Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
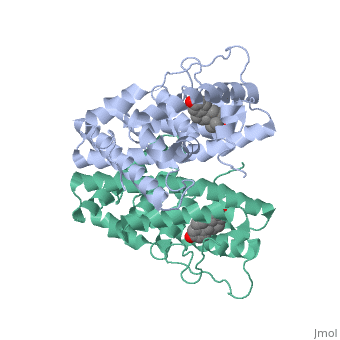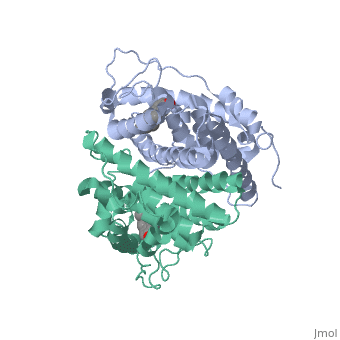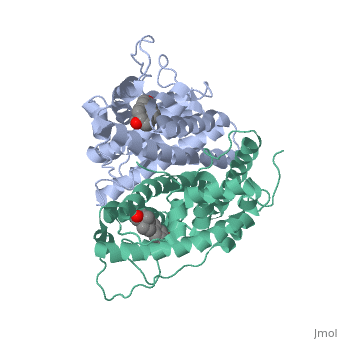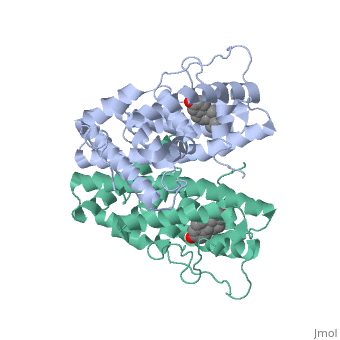
| - | ER is a modular protein composed of a ligand binding domain, a DNA binding domain and the N terminal transactivation domain. ER is a DNA-binding transcription factor. <scene name='71/714947/Er_bound_to_dna_dnadomain/1'>ER bound to DNA with one DNA binding helix highlighted yellow </scene> The | + | ER is a modular protein composed of a ligand binding domain, a DNA binding domain and the N terminal transactivation domain. ER is a DNA-binding transcription factor. <scene name='71/714947/Er_bound_to_dna_dnadomain/1'>ER bound to DNA with one DNA binding helix highlighted yellow </scene> The DNA binding domain can be clearly observed in this scene with the highlighted helix. Unbound ER normally exists loosly around the nucleus; this is subject to change depending on a multitude of factors including cell type, progress through cell cycle and reception of cellular signals. When estrogen enters the cell and binds ER, ER will trans-locates and undergoes a conformation shift.<ref> Beato, M., Chavez, S., and Truss, M. (1996). Transcriptional regulation by steroid hormones. Steroids 61: 240–251. </ref> Ligand bound estrogen receptor associates more tightly with the nucleus. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| Line 31: | Line 28: | ||
| - | ER is functional as a ligand-dependent transcription factor. <ref> Wang C, Fu M, Angeletti RH, Siconolfi-Baez L, Reutens AT, Albanese C, Lisanti MP, Katzenellenbogen BS, Kato S, Hopp T, Fuqua SA, Lopez GN, Kushner PJ, Pestell RG (25 May 2001)."Direct acetylation of the estrogen receptor alpha hinge region by p300 regulates transactivation and hormone sensitivity.". J Biol Chem. 276 (21): 18375–83. </ref> ER responds to both agonist and antagonist ligands and can associate with the nuclear matrix. The location of the receptor bound and unbound to ligand varies amongst different cell types. In general, an antagonist ligand will cause partial accumulation in the cytoplasm of a cell. The agonist ligand causes the translocation to the nucleus described above. | + | ER is functional as a ligand-dependent transcription factor. <ref> Wang C, Fu M, Angeletti RH, Siconolfi-Baez L, Reutens AT, Albanese C, Lisanti MP, Katzenellenbogen BS, Kato S, Hopp T, Fuqua SA, Lopez GN, Kushner PJ, Pestell RG (25 May 2001)."Direct acetylation of the estrogen receptor alpha hinge region by p300 regulates transactivation and hormone sensitivity.". J Biol Chem. 276 (21): 18375–83. </ref> ER responds to both agonist and antagonist ligands and can associate with the nuclear matrix. Differences in the structure of the receptor may be observed through comparisons of ER bound to agonist and antagonist liggnds. <scene name='71/714947/Agonist_estradiol_bound_er/2'>Agonist_estradiol_bound_er</scene>The specific conformation of this tight loop creates part of the activation signal that will stimulate normal growth, as estradiol is a normal ligand for ER.The location of the receptor bound and unbound to ligand varies amongst different cell types. In general, an antagonist ligand will cause partial accumulation in the cytoplasm of a cell. The agonist ligand causes the translocation to the nucleus described above. |
A group bound GFP to ER and studied the location of GFP-ER upon binding of agonists and antagonist ligands. <ref> Htun H, Holth LT, Walker D, Davie JR, Hager GL (1 February 1999). "Direct visualization of the human estrogen receptor alpha reveals a role for ligand in the nuclear distribution of the receptor". Mol Biol Cell 10 (2): 471–86. </ref> GFP-ER activates the reporter gene in a dose-dependent manner and shows additional activation in the presence of agonist ligand 17-bestradiol. ICI 182780, a pure antagonist for ER, completely inhibited GFP-ER activation of the reporter gene. | A group bound GFP to ER and studied the location of GFP-ER upon binding of agonists and antagonist ligands. <ref> Htun H, Holth LT, Walker D, Davie JR, Hager GL (1 February 1999). "Direct visualization of the human estrogen receptor alpha reveals a role for ligand in the nuclear distribution of the receptor". Mol Biol Cell 10 (2): 471–86. </ref> GFP-ER activates the reporter gene in a dose-dependent manner and shows additional activation in the presence of agonist ligand 17-bestradiol. ICI 182780, a pure antagonist for ER, completely inhibited GFP-ER activation of the reporter gene. | ||
The group found that in the absence of ligand, the unoccupied ER is loosely associated with the nucleus. | The group found that in the absence of ligand, the unoccupied ER is loosely associated with the nucleus. | ||
Revision as of 02:27, 27 October 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Beato, M., Chavez, S., and Truss, M. (1996). Transcriptional regulation by steroid hormones. Steroids 61: 240–251.
- ↑ Wang C, Fu M, Angeletti RH, Siconolfi-Baez L, Reutens AT, Albanese C, Lisanti MP, Katzenellenbogen BS, Kato S, Hopp T, Fuqua SA, Lopez GN, Kushner PJ, Pestell RG (25 May 2001)."Direct acetylation of the estrogen receptor alpha hinge region by p300 regulates transactivation and hormone sensitivity.". J Biol Chem. 276 (21): 18375–83.
- ↑ Htun H, Holth LT, Walker D, Davie JR, Hager GL (1 February 1999). "Direct visualization of the human estrogen receptor alpha reveals a role for ligand in the nuclear distribution of the receptor". Mol Biol Cell 10 (2): 471–86.