([[1rtq]]) bridging two Zn<sup>2+</sup> and <font color='darkmagenta'><b>AAP–8-HQ complex (darkmagenta,</b></font> [[3vh9]]). <font color='magenta'><b>Two Zn<sup>2+</sup> are depicted as magenta spheres</b></font>. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
== ''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase == | == ''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase == | ||
| - | + | ||
''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase (SGAP) cleaves the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein, and is specific for larger hydrophobic acids, especially leucine. No cleavage occurs if the next residue is proline.<br/> | ''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase (SGAP) cleaves the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein, and is specific for larger hydrophobic acids, especially leucine. No cleavage occurs if the next residue is proline.<br/> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
The <scene name='Aminopeptidase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> of the enzyme contains two Zn2+ ions with His85 and Asp160 as ligands for one ion, and Glu132 and His247 as ligands for the second ion. Asp97 is a common ligand to both ions. What appears to be a phosphate anion is bound to both zinc atoms, replacing the water molecule/hydroxide ion normally found in this class of enzyme. See details of SGAP in [[Streptomyces griseus Aminopeptidase (SGAP)]]. | The <scene name='Aminopeptidase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> of the enzyme contains two Zn2+ ions with His85 and Asp160 as ligands for one ion, and Glu132 and His247 as ligands for the second ion. Asp97 is a common ligand to both ions. What appears to be a phosphate anion is bound to both zinc atoms, replacing the water molecule/hydroxide ion normally found in this class of enzyme. See details of SGAP in [[Streptomyces griseus Aminopeptidase (SGAP)]]. | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
== 3D Structures of Aminopeptidase == | == 3D Structures of Aminopeptidase == | ||
Revision as of 14:46, 27 February 2013
|
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Aminopeptidase
Update January 2013
Cysteine aminopeptidase
3pw3 – PdCys-AP – Parabacteroides distasonis
Glutamic acid aminopeptidase
2wyr – PhGlu-AP+Co – Pyrococcus horikoshii
3kl9 – Glu-AP – Streptococcus pneumoniae
Alanine aminopeptidase
3ebg – PfAla-AP - Plasmodium falciparum
3ebh - PfAla-AP+bestatin
3ebi - PfAla-AP+dipeptide analog
4fke – pAla-AP + Zn – pig
4fkh – pAla-AP + Zn + alanine
4h5h, 4hol – pAla-AP + Zn + polyalanine
4hom – pAla-AP + Zn + substance P
4fkk – pAla-AP + Zn + bestatin
4f5c – pAla-AP + PRCV spike protein + Zn
4fyq - hAla-AP + Zn
4fyr - hAla-AP + Zn + bestatin
