6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='Journal:JBSD:27/Cv/1' caption=''> | ||
One of the '''[[CBI Molecules]]''' being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | One of the '''[[CBI Molecules]]''' being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org/ Molecular Playground]. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
In Nature, polyketides are synthesized by large multifunctional proteins called polyketide synthases (PKSs).. Among several characterized PKSs, the biosynthesis of the polyketide Core of erythromycin A, 6-deoxyerythronolide B (6-dEB), has provided the paradigm for understanding the structure and function of the PKSs that are responsible for assembling complex polyketides . | In Nature, polyketides are synthesized by large multifunctional proteins called polyketide synthases (PKSs).. Among several characterized PKSs, the biosynthesis of the polyketide Core of erythromycin A, 6-deoxyerythronolide B (6-dEB), has provided the paradigm for understanding the structure and function of the PKSs that are responsible for assembling complex polyketides . | ||
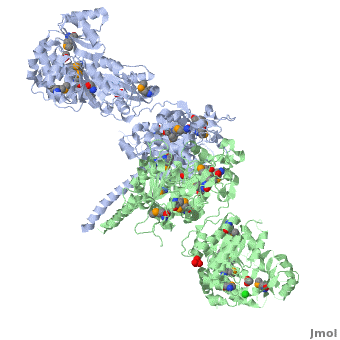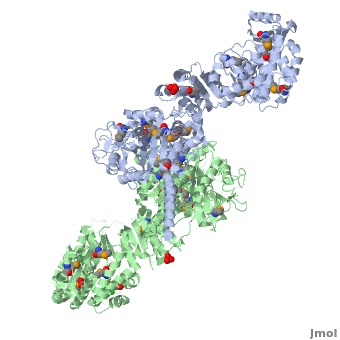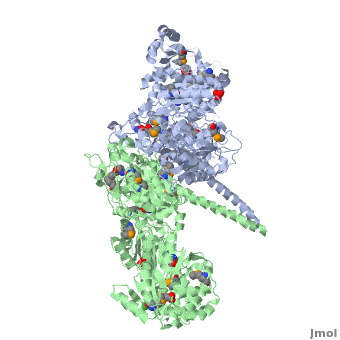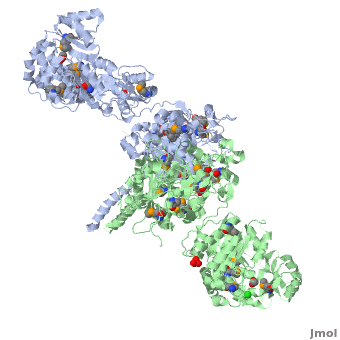
| - | [[Image:DEBS.png| | + | [[Image:DEBS.png|left|300px|thumb|6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)]] |
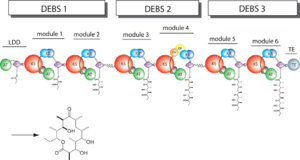
The 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS), which catalyzes the formation of 6-dEB, consists of three large subunits, DEBS1, DEBS2 and DEBS3, each containing two modules and above 300 kD in size. There are 2 domains in the N-terminal loading module, responsible for priming the synthase with a proprionate starter unit, and 26 domains in the six extender modules, Each extender module contains at least three essential domains: a ketosynthase (KS), an acyl transferase (AT) and an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In detail, the AT domain selects the appropriate carbon extender unit and transfers the units from acyl-CoA onto the phosphopantetheine arm of ACP. The KSdomain accepts the polyketide chain from the previous module and catalyzes chain elongation reaction by adding an ACP-bound extender unit through decarboxylative condensation. | The 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS), which catalyzes the formation of 6-dEB, consists of three large subunits, DEBS1, DEBS2 and DEBS3, each containing two modules and above 300 kD in size. There are 2 domains in the N-terminal loading module, responsible for priming the synthase with a proprionate starter unit, and 26 domains in the six extender modules, Each extender module contains at least three essential domains: a ketosynthase (KS), an acyl transferase (AT) and an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In detail, the AT domain selects the appropriate carbon extender unit and transfers the units from acyl-CoA onto the phosphopantetheine arm of ACP. The KSdomain accepts the polyketide chain from the previous module and catalyzes chain elongation reaction by adding an ACP-bound extender unit through decarboxylative condensation. | ||
Revision as of 12:05, 1 May 2013
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Tsung-Yi Lin, Alexander Berchansky, Lawrence Sheringham Borketey, Joel L. Sussman, Jon Amoroso, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky