Overview
There are two flavors of estrogen receptor: intracellular receptor - ER and G protein coupled receptors - GPER. ERs are transcription factors while GPER are not transcription factors. ERs are the focus of this page.
Function
Like other steroid hormones estrogen effects the transcription of a large number of genes via its interactions with its intracellular receptors, estrogen receptors. ER plays a major role in the signaling of growth and development of people. Estrogen receptors are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (Example of an estrogen; 17β-estradiol). Estrogens, compared to other hormones such as growth hormone or insulin are relatively small. Estrogen is made from cholesterol and is rich in carbons. Estrogen (because it is a steroid) passes directly into cells through the phospholipid bilayer. When estrogen meets an ER the ER changes shape with assistance from chaperon proteins and forms a dimer of two ERs.
Structural Highlights
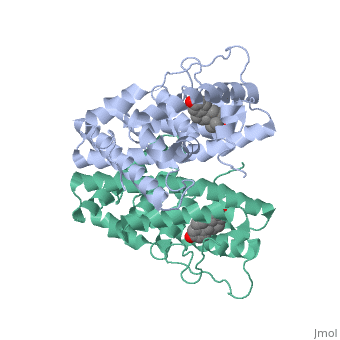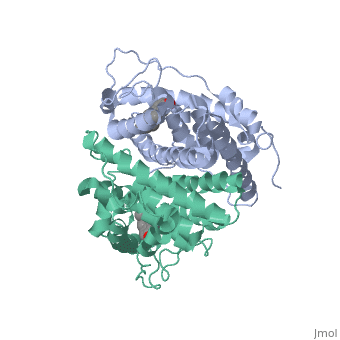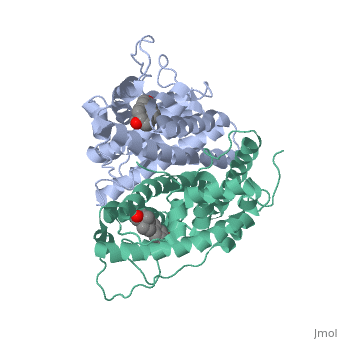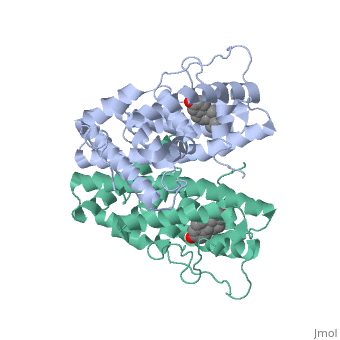
ER is a modular protein composed of a ligand binding domain, a DNA binding domain and a transactivation domain. ER is a DNA-binding transcription factor. The DNA binding domain can be clearly observed in this scene; the highlighted yellow helix in close proximity to the DNA is part of the DNA binding domain. The blue beta sheet close to the yellow DNA binding alpha helix is also part of the DNA binding domain. The transactivation domain forms an alpha helix which is colored in purple. The transactivation domain activates RNA polymerase when the receptor binds to DNA. The ligand binding domain may be observed here with the following scene. The ligand ferutinine (highlighted in pink) is bound by the ligand binding domain, composed of the blue colored alpha helices immediately surrounding the purple ligand. Another view of the ligand binding domain is shown here, with estradiol bound.
