Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='1dks' size='340' side='right' caption='Human CKS 1 (PDB code 1dks)' scene=''> <StructureSection load='4yc6' size='340' side='left' caption='Human CKS 1 complex...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
<StructureSection load='1dks' size='340' side='right' caption='Human CKS 1 (PDB code [[1dks]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1dks' size='340' side='right' caption='Human CKS 1 (PDB code [[1dks]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | ||
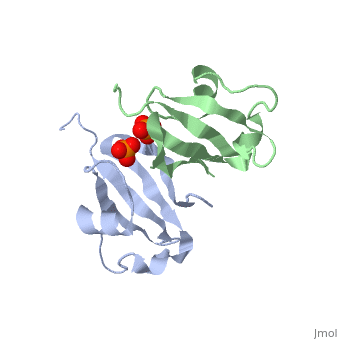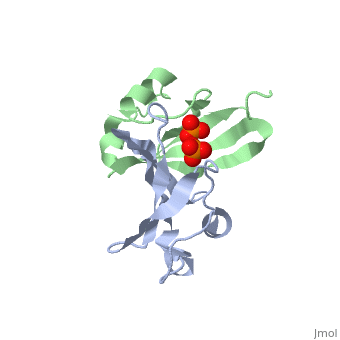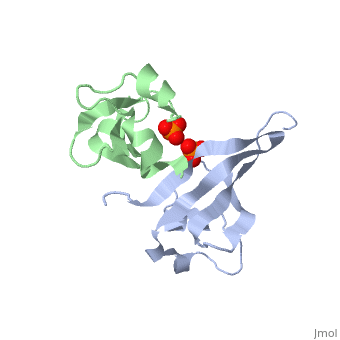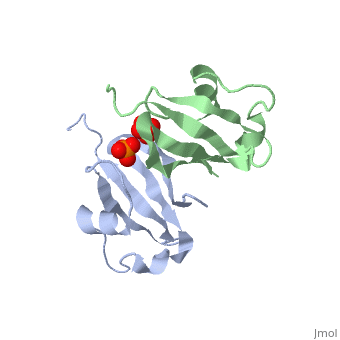
'''Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit''' (CKS) is a small protein which is essential for the functioning of CDK-cyclin complex. CKS binds to the catalytic subunit of CDK see complex structure in the figure at top left. CKS1 is essential for CDK5 functioning in neuronal diferentiation. CKS exists as hexamer of homodimers and can bind six kinase molecules. | '''Cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit''' (CKS) is a small protein which is essential for the functioning of CDK-cyclin complex. CKS binds to the catalytic subunit of CDK see complex structure in the figure at top left. CKS1 is essential for CDK5 functioning in neuronal diferentiation. CKS exists as hexamer of homodimers and can bind six kinase molecules. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 06:36, 12 October 2015
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit
Updated on 12-October-2015 {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0|
- CKS
- CKS complexes
}