Telomerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
'''Overall Structure''' | '''Overall Structure''' | ||
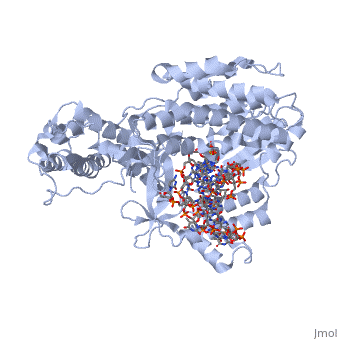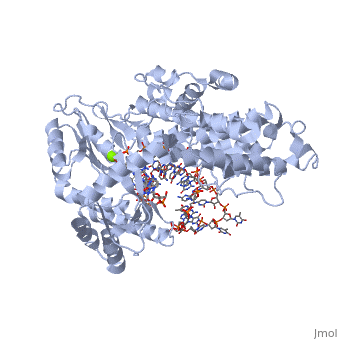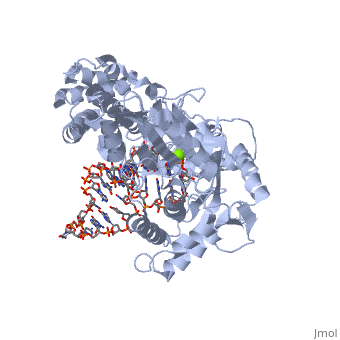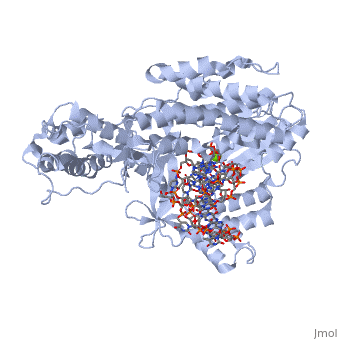
| - | <scene name='60/602706/Telomerase/1'>Telomerase</scene> (protein in blue; RNA in green; DNA in red) acts as both a monomer and dimer. The monomer refers to the overall protein and its catalytic subunit TERT, made up of an amino acid polymer, containing approximately 5,000 atoms. This protein binds with the RNA template, <scene name='60/602706/Ter/1'>TER</scene>, that TERT uses to add DNA to form a dimer-like structure (4). The RNA has a molecular size between 200 and 500 kDA, depending on the organism <ref name='complex'>. Both the protein and RNA components are highly conserved structures among phylogenetic groups. <scene name='60/602706/Tert/2'>TERT</scene> is organized into a ring-like structure that shares common features with other reverse transcriptases (in viruses for example) and DNA polymerases. The RNA-DNA heteroduplex lies in the interior of the ring and positions the 3' end of the DNA primer at the active site to the telomerse can be enlongated. The substrate binding within the ring can accomodate 7 to 8 bases of double-stranded nucleic acid (4). | + | <scene name='60/602706/Telomerase/1'>Telomerase</scene> (protein in blue; RNA in green; DNA in red) acts as both a monomer and dimer. The monomer refers to the overall protein and its catalytic subunit TERT, made up of an amino acid polymer, containing approximately 5,000 atoms. This protein binds with the RNA template, <scene name='60/602706/Ter/1'>TER</scene>, that TERT uses to add DNA to form a dimer-like structure (4). The RNA has a molecular size between 200 and 500 kDA, depending on the organism <ref name='complex'/>. Both the protein and RNA components are highly conserved structures among phylogenetic groups. <scene name='60/602706/Tert/2'>TERT</scene> is organized into a ring-like structure that shares common features with other reverse transcriptases (in viruses for example) and DNA polymerases. The RNA-DNA heteroduplex lies in the interior of the ring and positions the 3' end of the DNA primer at the active site to the telomerse can be enlongated. The substrate binding within the ring can accomodate 7 to 8 bases of double-stranded nucleic acid (4). |
'''Architecture of TERT Structure''' | '''Architecture of TERT Structure''' | ||
| - | <scene name='60/602706/Tert_catalytic_subunit/1'>TERT catalytic subunit</scene> contains 3 domains: reverse transcriptase domain (in green), and carboxy-terminal extension (CTE)(in blue), RNA binding domain (TRBD)(in red). Similar to its structural homologs, as noted above, the ring contains fingers, palm, and thumb sections (4). The reverse transcriptase domain represents the fingers and palm. It consists of a mixture of alpha helices and beta strands The TRBD domain is a helical structure that binds double and single stranded RNA, and is essential for RNP assembly and repeat addition processivity <ref name='RNP'>doi | + | <scene name='60/602706/Tert_catalytic_subunit/1'>TERT catalytic subunit</scene> contains 3 domains: reverse transcriptase domain (in green), and carboxy-terminal extension (CTE)(in blue), RNA binding domain (TRBD)(in red). Similar to its structural homologs, as noted above, the ring contains fingers, palm, and thumb sections (4). The reverse transcriptase domain represents the fingers and palm. It consists of a mixture of alpha helices and beta strands The TRBD domain is a helical structure that binds double and single stranded RNA, and is essential for RNP assembly and repeat addition processivity <ref name='RNP'>doi 10.1038/nsmb.1777</ref>. This fingers and palm is one of the most conserved portions across similar phylogeny. The thumb corresponds to the CTE, which is an elongated helical bundle that contains several surface-exposed long loops. Lastly, the TRBD is a helical structure that binds double and single stranded RNA. CTE and TRBD, the two terminal ends of the protein come together to form the ring-like structure <ref name='RNP'/>. |
== Active Site Chemistry == | == Active Site Chemistry == | ||
Revision as of 09:00, 6 November 2014
| |||||||||||