DNA Protein Interaction and ER Regulation
ER is functional as a ligand-dependent transcription factor. [1] ER responds to both agonist and antagonist ligands and can associate with the nuclear matrix. Differences in the structure of the receptor are observed depending on what ligand ER has bound. Through comparisons of ER bound to agonist and antagonist ligands, some structural components may be highlighted. The specific conformation of this tight loop of alpha helices and beta sheets around the ligand creates part of the activation signal that will stimulate normal growth; normal growth is stimulated by chaperon proteins recognizing the estrogen receptor ligand complex and facilitating the trans-location of the complex to the nucleus. Eventually the complex will reach specific euchromatin, at which point the chaperon protein and estrogen receptor ligand complex changes conformation so as to allow the estrogen receptor to bind the major groove at specific palindromic sequences. Estradiol is a normal ligand for ER and allows for binding in the major groove of DNA. If the ligand is an antagonist the transcription factor function of estrogen receptor becomes hindered. The conformation of ER bound to the partial agonist genistein has a loop which is not as tight around the ligand as those found on ER with a complete agonist ligand. The ligands themselves take up different amounts of space and have varying interactions within ER. This slight difference effects the ability of the chaperon to be able to bind the receptor ligand complex to the major groove of DNA. There is a noticeable difference in the size of the pure agonist vs partial agonist scenes. Specifically, look at the width of the agonist compared to the partial agonist. Similar differences may be observed between ER which has bound the partial agonist and antagonist ligands. Special attention should be given to the bottom right alpha helices and beta sheets that are pushed out more in the antagonist compared to the agonist bound ER. Tamoxifen is a drug created to bind ER and inhibit the transcription factor activity of ER. Tamoxifen is larger than the normal hormone ER binds (estradiol); for this reason added with the conformation estrogen receptor takes on, the activation loop is pushed into an inactive conformation. This blocks ER from giving the signal to grow. Antagonists are generally larger and cause estrogen receptors to be too hindered sterically to be able to bind to the major groove of DNA, inhibiting the receptor. The antagonist bound estrogen receptor is noticeably larger than the agonist bound version. Further inhibition occurs when ER has bound an antagonist ligand. Antagonist bound ER is still brought to Euchromatin in the nucleus. The larger than agonist bound ER ligand chaperon complex is not capable of binding the major groove of DNA, but still occupies the space around specific palindromic sites which ER binds and modifies the transcription of local genes to these palindromic sequence areas. This blocks agonist bound ER from being able to reach these specific palindromic major groove target loci in DNA.
Changes in Location of ER
The conformation of ER depends on where it is in the cell. When ER is in the nucleus it takes on a different shape in order to bind DNA. When ER is in the cytoplasm and unbound by ligand it remains in a ligand binding conformation. Unbound ER normally exists loosely around the nucleus; this is subject to change depending on a multitude of factors including cell type, progress through cell cycle and reception of cellular signals. When estrogen enters the cell and binds ER, ER trans-locates and undergoes a conformation shift.[2] Ligand bound estrogen receptor associates more tightly with the nucleus. The location of the receptor bound and unbound to ligand varies amongst different cell types. In general, an antagonist ligand will cause partial accumulation in the cytoplasm of a cell. The agonist ligand causes the translocation to the nucleus described above. This is important as ER function has been shown to vary within different phases of the cell cycle. A group bound GFP to ER and studied the location of GFP-ER upon binding of agonists and antagonist ligands. [3] GFP-ER activates the reporter gene in a dose-dependent manner and shows additional activation in the presence of agonist ligand 17-bestradiol. ICI 182780, a pure antagonist for ER, completely inhibited GFP-ER activation of the reporter gene. The group found that in the absence of ligand, the unoccupied ER is loosely associated with the nucleus and binding of a ligand causes a biochemical transformation into a complex that associates more tightly with the nucleus.
Summary of ER DNA Interaction
Before ER binds its hormone the receptor is part of a complex that has many chaperones that maintain the receptor in a steroid binding configuration. Post hormone binding, the receptor dissociates from its original complex and binds to hormone responsive elements in chromatin. Gene expression is then regulated by interaction of DNA bound receptors with sequence specific transcription factors and general transcription factors which are mediated by co-activators and co-repressors. The arrangement of cis regulatory elements in a specific promoter or enhancer region and the current state of DNA sequences in nucleosomes determines the system of receptor interactions. Contingent upon the interactions occurring, the result may be induction or repression of transcription.
ERα-regulated gene expression involves interactions with cointegrators (ex. p300/CBP, P/CAF) that have the capacity to modify core histone acetyl groups. Two ER’s DNA binding domain is ordered around two zinc ions that allow the receptors to bind as homodimers to palindromic DNA sequences in such a way that each homodimer links to one half of the palindrome.
Acknowledgments
I thank Dr. Ann Taylor for her support, critical discussions and technical guidance. I thank Proteopedia and the provided scene editing tools which were used to help create images [4] shown in this article.