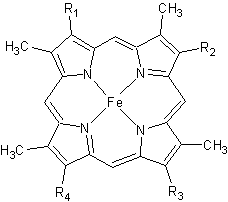
Cytochrome c
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
**[[3nwv]], [[3zoo]] – hCyt (mutant) – human<BR /> | **[[3nwv]], [[3zoo]] – hCyt (mutant) – human<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[3zcf]] – hCyt<br /> | ||
**[[1j3s]] – hCyt - NMR<BR /> | **[[1j3s]] – hCyt - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3nbs]], [[3nbt]], [[1crc]], [[1hrc]], [[3o1y]], [[3o20]], [[3wc8]] – hoCyt – horse<BR /> | + | **[[3nbs]], [[3nbt]], [[1crc]], [[1hrc]], [[3o1y]], [[3o20]], [[3wc8]], [[3wui]], [[4rsz]] – hoCyt – horse<BR /> |
**[[1lc1]], [[1lc2]], [[1m60]], [[1giw]], [[2giw]], [[1akk]], [[2frc]], [[1ocd]] – hoCyt – NMR<BR /> | **[[1lc1]], [[1lc2]], [[1m60]], [[1giw]], [[2giw]], [[1akk]], [[2frc]], [[1ocd]] – hoCyt – NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[1fi9]], [[1fi7]] - hoCyt + imidazole – NMR<BR /> | **[[1fi9]], [[1fi7]] - hoCyt + imidazole – NMR<BR /> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 78: | ||
**[[1rap]], [[1raq]], [[1ycc]]- yCyt iso-1<BR /> | **[[1rap]], [[1raq]], [[1ycc]]- yCyt iso-1<BR /> | ||
**[[1yic]] – yCyt iso-1 – NMR<BR /> | **[[1yic]] – yCyt iso-1 – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1irv]], [[1irw]], [[1lms]] – yCyt iso-1 (mutant) <BR /> | + | **[[1irv]], [[1irw]], [[1lms]], [[4mu8]], [[4n0k]] – yCyt iso-1 (mutant) <BR /> |
| - | **[[2hv4]], [[2lir]], [[2lit]] - yCyt iso-1 (mutant) - NMR<br /> | + | **[[2hv4]], [[2lir]], [[2lit]], [[2mhm]] - yCyt iso-1 (mutant) - NMR<br /> |
**[[1fhb]] - yCyt iso-1 (mutant) + CN - NMR<BR /> | **[[1fhb]] - yCyt iso-1 (mutant) + CN - NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[1nmi]] – yCyt iso-1 + imidazole<BR /> | **[[1nmi]] – yCyt iso-1 + imidazole<BR /> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 112: | ||
**[[2xl6]], [[2xld]], [[2xle]], [[2xlo]], [[2xlv]], [[2xlw]] – AxCyt (mutant) + NO – ''Achromobacter xylosoxidans''<BR /> | **[[2xl6]], [[2xld]], [[2xle]], [[2xlo]], [[2xlv]], [[2xlw]] – AxCyt (mutant) + NO – ''Achromobacter xylosoxidans''<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1cgn]], [[1cgo]], [[2ykz]], [[3zqv]], [[ | + | **[[1cgn]], [[1cgo]], [[2ykz]], [[3zqv]], [[2yli]], [[4cda]], [[4cdv]], [[4cdy]], [[4cip]], [[4cjo]], [[4wgy]], [[4wgz]] - AxCyt<BR /> |
**[[2xm0]], [[2xm4]], [[2xl8]], [[2xlh]], [[2yl0]], [[2yl7]], [[3ztm]] - AxCyt (mutant) <BR /> | **[[2xm0]], [[2xm4]], [[2xl8]], [[2xlh]], [[2yl0]], [[2yl7]], [[3ztm]] - AxCyt (mutant) <BR /> | ||
**[[2yl1]], [[2yl3]], [[2ylg]], [[3zqy]], [[3ztz]] - AxCyt (mutant) + CO<br /> | **[[2yl1]], [[2yl3]], [[2ylg]], [[3zqy]], [[3ztz]] - AxCyt (mutant) + CO<br /> | ||
**[[2yld]], [[3zwi]] - AxCyt + CO<br /> | **[[2yld]], [[3zwi]] - AxCyt + CO<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xlm]] - AxCyt + NO<BR /> | + | **[[2xlm]], [[4cjg]] - AxCyt + NO<BR /> |
**[[2j9b]], [[2j8w]] – Cyt – ''Rubrivivax gelatinosus''<BR /> | **[[2j9b]], [[2j8w]] – Cyt – ''Rubrivivax gelatinosus''<BR /> | ||
**[[1gqa]] – RsCyt<BR /> | **[[1gqa]] – RsCyt<BR /> | ||
| Line 278: | Line 279: | ||
**[[2w9k]], [[2yk3]] – Cyt – ''Crithidia fasciculate''<br /> | **[[2w9k]], [[2yk3]] – Cyt – ''Crithidia fasciculate''<br /> | ||
**[[4j20]] – CtCyt (mutant)<br /> | **[[4j20]] – CtCyt (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Cytochrome C557 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1foc]] – TtCyt – ''Thermus thermophilus''<br /> | ||
*Cytochrome C556 | *Cytochrome C556 | ||
