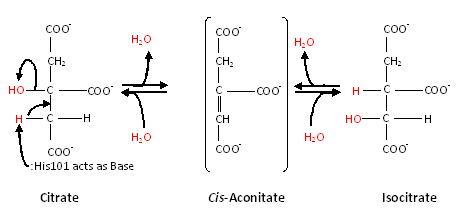
Aconitase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
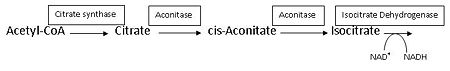
The Citric Acid Cycle works in such a way that the product of one reaction becomes the reactant of another, with different enzymes catalyzing each reaction. Aconitase is one such enzyme. Some of these enzymes are tightly regulated, either activated or inhibited, by the concentration of reactant, product, ATP or NADH, and thus are rate-determining. Aconitase is not one of the three rate-determining enzymes of the Citric Acid Cycle as its ΔG is not negative (ΔG°′≈5 kJ/mol and ΔG≈0 kJ/mol).<ref name="Voet" /> Aconitase functions close to equilibrium and the rate of citrate consumption depends on the activity of NAD<sup>+</sup>-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase, which is one of the three rate-determining enyzmes. Isocitrate dehydrogenase uses the product of the reaction aconitase catalyzes. Both Citrate synthase and Isocitrate dehydogenase are inhibited by NADH concentration, but aconitase itself is not.<ref name="Voet" /> Since the rate of aconitase depends on the activity of NAD<sup>+</sup>-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase, then citrate could build up on the reactant side, which would then inhibit the enzyme of the previous step, citrate synthase. An illustration of this is seen below, with the boxes representing the enzymes that are catalyzing each reaction. This is a common example of how the Citric Acid Cycle works in order to produce ATP without wasting resources. Similar inhibition/activation of enzymes occurs based on concentrations of ATP, NADH, Calcium, CoA, and others. | The Citric Acid Cycle works in such a way that the product of one reaction becomes the reactant of another, with different enzymes catalyzing each reaction. Aconitase is one such enzyme. Some of these enzymes are tightly regulated, either activated or inhibited, by the concentration of reactant, product, ATP or NADH, and thus are rate-determining. Aconitase is not one of the three rate-determining enzymes of the Citric Acid Cycle as its ΔG is not negative (ΔG°′≈5 kJ/mol and ΔG≈0 kJ/mol).<ref name="Voet" /> Aconitase functions close to equilibrium and the rate of citrate consumption depends on the activity of NAD<sup>+</sup>-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase, which is one of the three rate-determining enyzmes. Isocitrate dehydrogenase uses the product of the reaction aconitase catalyzes. Both Citrate synthase and Isocitrate dehydogenase are inhibited by NADH concentration, but aconitase itself is not.<ref name="Voet" /> Since the rate of aconitase depends on the activity of NAD<sup>+</sup>-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase, then citrate could build up on the reactant side, which would then inhibit the enzyme of the previous step, citrate synthase. An illustration of this is seen below, with the boxes representing the enzymes that are catalyzing each reaction. This is a common example of how the Citric Acid Cycle works in order to produce ATP without wasting resources. Similar inhibition/activation of enzymes occurs based on concentrations of ATP, NADH, Calcium, CoA, and others. | ||
| - | [[ Image:Regulation.JPG]] | + | [[Image:Regulation.JPG|left|450px|thumb]] |
== Cytosolic aconitase and its other function == | == Cytosolic aconitase and its other function == | ||
| - | + | A specialty of cAc is that in mammals it has developed a <scene name='Aconitase/2ipy-total/2'>second function</scene> as inhibitor of <scene name='Aconitase/2ipy-rna/1'>those mRNA</scene> that carry an <scene name='Aconitase/2ipy-rna-ire/1'>iron-responsive element (IRE)</scene>. Therefore, the cytosolic cAc is named IREBP for IRE-binding protein when this function is talked about. Only one of the two functions is active, depending on whether <scene name='Aconitase/2b3x-cluster/1'>the (4Fe-4S) cofactor</scene> is present in the molecule: it's essential for <scene name='Aconitase/2b3x-total/1'>the ACO function</scene>. You can see, by <scene name='Aconitase/Morph/2'>looking at the morph</scene>, how much the enzyme structure differs between those two functions. | |
Along with serving as a catalyst, aconitase is a member of the iron regulatory protien-1 (IRP-1) family. These enzymes have been found to play a role in regulatory RNA-binding proteins. This suggests a novel role for Fe-S clusters as post-translational regulatory switches.<ref name="Frishman" /> | Along with serving as a catalyst, aconitase is a member of the iron regulatory protien-1 (IRP-1) family. These enzymes have been found to play a role in regulatory RNA-binding proteins. This suggests a novel role for Fe-S clusters as post-translational regulatory switches.<ref name="Frishman" /> | ||
Revision as of 11:29, 16 October 2013
| |||||||||||
Updated on 16-October-2013
ACO
1b0k – pACO (mutant) – pig
5acn – pACO+Fe3S4
6acn - pACO+Fe4S4
1amj, 1nit – cACO - cow
ACO+citrate
1c96 - pACO (mutant)+citrate
1b0m - pACO (mutant)+fluorocitrate
ACO+aconitate
1fgh – cACO+4-hydroxy-aconitate
1aco – cACO+transaconitate
1nis - cACO+transaconitate+nitrocitrate
ACO+isocitrate
7acn - pACO +isocitrate
1c97, 1b0j - pACO (mutant)+isocitrate
1ami, 8acn – cACO+isocitrate
ACO1
2b3x, 2b3y – hACO1 – human
2ipy, 3snp – rACO1 (mutant)+ferritin H IRE-RNA – rabbit
ACO2
1l5j – ACO2 – Escherichia coli
Literature
- M. Claire Kennedy and Helmut Beinert: IX.4. Aconitase. in Ivano Bertini, Harry B. Gray, Edward I. Stiefel, Joan Selverstone Valentine (eds.): Biological Inorganic Chemistry: Structure and Reactivity. University Science Books, Herndon 2006. ISBN 1891389432 pp.209--
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Zheng L, Kennedy MC, Beinert H, Zalkin H. Mutational analysis of active site residues in pig heart aconitase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7895-903. PMID:1313811
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Frishman D, Hentze MW. Conservation of aconitase residues revealed by multiple sequence analysis. Implications for structure/function relationships. Eur J Biochem. 1996 Jul 1;239(1):197-200. PMID:8706708
- ↑ Dupuy J, Volbeda A, Carpentier P, Darnault C, Moulis JM, Fontecilla-Camps JC. Crystal structure of human iron regulatory protein 1 as cytosolic aconitase. Structure. 2006 Jan;14(1):129-39. PMID:16407072 doi:10.1016/j.str.2005.09.009
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Beinert, H., Kennedy, M. C., Stout, C.D. “Aconitase as Iron−Sulfur Protein, Enzyme, and Iron-Regulatory Protein.” Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2335−2373.
- ↑ Lauble H, Kennedy MC, Beinert H, Stout CD. Crystal structures of aconitase with trans-aconitate and nitrocitrate bound. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 8;237(4):437-51. PMID:8151704 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1246
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at the Molecular Level. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. p. 578-579. Print.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Flint, DH., and Allen, RM. "Iron-sulfur protein with nonredox functions.” Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2315−2334.
External links
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Ralf Stephan, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky, Anthony Noles, Angel Herraez, Eran Hodis