User:Michael Roberts/BIOL115 CaM
From Proteopedia
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| - | Click on the 'green links' in the text in the scrollable section below to examine this molecule in more detail.<StructureSection load='1cll' size=' | + | Click on the 'green links' in the text in the scrollable section below to examine this molecule in more detail.<StructureSection load='1cll' size='600' side='right' caption='Structure of Human calmodulin (PDB entry [[1cll]])' scene=''>Anything in this section will appear adjacent to the 3D structure and will be scrollable.</StructureSection> |
Let us color the two main forms of regular <scene name='Sandbox_LUBIOL115/Structure_plus_ca/1'>secondary structure</scene> in this protein. Alpha helix appears in red, beta sheet in yellow. | Let us color the two main forms of regular <scene name='Sandbox_LUBIOL115/Structure_plus_ca/1'>secondary structure</scene> in this protein. Alpha helix appears in red, beta sheet in yellow. | ||
Revision as of 23:38, 11 April 2013
Sequence and structure of EF hands
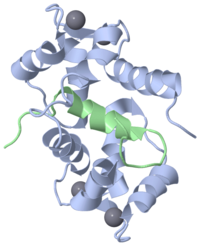
The EF hand motif is present in a many proteins and it commonly bestows the ability to bind Ca2+ ions. It was first identified in parvalbumin, a muscle protein. Here we will have a look at the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin, which possesses four EF hands. Calmodulin and its isoform, troponinC, are important intracellular Ca2+-binding proteins. The structure on the right, obtained by X-ray crystallography, represents the Ca2+-binding protein calmodulin. It has a dumbell-shaped structure with two identical lobes connected by a central alpha-helix. Each lobe comprises three a helices joined by loops. A helix-loop-helix motif forms the basis of each EF hand.
| |||||||||||
Let us color the two main forms of regular in this protein. Alpha helix appears in red, beta sheet in yellow.
Alpha Helices, Beta Strands , Turns.