4fys - hAla-AP + Zn + angiotensin
4fyt - hAla-AP + Zn + amastatin
3ked – EcAPN+2,4-diaminobutyric acid – Escherichia coli
2hpo, 2dq6, 3puu – EcAPN
2hpt, 2dqm – EcAPN+bestatin
2zxg – EcAPN+transition state analog
3b2p, 3b2x, 3b34, 3b37, 3b3b, 3qjx – EcAPN+amino acid
2gtq – APN – Neisseria meningitides
Proline aminopeptidase
3ovk – Xaa Pro-AP – Streptococcus pyogenes
3il0 - Xaa Pro-AP – Streptococcus thermophilus
2v3x, 2v3y, 2v3z - Xaa EcPro-AP (mutant)+tripeptide
1w7v, 2bh3 - Xaa EcPro-AP+Zn+Mg+polypeptide
2bn7 - Xaa EcPro-AP+Zn+Mg+Mn+polypeptide
2bha, 2bhd - Xaa EcPro-AP+Mg+polypeptide
1a16 - Xaa EcPro-AP+Mn+polypeptide
1wbq, 2bhb - Xaa EcPro-AP+Zn+Mg
2bhc - Xaa EcPro-AP+Na+Mg
1wl6 - Xaa EcPro-AP+Mg
1wi9, 1m35, 1jaw - Xaa EcPro-AP+Mn
1wlr - Xaa EcPro-AP
2bws, 2bwt, 2bwu, 2bwv, 2bww, 2bwx, 2bwy - Xaa EcPro-AP (mutant)
1w2m - Xaa EcPro-AP+Ca
1n51 – Xaa EcPro-AP+apstatin
3ig4 - Xaa Pro-AP+ Mn – Bacillus anthracis
4fkc – Xaa Pro-AP + Cd – Thermococcus sibiricus
2zsg – X TmPro-AP – Thermatoga maritima
3ctz – X hPro-AP – human
1x2b, 1x2e, 1wm1 – SmPro-AP + inhibitor – Serratia marcescens
1qtr – SmPro-AP
1xqv – TaPro-AP (mutant) – Thermoplasma acidophilum
1xqw, 1xqx, 1xqy, 1xrl, 1xrm, 1xrn, 1xro, 1xrp, 1xrq, 1xrr – TaPro-AP+polypeptide
3azo – SmPro-AP – Streptomyces morookaensis
3azp - SmPro-AP (mutant)
3azq - SmPro-AP (mutant) + PGG
Leucine aminopeptidase
3jru – Leu-AP – Xanthomonas oryzae
2hc9, 2hb6 – Leu-AP – Caenorhabditis elegans
2ewb – bLeu-AP+zofenoprilat – bovine
1lam, 1lap – bLue-AP
1bpm, 1bpn – bLue-AP+Zn+Mg
1lan, 1lcp – bLue-AP+leucine derivative
1bll – bLue-AP+amastatin
2xdt, 2yd0 – hLeu-AP soluble domain
3mdj - hLeu-AP soluble domain + inhibitor
3h8e, 3h8f, 3h8g – Leu-AP – Pseudomonas putida
3kqx, 3kqz, 3kr4, 3kr5 – PfLeu-AP
3fh4, 1rtq, 2dea – VpLeu-AP – Vibrio proteolyticus
3b35, 3b3t, 3b3v, 2anp - VpLeu-AP (mutant)
3b3c, 3b3s, 3b3w - VpLeu-AP (mutant)+Leu derivative
3b7i - VpLeu-AP (mutant)+Leu
1ft7 - VpLeu-AP +Leu derivative
2nyq, 2iq6 – VpLeu-AP+polypeptide
1lok – VpLeu-AP+Tris
2prq – VpLeu-AP+Co
1xry, 1txr – VpLeu-AP+bestatin
1gyt – EcLeu-AP
3qnf – hLeu-AP 1
3t8w – PfLeu-AP + Zn + inhibitor – Plasmodium falciparum
3tc8 - PdLeu-AP + Zn
4fuu - Leu-AP + Zn – Bacterioides thetaiotaomicron
Methionine aminopeptidase
3mr1, 3mx6 – Met-AP+Mn – Rickettsia prowazekii
2dfi, 1xgm, 1xgn, 1xgo, 1xgs – PfMet-AP+Co – Pyrococcus furiosus
1wkm - PfMet-AP+Mn
3iu7 – MtMet-AP+Mn +A02 – Mycobacterium tuberculosis
3iu8, 3iu9 - MtMet-AP+Ni + inhibitor
1yj3, 3ror - MtMet-AP+Co
3pka - MtMet-AP+Mn
3pkb, 3pkc, 3pkd, 3pke - MtMet-AP+bengamide inhibitor
3tav – Met-AP + Mg – Mycobacterium abscessus< br />
1y1n - MtMet-AP+K
3fm3 – EncMet-AP – Encephalitozoon cuniculi
3fmq, 3fmr - EncMet-AP+angiogenesis inhibitor
