Lotem haleva/test page
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==structure | + | ==structure== |
<StructureSection load='1y3v' size='340' side='right' caption='Trysine' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1y3v' size='340' side='right' caption='Trysine' scene=''> | ||
| - | This is a default text for your page '''Lotem haleva/test page'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
Trypsin is a serine protease, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyses proteins<ref>doi:10.1016/0076-6879(94)44004-2</ref>. | Trypsin is a serine protease, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyses proteins<ref>doi:10.1016/0076-6879(94)44004-2</ref>. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 8: | ||
The process is commonly referred to as trypsin proteolysis or trypsinisation, | The process is commonly referred to as trypsin proteolysis or trypsinisation, | ||
and proteins that have been digested/treated with trypsin are said to have been trypsinized. | and proteins that have been digested/treated with trypsin are said to have been trypsinized. | ||
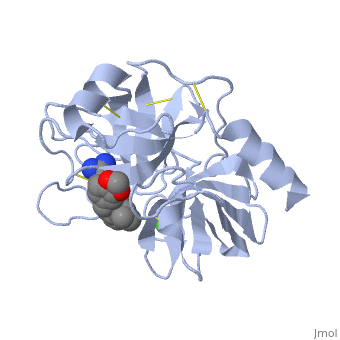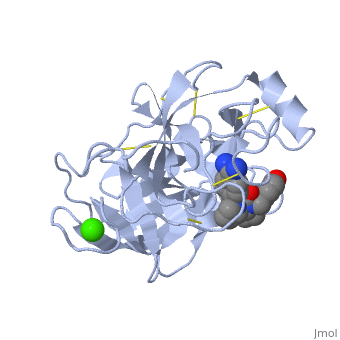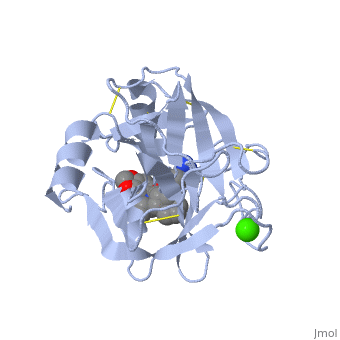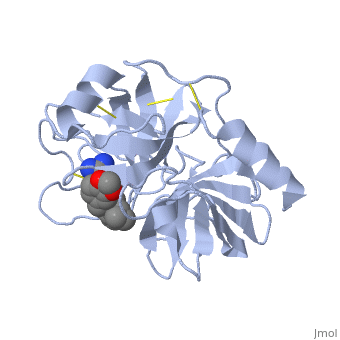
| - | + | Trypsin contains <scene name='60/607865/Helix/1'>alpha helix</scene> and <scene name='60/607865/Sheets/1'>beta sheets</scene>. | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
In the duodenum, trypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, breaking down proteins into smaller peptides. | In the duodenum, trypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, breaking down proteins into smaller peptides. | ||
| - | + | ||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| - | The enzymatic mechanism is similar to that of other serine proteases. These enzymes contain a catalytic triad consisting of <scene name='60/607865/Active_site/2'>histidine-57, aspartate-102, and serine-195</scene>. These three residues form a charge relay that serves to make the active site serine nucleophilic. | + | The enzymatic mechanism is similar to that of other serine proteases. These enzymes contain a catalytic triad consisting of <scene name='60/607865/Active_site/2'>histidine-57, aspartate-102, and serine-195</scene>. These three residues form a charge relay that serves to make the active site serine nucleophilic <ref>doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5160-x</ref>. |
Trypsin contains an "oxyanion hole" formed by the backbone amide hydrogen atoms of <scene name='60/607865/Oxyanion_hole/1'>Gly-193 and Ser-195</scene> , which serves to stabilize the developing negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen atom of the cleaved amides. | Trypsin contains an "oxyanion hole" formed by the backbone amide hydrogen atoms of <scene name='60/607865/Oxyanion_hole/1'>Gly-193 and Ser-195</scene> , which serves to stabilize the developing negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen atom of the cleaved amides. | ||
Revision as of 10:29, 23 November 2014
structure
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ. Families of serine peptidases. Methods Enzymol. 1994;244:19-61. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)44004-2. PMID:7845208 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(94)44004-2
- ↑ Polgar L. The catalytic triad of serine peptidases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Oct;62(19-20):2161-72. PMID:16003488 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5160-x