Elizeu/sandbox/citocromo c
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | == | + | == Example page for Green fluorescent protein ("GFP") == |
| + | <StructureSection load='1ema' size='300' frame='true' side='right' caption='GFP ([[1ema]])' scene=''> | ||
| + | [[Image:1ema.gif|thumb|left|450px|Green fluorescent protein (1ema)]] | ||
| + | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| - | <Structure load='1hho_mm1.pdb' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='OxyHb' /> | ||
| - | + | Green fluorescent protein ('''GFP'''), originally isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria (PDB entry [[1ema]]), fluorsceses green (509nm) when exposed to blue light (395nm and 475nm). It is one of the most important proteins used in biological research because it can be used to tag otherwise invisible gene products of interest and thus observe their existence, location and movement. | |
== Exploring the Structure == | == Exploring the Structure == | ||
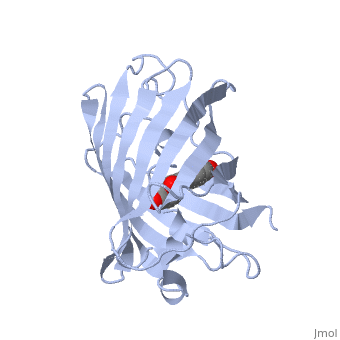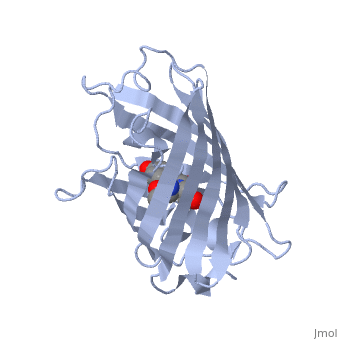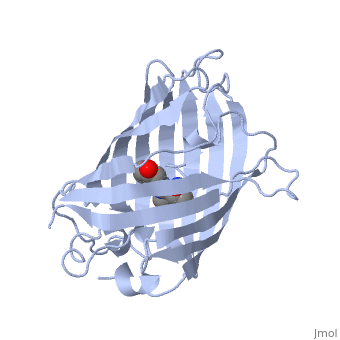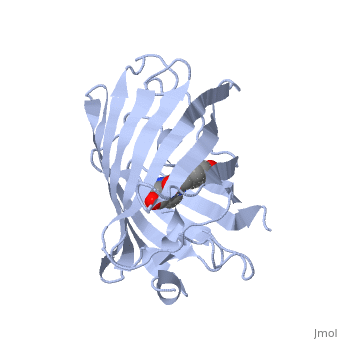
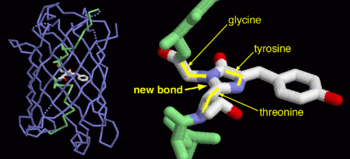
| - | + | GFP is a beta barrel protein with 11 beta sheets. It is a 26.9kDa protein made up of 238 amino acids. The | |
| - | + | <scene name='Sandbox_4/Green_fp/1'>chromophore</scene>, responsible for the fluorescent properties of the protein, is buried inside the beta barrel as part of the central alpha helix passing through the barrel. The chromophore forms via spontaneous cyclization and oxidation of three residues in the central alpha helix: -Thr65 (or Ser65)-Tyr66-Gly67. This cyclization and oxidation creates the chromophore's five-membered ring via a new bond between the threonine and the glycine residues.<ref>PMID:8703075</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ==References== | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
Revision as of 07:31, 17 April 2015
Example page for Green fluorescent protein ("GFP")
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ormo M, Cubitt AB, Kallio K, Gross LA, Tsien RY, Remington SJ. Crystal structure of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein. Science. 1996 Sep 6;273(5280):1392-5. PMID:8703075
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Julie Langlois, Atena Farhangian, Rebecca Holstein, Elizabeth A. Dunlap, Katherine Reynolds, Elizeu Santos, Noam Gonen, Anna Lohning, Idan Ben-Nachum, Brian Ochoa, Shai Biran, Gauri Misra, Shira Weingarten-Gabbay, Keni Vidilaseris, Jamie Costa, Abhinav Mittal, Urs Leisinger, Madison Walberry, Edmond R Atalla, Brett M. Thumm, Brooke Fenn, Joel L. Sussman, Mati Cohen, Vesta Nwankwo, Dotan Shaniv, Gulalai Shah