3d27, 2q92, 2q93, 2q94, 2q95, 2q96, 2p98, 2p99, 2p9a, 2gu4, 2gu5, 2gu6, 2evc, 2evm, 2evo, 2bbv, 1xnz, 4a6v, 4a6w – EcMet-AP+Mn+inhibitor
2gg0, 2gg2, 2gg3, 2gg5, 2gg7, 2gg8, 2gg9, 2ggb, 2ggc - EcMet-AP+Co+inhibitor
1c21, 1c22, 1c23, 1c24 - EcMet-AP +Co + methionine derivative
1c27 - EcMet-AP +Co +norleucine
3tb5 – Met-AP – Enterococcus faecalis
2ea2, 2ea4, 2ga2, 2nq6, 2nq7, 1yw7, 1yw8, 1yw9 - hMet-AP+Mn+inhibitor
2gtx, 2gu7 – EcMet-AP
1yvm – EcMet-AP (mutant)+Co+thiabendazole
1mat – EcMet-AP+Co
2mat, 4mat - EcMet-AP (mutant)+Co
3mat - EcMet-AP (mutant)+Co+bestatin derivative
2b3h, 2b3k - hMet-AP+Co
1boa - hMet-AP+Co+ angiogenesis inhibitor
2b3l – hMet-AP
1kq0, 1kq9 – hMet-AP+methionine
2gz5, 2adu, 1qzy, 1b59, 1b6a, 1bn5 – hMet-AP+Co+inhibitor
1r58, 1r5g, 1r5h, 4fli, 4flj, 4flk, 4fll - hMet-AP+Mn+inhibitor
2g6p - hMet-AP truncated+Mn+inhibitor
1qxw, 1qxy, 1qxz – Met-AP+Co+inhibitor - Staphylococcus aureus
1o0x – TmMet-AP
3s6b – PfMet-AP + Fe
4fuk – Met-AP + Zn – Trypanosoma brucei
Aspartic acid aminopeptidase
3l6s, 4dyo – hAsp-AP+aspartic hydroxamate
3var, 3vat – bAsp-AP
4eme – PfAsp-AP + Zn
Asparagine aminopeptidase
3c17, 2zak – EcAsn-AP (mutant)
2zal – EcAsn-AP+Asp
2gez – Asn-AP – Lupinus luteus
Serine aminopeptidase
1b65 – Ser-AP – Ochrobactrum anthropi
Cytosolic aminopeptidase
3pei – Cyt-AP – Francisella tularensis
3kzw – Cyt-AP – Staphylococcus aureus
3ij3 – Cyt-AP – Coxiella burnetii
Aminopeptidase 2
Non-specific aminopeptidase
2ek8 – AnAP – Aneurinibacillus
2ek9 – AnAP+bestatin
1y0r, 1xfo – PhAP
1y0y – PhAP+amastatin
1amp - VpAP
1cp6, 1igb – VpAP+inhibitor
3t8v – PfAP M1
Cold-activated aminopeptidase
3cia – Col-AP – Colwellia psychrerythraea
Deblocking aminopeptidase
2gre – DAP – Bacillus cereus
Heat stable aminopeptidase
2ayi – AmpT – Thermus thermophilus
Aminopeptidase from Staphylococcus aureus
1zjc - AmpS
Metalloaminopeptidase
3q43, 3q44 – PfPFAP (mutant) + bestatin derivative
Stereomyces griesus aminopeptidase
1xjo, 1cp7 - SGAP
1qq9, 1f2o, 1f2p, 1tf8, 1tf9, 1tkf, 1tkh, 1tkj, 1xbu - SGAP + amino acid
β-peptidyl AP
3n2w – SxBapA – Sphingosinicella xenopeptidilytica
3n5i – SxBapA (mutant)
3n33 – SxBapA + AEBSF
3ndv, 3nfb – SxBapA + ampicillin
Additional Resources
For additional information, see:
Amino Acid Synthesis & Metabolism
Streptomyces griseus Aminopeptidase (SGAP)
References
- ↑ Hanaya K, Suetsugu M, Saijo S, Yamato I, Aoki S. Potent inhibition of dinuclear zinc(II) peptidase, an aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica, by 8-quinolinol derivatives: inhibitor design based on Zn(2+) fluorophores, kinetic, and X-ray crystallographic study. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2012 Feb 5. PMID:22311113 doi:10.1007/s00775-012-0873-4
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Eran Hodis