Revision as of 07:44, 19 March 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of cytochrome C
Updated on 19-March-2015
References
- ↑ Gough J, Karplus K, Hughey R, Chothia C. Assignment of homology to genome sequences using a library of hidden Markov models that represent all proteins of known structure. J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 2;313(4):903-19. PMID:11697912 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5080
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 Stelter M, Melo AM, Pereira MM, Gomes CM, Hreggvidsson GO, Hjorleifsdottir S, Saraiva LM, Teixeira M, Archer M. A Novel Type of Monoheme Cytochrome c: Biochemical and Structural Characterization at 1.23 A Resolution of Rhodothermus marinus Cytochrome c. Biochemistry. 2008 Oct 15. PMID:18855424 doi:10.1021/bi800999g
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Reedy CJ, Gibney BR. Heme protein assemblies. Chem Rev. 2004 Feb;104(2):617-49. PMID:14871137 doi:10.1021/cr0206115
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ambler RP. Sequence variability in bacterial cytochromes c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 23;1058(1):42-7. PMID:1646017
- ↑ Cookson DJ, Moore GR, Pitt RC, Williams RJP, Campbell ID, Ambler RP, Bruschi M, Le Gall J. Structural homology of cytochromes c. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(1):261-75.
- ↑ Than ME, Hof P, Huber R, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Buse G, Soulimane T. Thermus thermophilus cytochrome-c552: A new highly thermostable cytochrome-c structure obtained by MAD phasing. J Mol Biol. 1997 Aug 29;271(4):629-44. PMID:9281430 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1181
- ↑ Soares CM, Baptista AM, Pereira MM, Teixeira M. Investigation of protonatable residues in Rhodothermus marinus caa3 haem-copper oxygen reductase: comparison with Paracoccus denitrificans aa3 haem-copper oxygen reductase. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2004 Mar;9(2):124-34. Epub 2003 Dec 23. PMID:14691678 doi:10.1007/s00775-003-0509-9
- ↑ Pereira MM, Santana M, Teixeira M. A novel scenario for the evolution of haem-copper oxygen reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Jun 1;1505(2-3):185-208. PMID:11334784
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Karp, Gerald (2008). Cell and Molecular Biology (5th edition). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0470042175.
- ↑ Rajagopal BS, Wilson MT, Bendall DS, Howe CJ, Worrall JA. Structural and kinetic studies of imidazole binding to two members of the cytochrome c (6) family reveal an important role for a conserved heme pocket residue. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011 Jan 26. PMID:21267610 doi:10.1007/s00775-011-0758-y
- ↑ Morelli X, Czjzek M, Hatchikian CE, Bornet O, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Palma NP, Moura JJ, Guerlesquin F. Structural model of the Fe-hydrogenase/cytochrome c553 complex combining transverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy experiments and soft docking calculations. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 28;275(30):23204-10. PMID:10748163 doi:10.1074/jbc.M909835199
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Melissa Morrison, Adis Hasic