Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1bdo' size='450' side='right' scene='49/492046/Cv/1' caption=''> | + | <StructureSection load='1bdo' size='450' side='right' scene='49/492046/Cv/1' caption='E. coli Acetyl-CoA carboxylase biotinyl domain complex with biotin (PDB code [[1bdo]]) '> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Acetyl-CoA carboxylase''' (ACC) catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Malonyl-CoA is a building block in in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. ACC is biotin- and ATP-dependent enzyme. In mammals, 2 forms of ACC exist. ACC1 and ACC2 differ in their tissue distribution and function. | '''Acetyl-CoA carboxylase''' (ACC) catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Malonyl-CoA is a building block in in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. ACC is biotin- and ATP-dependent enzyme. In mammals, 2 forms of ACC exist. ACC1 and ACC2 differ in their tissue distribution and function. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
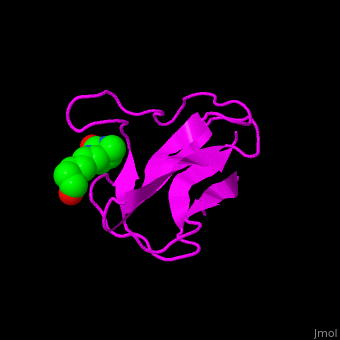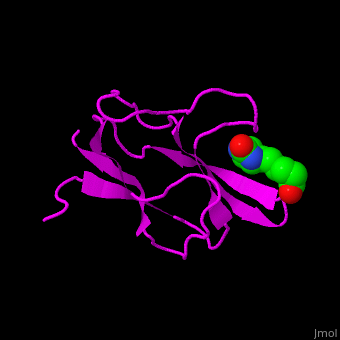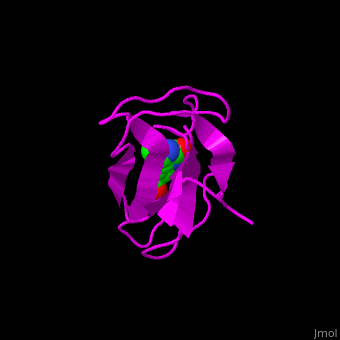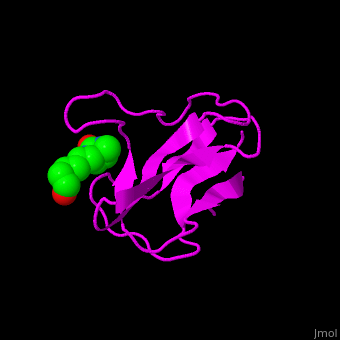
| - | ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in prokaryotes and plants. Each subunit catalyzes different reaction. These are – '''biotin carboxylase''' (BC) which carboxylates the biotin prosthetic group see [[Biotin carboxylase]], '''biotin carboxyl carrier protein''' (BCCP) which is linked covalently to biotin and '''carboxyltransferase''' (CT) which transfers the carboxyl group from biotin to acetyl-CoA. In eukaryotes these functions are performed by a single polypeptide chain. The biotindyl domain (residues 891-964 in human) transfers an activated carboxyl group from the BC domain to the CT domain. <scene name='49/492046/Cv/2'>E.coli biotin carboxylase complex with biotin</scene> ([[1bdo]]) is shown. | + | ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in prokaryotes and plants. Each subunit catalyzes different reaction. These are – '''biotin carboxylase''' (BC) which carboxylates the biotin prosthetic group see [[Biotin carboxylase]], '''biotin carboxyl carrier protein''' (BCCP) which is linked covalently to biotin and '''carboxyltransferase''' (CT) which transfers the carboxyl group from biotin to acetyl-CoA. In eukaryotes these functions are performed by a single polypeptide chain. The biotindyl domain (residues 891-964 in human, 75-156 in E.coli) transfers an activated carboxyl group from the BC domain to the CT domain. <scene name='49/492046/Cv/2'>E.coli biotin carboxylase complex with biotin</scene> ([[1bdo]]) is shown. |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
*Biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) domain | *Biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) domain | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1bnc]], [[1dv1]] - EcBCCP – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> |
| - | **[[2dn8]] – hBCCP2 – human - NMR<BR /> | + | **[[2gps]], [[2gpw]], [[3g8d]] - EcBCCP (mutant)<br /> |
| + | **[[1a6x]], [[3bdo]] – EcBCCP biotinyl domain – NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[2dn8]] – hBCCP2 residues 8-94 – human - NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[2kcc]] - hBCCP2 residues 891-964 – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3glk]], [[3jrw]] – hBCCP2<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4hq6]] – hBCCP2 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2yl2]] – hBCCP1<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2c00]] – BCCP – ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1w93]] – yBCCP – yeast <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) subunit complex | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1bdo]] - EcBCCP + biotin <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2bdo]] - EcBCCP + biotin – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1w96]] – yBCCP + soraphen <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3gid]], [[3jrx]] – hBCCP2 + soraphen <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2j9g]] – EcBCCP + AMPPNP + ADP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1dv2]] – EcBCCP (mutant) + ATP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3rup]] - EcBCCP + Ca + ADP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3rv3]] - EcBCCP + Mg + ADP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3rv4]] - EcBCCP + bicarbonate + Mg-ADP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3g8c]] - EcBCCP + biotin + bicarbonate + Mg + ADP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2vr1]] - EcBCCP + ATP analog<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2vpq]] - SaBCCP + AMPPNP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2vqd]] - SaBCCP + AMPCP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3ouz]] - CjBCCP + ADP – Campylobacter jejuni<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3ouu]] - CjBCCP + b-g-ATP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4hr7]] – EcBCCP + biotin carboxyl carrier protein<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mv1]] – HiBCCP + Pi + ADP – Haemophilus influenzae<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mv3]] – HiBCCP + bicarbonate + AMPCP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mv4]] – HiBCCP + Mg + AMPCP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mv8]] – HiBCCP + Pi + AMPCP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mv9]] – HiBCCP + bicarbonate <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4mv6]], [[4mv7]] – HiBCCP + phosphoacetamide <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) subunit complex with inhibitors | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2v58]], [[2v59]], [[2v5a]] - EcBCCP + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2w6m]], [[2w6n]], [[2w6o]], [[2w6p]], [[2w6q]], [[2w6z]], [[2w70]], [[2w71]] - EcBCCP + fragment-based inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3jzf]], [[3jzi]] - EcBCCP + benzimidazole inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1w96]] – yBCCP + soraphen <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3ff6]] – hBCCP2 + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3gid]], [[3jrx]] – hBCCP2 + soraphen <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3pgq]] - CjBCCP + pinoxaden | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
*Carboxyltransferase (CT) domain | *Carboxyltransferase (CT) domain | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 11 November 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Updated on 11-November-2015