Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Before ER binds its hormone the receptor is part of a complex that has many chaperones that maintain the receptor in a steroid binding configuration. Post hormone binding the receptor dissociates from its original complex and binds to hormone responsive elements in chromatin. Gene expression is then regulated by interaction of DNA bound receptors with sequence specific transcription factors and general transcription factors which are mediated by co-activators and co-repressors. The arrangement of cis regulatory elements in a specific promoter or enhancer region and the current state of DNA sequences in nucleosomes determines the system of receptor interactions. Contingent upon the interactions occurring, the result may be induction or repression of transcription. | Before ER binds its hormone the receptor is part of a complex that has many chaperones that maintain the receptor in a steroid binding configuration. Post hormone binding the receptor dissociates from its original complex and binds to hormone responsive elements in chromatin. Gene expression is then regulated by interaction of DNA bound receptors with sequence specific transcription factors and general transcription factors which are mediated by co-activators and co-repressors. The arrangement of cis regulatory elements in a specific promoter or enhancer region and the current state of DNA sequences in nucleosomes determines the system of receptor interactions. Contingent upon the interactions occurring, the result may be induction or repression of transcription. | ||
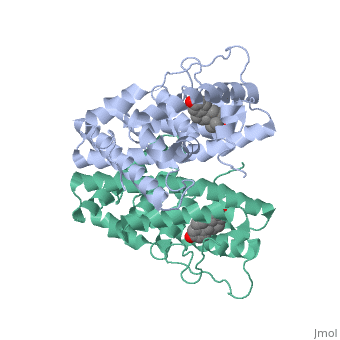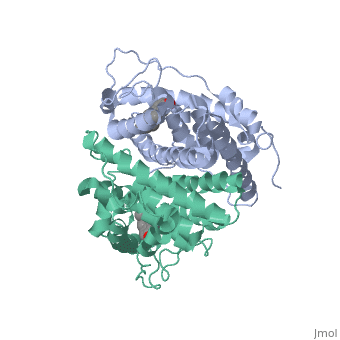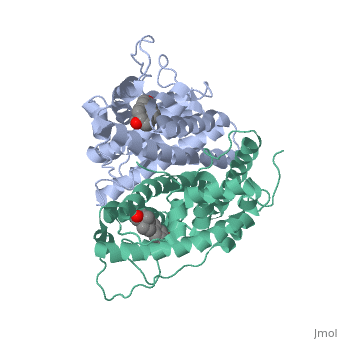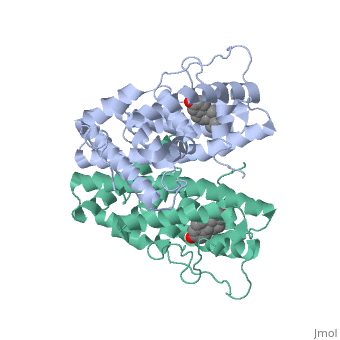
| - | ERα-regulated gene expression involves interactions with cointegrators (ex. p300/CBP, P/CAF) that have the capacity to modify core histone acetyl groups. 2 ER’s DNA binding domain is ordered around two zinc ions that allow the receptors to bind as homodimers to palindromic DNA sequences in such a way that each homodimer links to one half of the palindrome | + | ERα-regulated gene expression involves interactions with cointegrators (ex. p300/CBP, P/CAF) that have the capacity to modify core histone acetyl groups. 2 ER’s DNA binding domain is ordered around two zinc ions that allow the receptors to bind as homodimers to palindromic DNA sequences in such a way that each homodimer links to one half of the palindrome. |
1. Beato, M., Chavez, S., and Truss, M. (1996). Transcriptional regulation by steroid hormones. Steroids 61: 240–251. | 1. Beato, M., Chavez, S., and Truss, M. (1996). Transcriptional regulation by steroid hormones. Steroids 61: 240–251. | ||
Revision as of 02:34, 27 October 2015
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Beato, M., Chavez, S., and Truss, M. (1996). Transcriptional regulation by steroid hormones. Steroids 61: 240–251.
- ↑ Wang C, Fu M, Angeletti RH, Siconolfi-Baez L, Reutens AT, Albanese C, Lisanti MP, Katzenellenbogen BS, Kato S, Hopp T, Fuqua SA, Lopez GN, Kushner PJ, Pestell RG (25 May 2001)."Direct acetylation of the estrogen receptor alpha hinge region by p300 regulates transactivation and hormone sensitivity.". J Biol Chem. 276 (21): 18375–83.
- ↑ Htun H, Holth LT, Walker D, Davie JR, Hager GL (1 February 1999). "Direct visualization of the human estrogen receptor alpha reveals a role for ligand in the nuclear distribution of the receptor". Mol Biol Cell 10 (2): 471–86.